题解报告:hdu 1392 Surround the Trees(凸包入门)
Problem Description
The diameter and length of the trees are omitted, which means a tree can be seen as a point. The thickness of the rope is also omitted which means a rope can be seen as a line.
 There are no more than 100 trees.
There are no more than 100 trees.Input
Zero at line for number of trees terminates the input for your program.
Output
Sample Input
Sample Output
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
struct node{int x,y;};
node vex[maxn];//存入所有坐标点
node stackk[maxn];//凸包中所有的点
bool cmp1(node a,node b){//按点的坐标排序
if(a.y==b.y)return a.x<b.x;//如果纵坐标相同,则按横坐标升序排
else return a.y<b.y;//否则按纵坐标升序排
}
bool cmp2(node a,node b){//以基点为坐标原点,极角按升序排,这里可用atan2函数或者叉积来进行极角排序,但是用atan2函数来排序效率高时间快,不过精度比叉积低
double A=atan2(a.y-stackk[].y,a.x-stackk[].x);//返回的是原点至点(x,y)的方位角,即与x轴的夹角
double B=atan2(b.y-stackk[].y,b.x-stackk[].x);
if(A!=B)return A<B;//逆时针方向为正值,极角小的排在前面
else return a.x<b.x;//如果极角相同,则横坐标在前面的靠前排列
}
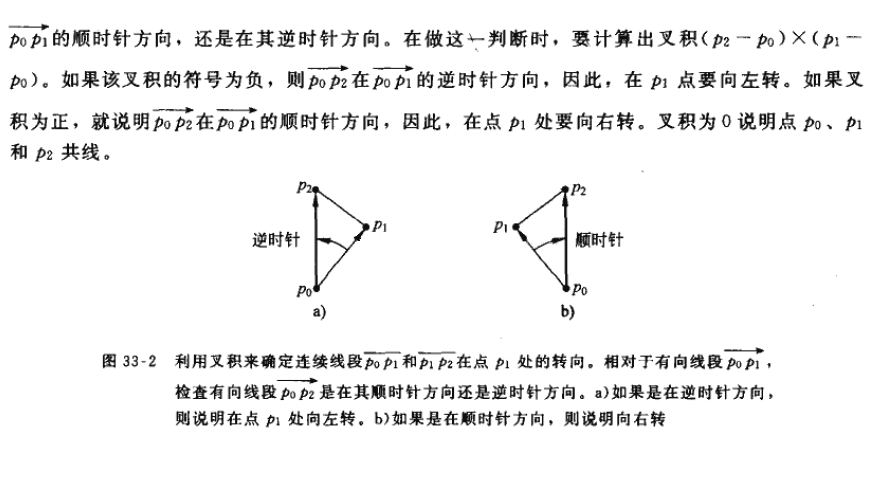
int cross(node p0,node p1,node p2){//计算两个向量a、b(a=(x1,y1),b=(x2,y2))的叉积公式:a×b=x1y2-x2y1 ===> p0p1=(x1-x0,y1-y0),p0p2=(x2-x0,y2-y0)
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
double dis(node a,node b){//计算两点之间的距离
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)*1.0+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
int main(){
int t;
while(~scanf("%d",&t)&&t){
for(int i=;i<t;++i)//输入t个点
scanf("%d%d",&vex[i].x,&vex[i].y);
if(t==)printf("%.2f\n",0.00);//如果只有一个点,则周长为0.00
else if(t==)printf("%.2f\n",dis(vex[],vex[]));//如果只有两个点,则周长为两个点的距离
else{
memset(stackk,,sizeof(stackk));//清0
sort(vex,vex+t,cmp1);//先按坐标点的位置进行排序
stackk[]=vex[];//取出基点
sort(vex+,vex+t,cmp2);//将剩下的坐标点按极角进行排序,以基点为坐标原点
stackk[]=vex[];//将凸包中的第二个点存入凸集中
int top=;//当前凸包中拥有点的个数为top+1
for(int i=;i<t;++i){//不断地找外围的坐标点
while(top>&&cross(stackk[top-],stackk[top],vex[i])<=)top--;//如果叉积为负数或0(0表示两向量共线),则弹出栈顶元素
//虽然第2个凸点显然是最外围的一点,但加上top>0保证了栈中至少有2个凸点
stackk[++top]=vex[i];
}
double s=;
for(int i=;i<=top;++i)//计算凸包的周长
s+=dis(stackk[i-],stackk[i]);
s+=dis(stackk[top],vex[]);//最后一个点和第一个点之间的距离
printf("%.2f\n",s);
}
}
return ;
}
AC代码二(31ms):Andrew算法,一次坐标排序,两次构造成一个完整的凸包,时间复杂度为O(nlogn),但实际上比Graham扫描算法快很多,具体讲解-->凸包解法总结。
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
struct node{int x,y;}vex[maxn],stackk[maxn];
bool cmp(node a,node b){//按点的坐标排序
return (a.y<b.y)||(a.y==b.y&&a.x<b.x);
}
int cross(node p0,node p1,node p2){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
double dis(node a,node b){
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)*1.0+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
int main(){
int t;
while(~scanf("%d",&t)&&t){
for(int i=;i<t;++i)//输入t个点
scanf("%d%d",&vex[i].x,&vex[i].y);
if(t==)printf("%.2f\n",0.00);
else if(t==)printf("%.2f\n",dis(vex[],vex[]));
else{
memset(stackk,,sizeof(stackk));//清0
sort(vex,vex+t,cmp);//一次坐标排序,两次构造成一个完整的凸包
int top=-;
for(int i=;i<t;++i){//构造凸包下侧
while(top>&&cross(stackk[top-],stackk[top],vex[i])<=)top--;
stackk[++top]=vex[i];
}
for(int i=t-,k=top;i>=;--i){//构造凸包上侧,默认此时凸包中只有一个顶点n-1,因此top要大于k,起点再被包含一次且一定被包含
while(top>k&&cross(stackk[top-],stackk[top],vex[i])<=)top--;
stackk[++top]=vex[i];
}
double s=;
for(int i=;i<=top;++i)//计算凸包周长
s+=dis(stackk[i-],stackk[i]);
printf("%.2f\n",s);
}
}
return ;
}
题解报告:hdu 1392 Surround the Trees(凸包入门)的更多相关文章
- HDU - 1392 Surround the Trees (凸包)
Surround the Trees:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1392 题意: 在给定点中找到凸包,计算这个凸包的周长. 思路: 这道题找出 ...
- HDU 1392 Surround the Trees (凸包周长)
题目链接:HDU 1392 Problem Description There are a lot of trees in an area. A peasant wants to buy a rope ...
- hdu 1392 Surround the Trees 凸包模板
Surround the Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- hdu 1392 Surround the Trees (凸包)
Surround the Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- hdu 1392 Surround the Trees 凸包裸题
Surround the Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- HDU 1392 Surround the Trees(凸包*计算几何)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1392 这里介绍一种求凸包的算法:Graham.(相对于其它人的解释可能会有一些出入,但大体都属于这个算 ...
- HDU 1392 Surround the Trees(凸包入门)
Surround the Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- hdu 1392:Surround the Trees(计算几何,求凸包周长)
Surround the Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- HDUJ 1392 Surround the Trees 凸包
Surround the Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- HDU-1392 Surround the Trees,凸包入门!
Surround the Trees 此题讨论区里大喊有坑,原谅我没有仔细读题还跳过了坑点. 题意:平面上有n棵树,选一些树用绳子围成一个包围圈,使得所有的树都在这个圈内. 思路:简单凸包入门题,凸包 ...
随机推荐
- HDU 1032.The 3n + 1 problem【注意细节】【预计数据不强】【8月21】
The 3n + 1 problem Problem Description Problems in Computer Science are often classified as belongin ...
- C++ 四种强制类型转变与区别之处
使用标准C++的类型转换符:static_cast.dynamic_cast.reinterpret_cast和const_cast.1.static_cast 用法:static_cast&l ...
- Hadoop 文件压缩
一.目的 a. 减小磁盘占用 b. 加速网络IO 二.几个常用压缩算法 是否可切分:是指压缩后的文件能否支持在任意位置往后读取数据. 各种压缩格式特点: 压缩算法都需要权衡 空间/时间 :压缩率越高, ...
- Silverlight DataBinding Converter:根据binding对象调整显示
Silverlight DataBinding Converter:根据binding对象调整显示 我希望写一系列关于Silverlight DataBinding的文章,分别讲解Silverligh ...
- 安装YCM出现:YouCompleteMe unavailable no module named frozendict或者 YouCompleteMe unavailable no module named future
参考博文:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_8f70642d0102wo57.html 原因就是你或者没用Vundle安装,或者Vundle由于网速太慢下载到一半不能把安装 ...
- CreateRemoteThread注入DLL
DLL注入的常用方式之一远程线程注入,实现代码如下 // CreateRemoteThread.cpp : Defines the entry point for the application.// ...
- bzoj 2083 Intelligence test —— 思路+vector
题目:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2083 先把所有子序列都存下来,总长度应该有限制,所以用 vector 存: 要做到 O(n) ...
- CCRect 构造函数的几个参数解释
转自: http://blog.163.com/hzklclick_wy/blog/static/21550517520137139511839/ void CCRect::setRect(f ...
- mysql负载均衡方案
mysql负载均衡方案 一.直接连接 数据库的读写分离方案很多,这里介绍基于mysql数据库的读写分离方案. 比较常见的读写分离方案如下: 1 基于查询分离 最简单的分离方法是将读和写分发到主和从服务 ...
- JavaScript-Tool:jquery.jsprint.js
ylbtech-JavaScript-Tool:jquery.jsprint.js 一个通过单击页面按钮,便实现页面打印的jQuery插件jqprint. 1.返回顶部 1. 插件描述:一个通过单击页 ...
