Netty源码 新连接处理
上文我们阐述了Netty的Reactor模型。在Reactor模型的第二阶段,Netty会处理各种io事件。对于客户端的各种请求就是在这个阶段去处理的。本文便来分析一个新的连接是如何被处理的。
代码的入口就从read方法开始。这里的unsafe的类型是NioMessageUnsafe,在服务端启动时就确定下来了。
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
if (!ch.isOpen()) {
// Connection already closed - no need to handle write.
return;
}
}
我们省去部分代码,read方法逻辑非常简单。就是一个读出加处理的过程
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
do {
//读取消息
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
//循环处理消息
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
//触发读取完毕事件
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
}
1.读取消息
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
SocketChannel ch = javaChannel().accept();
try {
if (ch != null) {
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to create a new channel from an accepted socket.", t);
try {
ch.close();
} catch (Throwable t2) {
logger.warn("Failed to close a socket.", t2);
}
}
return 0;
}
在doReadMessages首先accept一个新连接,由于在一阶段的时候已经有io事件产生了,所以这里不会等待而是立即接受一个新连接并用SocketChannel表示。
接着又构造出了一个NioSocketChannel将java的channel封装成netty自己的channel并添加到list中,我们点进去看看。
public NioSocketChannel(Channel parent, SocketChannel socket) {
super(parent, socket);
config = new NioSocketChannelConfig(this, socket.socket());
}
protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId();
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = newChannelPipeline();
}
最终我们到了AbstractChannel的类中,发现NioSocketChannel的建立会创建unsafe和pipeline。这里我们看下具体类型
unsafe的具体类型是由子类io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel#newUnsafe决定的
protected AbstractNioUnsafe newUnsafe() {
return new NioSocketChannelUnsafe();
}
pipeline则是默认的DefaultChannelPipeline
protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) {
this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel");
succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null);
voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true);
tail = new TailContext(this);
head = new HeadContext(this);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
这里我们便引出了pipeline的概念,看上述代码便知pipeline的数据结构是一个双向链表。我们也可以把它想象成一个责任链或者更直白点就是流水线。任何连接请求都会通过pipeline处理最终返回到客户端。
现在显得连接已经封装成channel并添加到list中了,现在我们再看下消息处理
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
2.消息处理
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}
消息处理实际就是pipeline链式执行handle的过程。那么对于服务端的channel,他在接受新连接的时候先执行那个handle呢。服务端处理新连接的pipeline中,已经自动添加了一个pipeline处理器 ServerBootstrapAcceptor
所以我们先看下ServerBootstrapAcceptor的channelRead方法
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
//1.泛型转换新连接创建的channel
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
//2.设置channel的handler
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
for (Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: childOptions) {
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption<Object>) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, t);
}
}
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
//channel绑定到一个raector线程上
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
1.将刚刚创建的channel泛型转换出来
2.调用用户代码的childHandler属性,注意,这里只是添加了一个ChannelInitializer,相应的初始化还未运行,

3.注册该channel,将该channel绑定到一个reactor线程,后续关于这个channel的事件,任务都是由该reactor线程处理。
现在我们点进注册的代码
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return next().register(channel);
}
public EventLoop next() {
return (EventLoop) super.next();
}
next方法返回的是一个reactor线程,我们看下netty是如何挑选线程的。点击super.next
public EventExecutor next() {
return chooser.next();
}
这里出现一个chooser代表的是一个选择策略,下面直接上代码了
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
public EventExecutorChooser newChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
if (isPowerOfTwo(executors.length)) {
return new PowerOfTowEventExecutorChooser(executors);
} else {
return new GenericEventExecutorChooser(executors);
}
}
netty根据线程数量的奇偶性 会选择出不同的选择策略。两者唯一的区别就是一个是与运算,一个是取余
private static final class PowerOfTowEventExecutorChooser implements EventExecutorChooser {
private final AtomicInteger idx = new AtomicInteger();
private final EventExecutor[] executors;
PowerOfTowEventExecutorChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
this.executors = executors;
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return executors[idx.getAndIncrement() & executors.length - 1];
}
}
private static final class GenericEventExecutorChooser implements EventExecutorChooser {
private final AtomicInteger idx = new AtomicInteger();
private final EventExecutor[] executors;
GenericEventExecutorChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
this.executors = executors;
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return executors[Math.abs(idx.getAndIncrement() % executors.length)];
}
}
在我们确定一个reactor线程之后,我们便开始了注册的流程
io.netty.channel.SingleThreadEventLoop#register(io.netty.channel.Channel)
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return register(new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, this));
}
io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe#register
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
注册的核心代码便是register0了
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
// check if the channel is still open as it could be closed in the mean time when the register
// call was outside of the eventLoop
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
- doRegister之前在服务端分析时有过讲解,这里真正的吧channel与reactor线程绑定在一起
- pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
为channel添加Handler,这里将添加handler任务包装成Task
private final class PendingHandlerAddedTask extends PendingHandlerCallback {
PendingHandlerAddedTask(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
super(ctx);
}
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerAdded0(ctx);
}
@Override
void execute() {
EventExecutor executor = ctx.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
callHandlerAdded0(ctx);
} else {
try {
executor.execute(this);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn(
"Can't invoke handlerAdded() as the EventExecutor {} rejected it, removing handler {}.",
executor, ctx.name(), e);
}
remove0(ctx);
ctx.setRemoved();
}
}
}
}
最终调用io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer#handlerAdded
private void callHandlerAdded0(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.handler().handlerAdded(ctx);
ctx.setAddComplete();
}
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
if (ctx.channel().isRegistered()) {
initChannel(ctx);
}
}
这也就是我们的用户代码

- pipeline.fireChannelRegistered(); channel注册完之后的回调
- pipeline.fireChannelActive() channel激活的回调
到这里其实已经接近尾声了。但是我们的channel目前还是无法使用的。因为他并没有注册他感兴趣的事件。他现在是一个没有梦想的channel。所以我们看下channel激活的具体逻辑
private void invokeChannelActive() {
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelActive(this);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
} else {
fireChannelActive();
}
}
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
private void readIfIsAutoRead() {
if (channel.config().isAutoRead()) {
channel.read();
}
}
public Channel read() {
pipeline.read();
return this;
}
public final ChannelPipeline read() {
tail.read();
return this;
}
.......
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
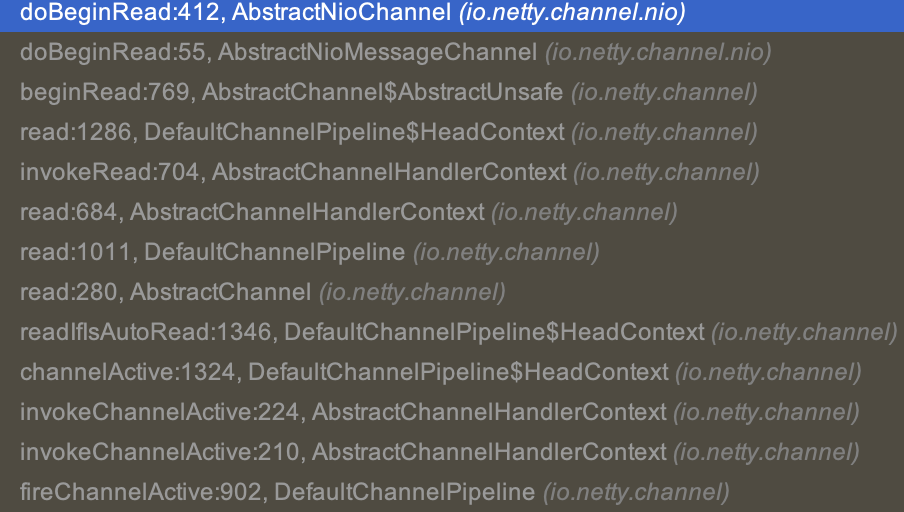
最终在io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioChannel#doBeginRead中设置selectionKey对读事件感兴趣。
以上便是netty对新连接的处理
参考
https://www.jianshu.com/p/0242b1d4dd21 【netty源码分析之新连接接入全解析】
Netty源码 新连接处理的更多相关文章
- Netty源码剖析-断开连接
参考文献:极客时间傅健老师的<Netty源码剖析与实战>Talk is cheap.show me the code! ----主线: ----源码: 在NioEventLoop的unsa ...
- Netty源码—一、server启动(1)
Netty作为一个Java生态中的网络组件有着举足轻重的位置,各种开源中间件都使用Netty进行网络通信,比如Dubbo.RocketMQ.可以说Netty是对Java NIO的封装,比如ByteBu ...
- netty源码解解析(4.0)-11 Channel NIO实现-概览
结构设计 Channel的NIO实现位于io.netty.channel.nio包和io.netty.channel.socket.nio包中,其中io.netty.channel.nio是抽象实 ...
- Netty 源码 NioEventLoop(三)执行流程
Netty 源码 NioEventLoop(三)执行流程 Netty 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10117436.html) 上文提到在启动 N ...
- Netty源码分析第1章(Netty启动流程)---->第5节: 绑定端口
Netty源码分析第一章:Netty启动步骤 第五节:绑定端口 上一小节我们学习了channel注册在selector的步骤, 仅仅做了注册但并没有监听事件, 事件是如何监听的呢? 我们继续跟第一小节 ...
- Netty源码分析第3章(客户端接入流程)---->第5节: 监听读事件
Netty源码分析第三章: 客户端接入流程 第五节: 监听读事件 我们回到AbstractUnsafe的register0()方法: private void register0(ChannelPro ...
- Netty源码分析第5章(ByteBuf)---->第7节: page级别的内存分配
Netty源码分析第五章: ByteBuf 第六节: page级别的内存分配 前面小节我们剖析过命中缓存的内存分配逻辑, 前提是如果缓存中有数据, 那么缓存中没有数据, netty是如何开辟一块内存进 ...
- Netty源码分析第8章(高性能工具类FastThreadLocal和Recycler)---->第6节: 异线程回收对象
Netty源码分析第八章: 高性能工具类FastThreadLocal和Recycler 第六节: 异线程回收对象 异线程回收对象, 就是创建对象和回收对象不在同一条线程的情况下, 对象回收的逻辑 我 ...
- EventLoop(netty源码死磕4)
精进篇:netty源码 死磕4-EventLoop的鬼斧神工 目录 1. EventLoop的鬼斧神工 2. 初识 EventLoop 3. Reactor模式回顾 3.1. Reactor模式的组 ...
随机推荐
- Python_微信支付(云开发)
一.创建云开发小程序 1.初始化云开发环境 //app.js App({ onLaunch: function () { wx.cloud.init({ //初始化云开发环境 env: 'wxypay ...
- WebVR & CSS 3D & WebGL
WebVR & CSS 3D & WebGL VR https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebVR_API https:/ ...
- react & redux data flow diagram
react & redux data flow diagram Redux 数据流程图
- js & bitwise-operators
js & bitwise-operators 不用加减乘除运算符, 求整数的7倍 "use strict"; /** * * @author xgqfrms * @lice ...
- ES6 & Classes & Interface
ES6 & Classes & Interface what's the difference between javascript Classes & Interface ? ...
- AMP & PWA
AMP & PWA AMP is a web component framework to easily create user-first websites. stories. ads. e ...
- The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard of Linux
The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard of Linux linux directory https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/23862856 htt ...
- HTML Imports & deprecated
HTML Imports & deprecated https://caniuse.com/#search=html imports https://www.chromestatus.com/ ...
- 云原生系列5 容器化日志之EFK
上图是EFK架构图,k8s环境下常见的日志采集方式. 日志需求 1 集中采集微服务的日志,可以根据请求id追踪到完整的日志: 2 统计请求接口的耗时,超出最长响应时间的,需要做报警,并针对性的进行调优 ...
- 【Python核心编程笔记】一、Python中一切皆对象
Python中一切皆对象 本章节首先对比静态语言以及动态语言,然后介绍 python 中最底层也是面向对象最重要的几个概念-object.type和class之间的关系,以此来引出在python如何做 ...
