Machine learning第四周code 编程作业
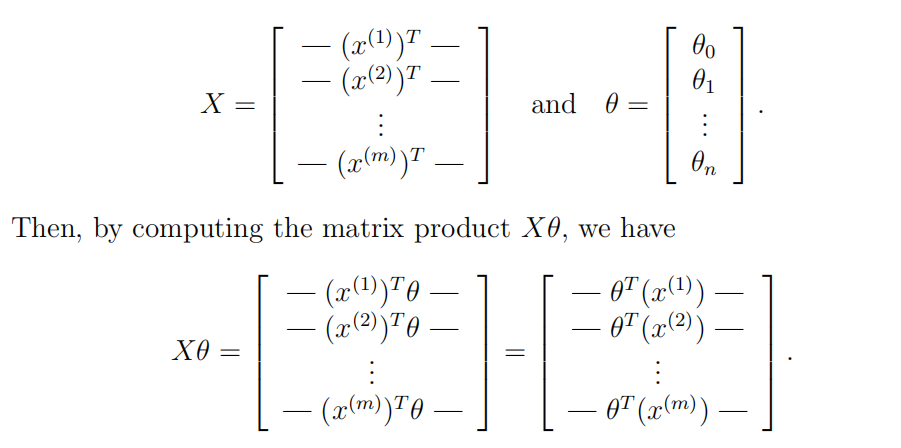
1.lrCostFunction:
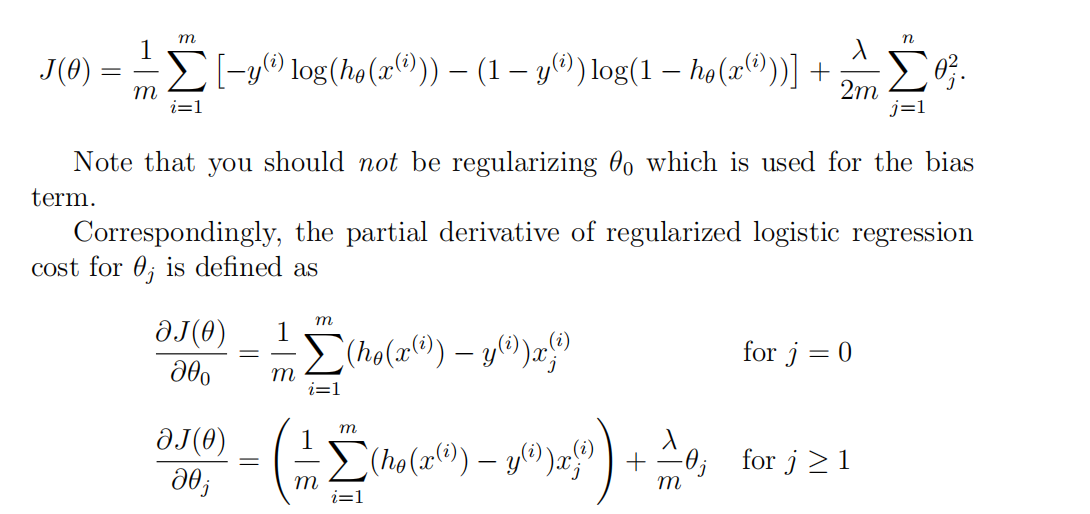
和第三周的那个一样的;
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda)
%LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with
%regularization
% J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Hint: The computation of the cost function and gradients can be
% efficiently vectorized. For example, consider the computation
%
% sigmoid(X * theta)
%
% Each row of the resulting matrix will contain the value of the
% prediction for that example. You can make use of this to vectorize
% the cost function and gradient computations.
%
% Hint: When computing the gradient of the regularized cost function,
% there're many possible vectorized solutions, but one solution
% looks like:
% grad = (unregularized gradient for logistic regression)
% temp = theta;
% temp(1) = 0; % because we don't add anything for j = 0
% grad = grad + YOUR_CODE_HERE (using the temp variable)
% h=sigmoid(X*theta);
for i=1:m,
J=J+1/m*(-y(i)*log(h(i))-(1-y(i))*log(1-h(i)));
endfor
n=length(theta);
for i=2:n,
J=J+lambda/(2*m)*theta(i)^2;
endfor grad(1)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,1);
for i=2:n,
grad(i)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,i)+lambda/m*theta(i);
endfor % ============================================================= grad = grad(:); end
2.oneVsAll
注意的一点是:
fmincg中的 initial_theta为列向量,所以需要转置一下;
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i % Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2); % You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the following code to train num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers with regularization
% parameter lambda.
%
% Hint: theta(:) will return a column vector.
%
% Hint: You can use y == c to obtain a vector of 1's and 0's that tell you
% whether the ground truth is true/false for this class.
%
% Note: For this assignment, we recommend using fmincg to optimize the cost
% function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c = 1:num_labels) to
% loop over the different classes.
%
% fmincg works similarly to fminunc, but is more efficient when we
% are dealing with large number of parameters.
%
% Example Code for fmincg:
%
% % Set Initial theta
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
%
% % Set options for fminunc
% options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
%
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% % This function will return theta and the cost
% [theta] = ...
% fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), ...
% initial_theta, options);
% options=optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',50); for i=1:num_labels,
all_theta(i,:)=fmincg(@(t)(lrCostFunction(t,X,(y==i),lambda)),all_theta(i,:)',options);
endfor % ========================================================================= end
3.PredictOneVSAll
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels
%are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1).
% p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions
% for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in
% rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic
% regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector
% of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2
% for 4 examples) m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all).
% You should set p to a vector of predictions (from 1 to
% num_labels).
%
% Hint: This code can be done all vectorized using the max function.
% In particular, the max function can also return the index of the
% max element, for more information see 'help max'. If your examples
% are in rows, then, you can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max
% for each row.
% [Max,p]=max(X*all_theta',[],2); % ========================================================================= end
4.predict

function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2) % Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
% X=[ones(m,1) X];
a2=[ones(m,1) sigmoid(X*Theta1')]; [Max,p]=max(sigmoid(a2*Theta2'),[],2); % ========================================================================= end
Machine learning第四周code 编程作业的更多相关文章
- Machine learning 第7周编程作业 SVM
1.Gaussian Kernel function sim = gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma) %RBFKERNEL returns a radial basis fun ...
- Machine learning第6周编程作业
1.linearRegCostFunction: function [J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, lambda) %LINEARREGC ...
- Machine learning 第8周编程作业 K-means and PCA
1.findClosestCentroids function idx = findClosestCentroids(X, centroids) %FINDCLOSESTCENTROIDS compu ...
- Machine learning 第5周编程作业
1.Sigmoid Gradient function g = sigmoidGradient(z) %SIGMOIDGRADIENT returns the gradient of the sigm ...
- Hand on Machine Learning第三章课后作业(1):垃圾邮件分类
import os import email import email.policy 1. 读取邮件数据 SPAM_PATH = os.path.join( "E:\\3.Study\\机器 ...
- 【machine learning通俗讲解code逐行注释】之线性回归实现
现在机器学习算法在分类.回归.数据挖掘等问题上运用的十分广泛,对于初学者来说,可能一听到'算法'或其他的专属名词都感觉高深莫测,以致很多人望而却步,这让很多人在处理很多问题上失去了一个很有用的工具.机 ...
- Hand on Machine Learning第三章课后作业(2):其余小练习
-#!/usr/bin/env python -# # # -- coding: utf-8 -- -# # # @Time : 2019.5.22 14:09 -# # # @Author : An ...
- 機器學習基石 (Machine Learning Foundations) 作业1 Q15-17的C++实现
大家好,我是Mac Jiang.今天和大家分享Coursera-台湾大学-機器學習基石 (Machine Learning Foundations) -作业1的Q15-17题的C++实现. 这部分作业 ...
- 機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations) 机器学习基石 作业三 课后习题解答
今天和大家分享coursera-NTU-機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations)-作业三的习题解答.笔者在做这些题目时遇到非常多困难,当我在网上寻找答案时却找不到,而林 ...
随机推荐
- scrollView不能进行滚动
原因:scrollView里只能包含一个layout,多个时,是不能进行滚动的.
- MVC和WebApi 使用get和post 传递参数(转)
出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq373591361/article/details/51508806 我们总结一下用js请求服务器的传参方法. Get方式 Get主要是用来查询,一 ...
- curl:get,post 以及SoapClien访问webservice数据
一.curl get模式 public function close_order(){ $url="http://192.168.2.50:7777/U8API.asmx?op=Insert ...
- msfvenom木马生成+免杀+壳(实测并不能免杀)
msfvenom 选项: -p, --payload 有效载荷使用.指定一个有效的自定义载荷 --payload-options 列出有效载荷的标准选项 -l, --list [type] 列出一个模 ...
- C# Http请求接口数据的两种方式Get and Post
面向接口编程是一种设计思想,无论用什么语言都少不了面向接口开发思想,在软件开发过程中,常常要调用接口,接下来就是介绍C#调用其它开发商提供的接口进行获取数据,http接口方式获取接口数据. Get请求 ...
- Java之RandomAccessFile小结
今天跟大家分享一下javase中的关于I/O的操作: 有时我们需要在文件的末尾追加一些内容,在这时用RandomAccessFile就很好. 这个类有两个构造方法: RandomAccessFile( ...
- Android-GsonUtil工具类
JSON解析封装相关工具类 public class GsonUtil { private static Gson gson = null; static { if (gson == null) { ...
- kubernetes 滚动更新发布及回滚
基本命令 记录历史 --record kubectl apply -f **** --record 查看当前状态 kubectl rollout status deployment/demo -w ...
- BFC开启条件
当元素CSS属性设置了下列之一时,即可创建一个BFC: float:left|right position:absolute|fixed display: table-cell|table-capti ...
- [node.js]express+mongoose+mongodb的开发笔记
时间过得很快,6月和7月忙的不可开交,糟心的事儿也是不少,杭州大连来回飞,也是呵呵. 希望下个阶段能沉浸下来,接着学自己想学的.记一下上几周用了几天时间写的课设.因为课设的缘故,所以在短时间里了解下e ...
