PCL学习(二)三维模型转点云 obj转pcd----PCL实现
#include <pcl/io/io.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/io/obj_io.h>
#include <pcl/PolygonMesh.h>
//#include <pcl/ros/conversions.h>//formROSMsg所属头文件;
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/io/vtk_lib_io.h>//loadPolygonFileOBJ所属头文件;
//#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> using namespace std;
using namespace pcl;
int main()
{
pcl::PolygonMesh mesh;
pcl::io::loadPolygonFile("sofa.obj", mesh); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::fromPCLPointCloud2(mesh.cloud, *cloud);
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII("result.pcd", *cloud); cout << cloud->size() << endl; cout << "OK!";
cin.get();
return 0;
}
- 转换前的obj模型
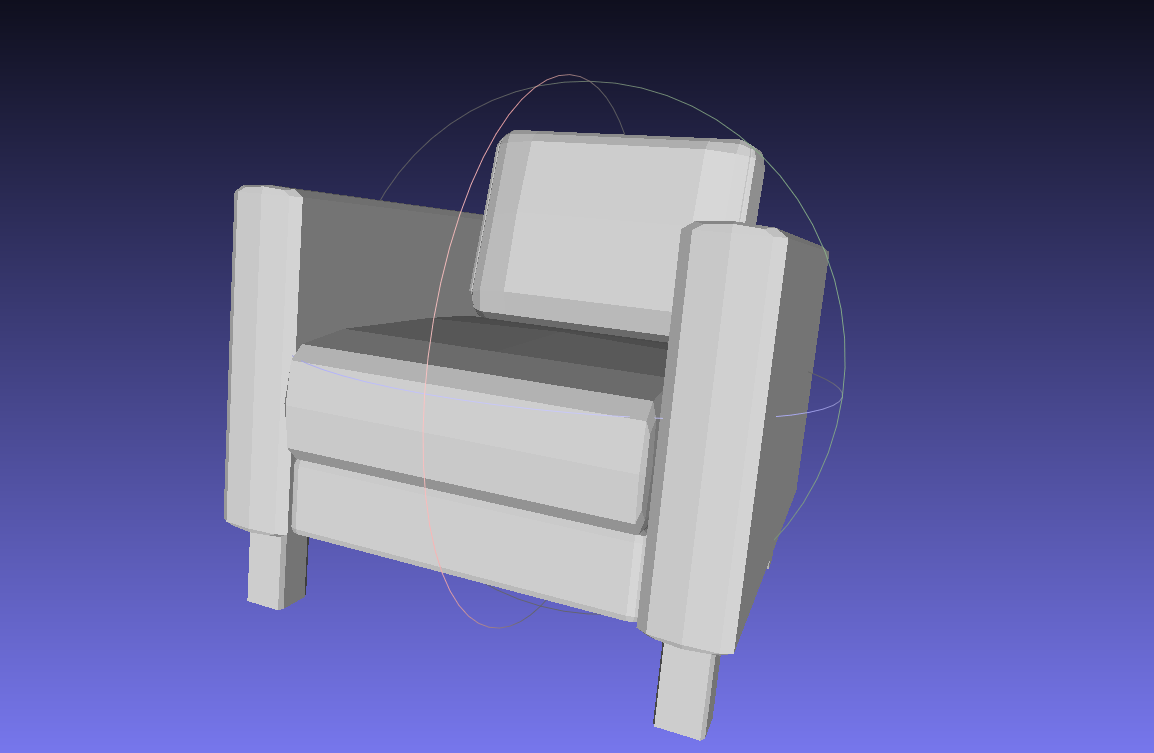
- 转换成pcd点云后

提取3D模型的meshes的顶点(Vertex)坐标,对于点云来说点数不够,而且在3D模型存在平面或者是简单立方体的情况下几乎没有点。
所以又需要PCL库了,pcl_mesh_sampling可以轻松解决这个问题。
它是通过调用VTK(Visualization ToolKit)读取模型,在3D模型平面均匀地采样点然后生成点云,并且你可以选择需要的点数, 以及voxel grid的采样距离。
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/io/vtk_lib_io.h>
#include <pcl/common/transforms.h>
#include <vtkVersion.h>
#include <vtkPLYReader.h>
#include <vtkOBJReader.h>
#include <vtkTriangle.h>
#include <vtkTriangleFilter.h>
#include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/console/print.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h> inline double
uniform_deviate (int seed)
{
double ran = seed * (1.0 / (RAND_MAX + 1.0));
return ran;
} inline void
randomPointTriangle (float a1, float a2, float a3, float b1, float b2, float b3, float c1, float c2, float c3,
Eigen::Vector4f& p)
{
float r1 = static_cast<float> (uniform_deviate (rand ()));
float r2 = static_cast<float> (uniform_deviate (rand ()));
float r1sqr = std::sqrt (r1);
float OneMinR1Sqr = (1 - r1sqr);
float OneMinR2 = (1 - r2);
a1 *= OneMinR1Sqr;
a2 *= OneMinR1Sqr;
a3 *= OneMinR1Sqr;
b1 *= OneMinR2;
b2 *= OneMinR2;
b3 *= OneMinR2;
c1 = r1sqr * (r2 * c1 + b1) + a1;
c2 = r1sqr * (r2 * c2 + b2) + a2;
c3 = r1sqr * (r2 * c3 + b3) + a3;
p[0] = c1;
p[1] = c2;
p[2] = c3;
p[3] = 0;
} inline void
randPSurface (vtkPolyData * polydata, std::vector<double> * cumulativeAreas, double totalArea, Eigen::Vector4f& p, bool calcNormal, Eigen::Vector3f& n)
{
float r = static_cast<float> (uniform_deviate (rand ()) * totalArea); std::vector<double>::iterator low = std::lower_bound (cumulativeAreas->begin (), cumulativeAreas->end (), r);
vtkIdType el = vtkIdType (low - cumulativeAreas->begin ()); double A[3], B[3], C[3];
vtkIdType npts = 0;
vtkIdType *ptIds = NULL;
polydata->GetCellPoints (el, npts, ptIds);
polydata->GetPoint (ptIds[0], A);
polydata->GetPoint (ptIds[1], B);
polydata->GetPoint (ptIds[2], C);
if (calcNormal)
{
// OBJ: Vertices are stored in a counter-clockwise order by default
Eigen::Vector3f v1 = Eigen::Vector3f (A[0], A[1], A[2]) - Eigen::Vector3f (C[0], C[1], C[2]);
Eigen::Vector3f v2 = Eigen::Vector3f (B[0], B[1], B[2]) - Eigen::Vector3f (C[0], C[1], C[2]);
n = v1.cross (v2);
n.normalize ();
}
randomPointTriangle (float (A[0]), float (A[1]), float (A[2]),
float (B[0]), float (B[1]), float (B[2]),
float (C[0]), float (C[1]), float (C[2]), p);
} void
uniform_sampling (vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polydata, size_t n_samples, bool calc_normal, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal> & cloud_out)
{
polydata->BuildCells ();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells = polydata->GetPolys (); double p1[3], p2[3], p3[3], totalArea = 0;
std::vector<double> cumulativeAreas (cells->GetNumberOfCells (), 0);
size_t i = 0;
vtkIdType npts = 0, *ptIds = NULL;
for (cells->InitTraversal (); cells->GetNextCell (npts, ptIds); i++)
{
polydata->GetPoint (ptIds[0], p1);
polydata->GetPoint (ptIds[1], p2);
polydata->GetPoint (ptIds[2], p3);
totalArea += vtkTriangle::TriangleArea (p1, p2, p3);
cumulativeAreas[i] = totalArea;
} cloud_out.points.resize (n_samples);
cloud_out.width = static_cast<pcl::uint32_t> (n_samples);
cloud_out.height = 1; for (i = 0; i < n_samples; i++)
{
Eigen::Vector4f p;
Eigen::Vector3f n;
randPSurface (polydata, &cumulativeAreas, totalArea, p, calc_normal, n);
cloud_out.points[i].x = p[0];
cloud_out.points[i].y = p[1];
cloud_out.points[i].z = p[2];
if (calc_normal)
{
cloud_out.points[i].normal_x = n[0];
cloud_out.points[i].normal_y = n[1];
cloud_out.points[i].normal_z = n[2];
}
}
} using namespace pcl;
using namespace pcl::io;
using namespace pcl::console; const int default_number_samples = 100000;
const float default_leaf_size = 0.01f; void
printHelp (int, char **argv)
{
print_error ("Syntax is: %s input.{ply,obj} output.pcd <options>\n", argv[0]);
print_info (" where options are:\n");
print_info (" -n_samples X = number of samples (default: ");
print_value ("%d", default_number_samples);
print_info (")\n");
print_info (
" -leaf_size X = the XYZ leaf size for the VoxelGrid -- for data reduction (default: ");
print_value ("%f", default_leaf_size);
print_info (" m)\n");
print_info (" -write_normals = flag to write normals to the output pcd\n");
print_info (
" -no_vis_result = flag to stop visualizing the generated pcd\n");
} /* ---[ */
int
main (int argc, char **argv)
{
print_info ("Convert a CAD model to a point cloud using uniform sampling. For more information, use: %s -h\n",
argv[0]); if (argc < 3)
{
printHelp (argc, argv);
return (-1);
} // Parse command line arguments
int SAMPLE_POINTS_ = default_number_samples;
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-n_samples", SAMPLE_POINTS_);
float leaf_size = default_leaf_size;
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-leaf_size", leaf_size);
bool vis_result = ! find_switch (argc, argv, "-no_vis_result");
const bool write_normals = find_switch (argc, argv, "-write_normals"); // Parse the command line arguments for .ply and PCD files
std::vector<int> pcd_file_indices = parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".pcd");
if (pcd_file_indices.size () != 1)
{
print_error ("Need a single output PCD file to continue.\n");
return (-1);
}
std::vector<int> ply_file_indices = parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".ply");
std::vector<int> obj_file_indices = parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".obj");
if (ply_file_indices.size () != 1 && obj_file_indices.size () != 1)
{
print_error ("Need a single input PLY/OBJ file to continue.\n");
return (-1);
} vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polydata1 = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New ();
if (ply_file_indices.size () == 1)
{
pcl::PolygonMesh mesh;
pcl::io::loadPolygonFilePLY (argv[ply_file_indices[0]], mesh);
pcl::io::mesh2vtk (mesh, polydata1);
}
else if (obj_file_indices.size () == 1)
{
vtkSmartPointer<vtkOBJReader> readerQuery = vtkSmartPointer<vtkOBJReader>::New ();
readerQuery->SetFileName (argv[obj_file_indices[0]]);
readerQuery->Update ();
polydata1 = readerQuery->GetOutput ();
} //make sure that the polygons are triangles!
vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangleFilter> triangleFilter = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangleFilter>::New ();
#if VTK_MAJOR_VERSION < 6
triangleFilter->SetInput (polydata1);
#else
triangleFilter->SetInputData (polydata1);
#endif
triangleFilter->Update (); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> triangleMapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New ();
triangleMapper->SetInputConnection (triangleFilter->GetOutputPort ());
triangleMapper->Update ();
polydata1 = triangleMapper->GetInput (); bool INTER_VIS = false; if (INTER_VIS)
{
visualization::PCLVisualizer vis;
vis.addModelFromPolyData (polydata1, "mesh1", 0);
vis.setRepresentationToSurfaceForAllActors ();
vis.spin ();
} pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_1 (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);
uniform_sampling (polydata1, SAMPLE_POINTS_, write_normals, *cloud_1); if (INTER_VIS)
{
visualization::PCLVisualizer vis_sampled;
vis_sampled.addPointCloud<pcl::PointNormal> (cloud_1);
if (write_normals)
vis_sampled.addPointCloudNormals<pcl::PointNormal> (cloud_1, 1, 0.02f, "cloud_normals");
vis_sampled.spin ();
} // Voxelgrid
VoxelGrid<PointNormal> grid_;
grid_.setInputCloud (cloud_1);
grid_.setLeafSize (leaf_size, leaf_size, leaf_size); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr voxel_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);
grid_.filter (*voxel_cloud); if (vis_result)
{
visualization::PCLVisualizer vis3 ("VOXELIZED SAMPLES CLOUD");
vis3.addPointCloud<pcl::PointNormal> (voxel_cloud);
if (write_normals)
vis3.addPointCloudNormals<pcl::PointNormal> (voxel_cloud, 1, 0.02f, "cloud_normals");
vis3.spin ();
} if (!write_normals)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_xyz (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// Strip uninitialized normals from cloud:
pcl::copyPointCloud (*voxel_cloud, *cloud_xyz);
savePCDFileASCII (argv[pcd_file_indices[0]], *cloud_xyz);
}
else
{
savePCDFileASCII (argv[pcd_file_indices[0]], *voxel_cloud);
}
}
PCL学习(二)三维模型转点云 obj转pcd----PCL实现的更多相关文章
- PCL学习(四)点云转换为网格
Remove needless points compute normals surface reconstruction get texture(param 4096 basic) save pro ...
- 点云库PCL学习
1. 点云的提取 点云的获取:RGBD获取 点云的获取:图像匹配获取(通过摄影测量提取点云数据) 点云的获取:三维激光扫描仪 2. PCL简介 PCL是Point Cloud Library的简称,是 ...
- PCL学习(一)从PLY文件读入点云数据
#include <iostream> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #inclu ...
- 从零开始一起学习SLAM | 你好,点云
本文提纲 先热热身点云是啥你知道点云优缺点吗?点云库PCL:开发者的福音PCL安装指北炒鸡简单的PCL实践留个作业再走先热热身 小白:hi,师兄,好久不见师兄:师妹好,上周单应矩阵作业做了吗?小白:嗯 ...
- PCL学习八叉树
建立空间索引在点云数据处理中有着广泛的应用,常见的空间索引一般 是自顶而下逐级划分空间的各种空间索引结构,比较有代表性的包括BSP树,KD树,KDB树,R树,四叉树,八叉树等索引结构,而这些结构中,K ...
- SpringCloud学习(二):微服务入门实战项目搭建
一.开始使用Spring Cloud实战微服务 1.SpringCloud是什么? 云计算的解决方案?不是 SpringCloud是一个在SpringBoot的基础上构建的一个快速构建分布式系统的工具 ...
- DjangoRestFramework学习二之序列化组件、视图组件 serializer modelserializer
DjangoRestFramework学习二之序列化组件.视图组件 本节目录 一 序列化组件 二 视图组件 三 xxx 四 xxx 五 xxx 六 xxx 七 xxx 八 xxx 一 序列化组 ...
- PCL学习笔记1
先贴一段代码,从别处抄来的 #include <iostream> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/point_type ...
- Android JNI学习(二)——实战JNI之“hello world”
本系列文章如下: Android JNI(一)——NDK与JNI基础 Android JNI学习(二)——实战JNI之“hello world” Android JNI学习(三)——Java与Nati ...
随机推荐
- Vue.js 中的 v-cloak 指令
可以使用 v-cloak 指令设置样式,这些样式会在 Vue 实例编译结束时,从绑定的 HTML 元素上被移除. 当网络较慢,网页还在加载 Vue.js ,而导致 Vue 来不及渲染,这时页面就会显示 ...
- git 文件名大小写不敏感
1. 通过修改 git 配置: git config core.ignorecase false 2. 强制执行修改文件名命令: 需要重命名已添加到git的文件时,git mv --f oldFile ...
- splay树 序列终结者
/* 4655 序列终结者 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 大师 Master 题解 题目描述 Description 网上有许多题,就是给定一个序 ...
- Fidller抓包分析post请求
目的:抓包是为了最近做接口测试做准备,以前没有用过这个工具,最近来学下,但是网上很多文章了,所以不一一记录,有一部分参考即可 1.如何抓取想要的web端或者手机端包,已经有很多文章谢了,推荐的参考文章 ...
- 微信小程序入门与实战 从0到1进行细致讲解 涵盖小程序开发核心技能下载
第1章 什么是微信小程序? 第2章 小程序环境搭建与开发工具介绍 第3章 从一个简单的“欢迎“页面开始小程序之旅 第4章 第二个页面:新闻阅读列表 第5章 小程序的模板化与模块化 第6章 构建新闻详情 ...
- Java基础系列 - 查找数组的最大值和最小值
package com.test6; public class test5 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 2, ...
- C语言应用--数据类型定制一定义和引用
目前,定制正在变的越来越普遍,定制服务.定制衣服.甚至使用的键盘都是定制了.在C语言中虽然也包括了整型.字符型和浮点型等基本类型,也有基本的组合数据类型数组.但是这些类型都是针对某一种特定类型时应用没 ...
- vue.js 中this.$router.push()的使用
在vue项目中,跳转可以用router-link直接跳到某个页面 因为有时候会需要做一些判断等情况,所以要用到 this.$router.push() 因为外链跳转根本就不在router的设计考虑范围 ...
- javascript中的contains方法和compareDocumentPosition方法
IE有许多好用的方法,后来都被其他浏览器抄袭了,比如这个contains方法.如果A元素包含B元素,则返回true,否则false.唯一不支持这个方法的是IE的死对头firefox.不过火狐支持com ...
- js的一些笔试面试题
1. 判断字符串是否是这样组成的,第一个必须是字母,后面可以是字母.数字.下划线,总长度为5-20 var reg = /^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z_0-9]{4,19}$/; reg.test ...
