Cartographer源码阅读(9):图优化的前端——闭环检测
约束计算
闭环检测的策略:搜索闭环,通过匹配检测是否是闭环,采用了分支定界法。
前已经述及PoseGraph的内容,此处继续。位姿图类定义了pose_graph::ConstraintBuilder constraint_builder_对象。
1.ConstraintBuilder类图
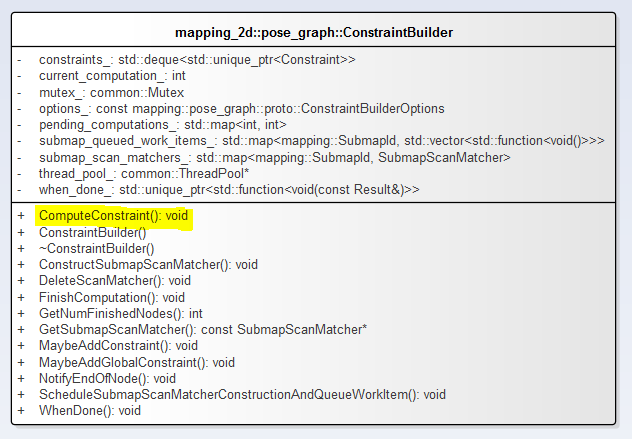
定义了SubmapScanMatcher的键值对。
// Map of already constructed scan matchers by 'submap_id'.
std::map<mapping::SubmapId, SubmapScanMatcher> submap_scan_matchers_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
SubmapScanMatcher结构体定义如下:
struct SubmapScanMatcher
{
const ProbabilityGrid* probability_grid;
std::unique_ptr<scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher>
fast_correlative_scan_matcher;
};
注意ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint方法,MaybeAddConstraint和MaybeAddGlobalConstraint都调用了该方法。
void ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint(
const mapping::SubmapId& submap_id, const Submap* const submap,
const mapping::NodeId& node_id, bool match_full_submap,
const mapping::TrajectoryNode::Data* const constant_data,
const transform::Rigid2d& initial_relative_pose,
std::unique_ptr<ConstraintBuilder::Constraint>* constraint) {
const transform::Rigid2d initial_pose =
ComputeSubmapPose(*submap) * initial_relative_pose;
const SubmapScanMatcher* const submap_scan_matcher =
GetSubmapScanMatcher(submap_id); // The 'constraint_transform' (submap i <- node j) is computed from:
// - a 'filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud' in node j,
// - the initial guess 'initial_pose' for (map <- node j),
// - the result 'pose_estimate' of Match() (map <- node j).
// - the ComputeSubmapPose() (map <- submap i)
float score = .;
transform::Rigid2d pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d::Identity(); // Compute 'pose_estimate' in three stages:
// 1. Fast estimate using the fast correlative scan matcher.
// 2. Prune if the score is too low.
// 3. Refine.
if (match_full_submap) {
if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->MatchFullSubmap(
constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud,
options_.global_localization_min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) {
CHECK_GT(score, options_.global_localization_min_score());
CHECK_GE(node_id.trajectory_id, );
CHECK_GE(submap_id.trajectory_id, );
} else {
return;
}
} else {
if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->Match(
initial_pose, constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud,
options_.min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) {
// We've reported a successful local match.
CHECK_GT(score, options_.min_score());
} else {
return;
}
}
{
common::MutexLocker locker(&mutex_);
score_histogram_.Add(score);
} // Use the CSM estimate as both the initial and previous pose. This has the
// effect that, in the absence of better information, we prefer the original
// CSM estimate.
ceres::Solver::Summary unused_summary;
ceres_scan_matcher_.Match(pose_estimate.translation(), pose_estimate,
constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud,
*submap_scan_matcher->probability_grid,
&pose_estimate, &unused_summary); const transform::Rigid2d constraint_transform =
ComputeSubmapPose(*submap).inverse() * pose_estimate;
constraint->reset(new Constraint{submap_id,
node_id,
{transform::Embed3D(constraint_transform),
options_.loop_closure_translation_weight(),
options_.loop_closure_rotation_weight()},
Constraint::INTER_SUBMAP}); if (options_.log_matches()) {
std::ostringstream info;
info << "Node " << node_id << " with "
<< constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud.size()
<< " points on submap " << submap_id << std::fixed;
if (match_full_submap) {
info << " matches";
} else {
const transform::Rigid2d difference =
initial_pose.inverse() * pose_estimate;
info << " differs by translation " << std::setprecision()
<< difference.translation().norm() << " rotation "
<< std::setprecision() << std::abs(difference.normalized_angle());
}
info << " with score " << std::setprecision() << . * score << "%.";
LOG(INFO) << info.str();
}
}
这里出现了scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher,另一种扫描匹配的方法。论文中介绍的分支定界法就在这个类中实现。
以上FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::Match和FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchFullSubmap方法都调用了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters方法。
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters调用了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound方法。
|
Tips:总结一下出现的几种扫描匹配的方法? RealTimeCorrelativeScanMatcher FastCorrelativeScanMatcher |
bool FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters(
SearchParameters search_parameters,
const transform::Rigid2d& initial_pose_estimate,
const sensor::PointCloud& point_cloud, float min_score, float* score,
transform::Rigid2d* pose_estimate) const
{
CHECK_NOTNULL(score);
CHECK_NOTNULL(pose_estimate); const Eigen::Rotation2Dd initial_rotation = initial_pose_estimate.rotation();
const sensor::PointCloud rotated_point_cloud = sensor::TransformPointCloud(
point_cloud,
transform::Rigid3f::Rotation(Eigen::AngleAxisf(
initial_rotation.cast<float>().angle(), Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ())));
const std::vector<sensor::PointCloud> rotated_scans =
GenerateRotatedScans(rotated_point_cloud, search_parameters);
const std::vector<DiscreteScan> discrete_scans = DiscretizeScans(
limits_, rotated_scans,
Eigen::Translation2f(initial_pose_estimate.translation().x(),
initial_pose_estimate.translation().y()));
search_parameters.ShrinkToFit(discrete_scans, limits_.cell_limits()); const std::vector<Candidate> lowest_resolution_candidates =
ComputeLowestResolutionCandidates(discrete_scans, search_parameters);
const Candidate best_candidate = BranchAndBound(
discrete_scans, search_parameters, lowest_resolution_candidates,
precomputation_grid_stack_->max_depth(), min_score);//分支定界法
if (best_candidate.score > min_score) {
*score = best_candidate.score;
*pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d(
{initial_pose_estimate.translation().x() + best_candidate.x,
initial_pose_estimate.translation().y() + best_candidate.y},
initial_rotation * Eigen::Rotation2Dd(best_candidate.orientation));
return true;
}
return false;
}
2.分支定界法
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound,......
Candidate FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound(
const std::vector<DiscreteScan>& discrete_scans,
const SearchParameters& search_parameters,
const std::vector<Candidate>& candidates, const int candidate_depth,
float min_score) const
{
if (candidate_depth == )
{
// Return the best candidate.
return *candidates.begin();
} Candidate best_high_resolution_candidate(, , , search_parameters);
best_high_resolution_candidate.score = min_score;
for (const Candidate& candidate : candidates)
{
if (candidate.score <= min_score) { break; }
std::vector<Candidate> higher_resolution_candidates;
const int half_width = << (candidate_depth - );
for (int x_offset : {, half_width})
{
if (candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset >
search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_x) {
break;
}
for (int y_offset : {, half_width}) {
if (candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset >
search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_y) {
break;
}
higher_resolution_candidates.emplace_back(
candidate.scan_index, candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset,
candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset, search_parameters);
}
}
ScoreCandidates(precomputation_grid_stack_->Get(candidate_depth - ),
discrete_scans, search_parameters,
&higher_resolution_candidates);
best_high_resolution_candidate = std::max(
best_high_resolution_candidate,
BranchAndBound(discrete_scans, search_parameters,
higher_resolution_candidates, candidate_depth - ,
best_high_resolution_candidate.score));
}
return best_high_resolution_candidate;
}
Cartographer源码阅读(9):图优化的前端——闭环检测的更多相关文章
- Cartographer源码阅读(1):程序入口
带着几个思考问题: (1)IMU数据的使用,如何融合,Kalman滤波? (2)图优化的具体实现,闭环检测的策略? (3)3D激光的接入和闭环策略? 1. 安装Kdevelop工具: http://b ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(3):程序逻辑结构
Cartographer早期的代码在进行3d制图的时候使用了UKF方法,查看现有的tag版本,可以转到0.1.0和0.2.0查看,包含kalman_filter文件夹. 文件夹中的pose_track ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(5):PoseGraph位姿图
PoseGraph位姿图 mapping2D::PoseGraph类的注释: // Implements the loop closure method called Sparse Pose Adju ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(6):LocalTrajectoryBuilder和PoseExtrapolator
LocalTrajectoryBuilder意思是局部轨迹的构建,下面的类图中方法的参数没有画进去. 注意其中的三个类:PoseExtrapolator类,RealTimeCorrelativeSca ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(4):Node和MapBuilder对象2
MapBuilder的成员变量sensor::Collator sensor_collator_; 再次阅读MapBuilder::AddTrajectoryBuilder方法.首先构造了mappin ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(8):imu_tracker
IMU的输入为imu_linear_acceleration 和 imu_angular_velocity 线加速和角速度.最终作为属性输出的是方位四元数. Eigen::Quaterniond ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(2):Node和MapBuilder对象
上文提到特别注意map_builder_bridge_.AddTrajectory(x,x),查看其中的代码.两点: 首先是map_builder_.AddTrajectoryBuilder(...) ...
- Cartographer源码阅读(7):轨迹推算和位姿推算的原理
其实也就是包括两个方面的内容:类似于运动模型的位姿估计和扫描匹配,因为需要计算速度,所以时间就有必要了! 1. PoseExtrapolator解决了IMU数据.里程计和位姿信息进行融合的问题. 该类 ...
- 【原】SDWebImage源码阅读(四)
[原]SDWebImage源码阅读(四) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 SDWebImage中主要实现了NSURLConnectionDataDelega ...
随机推荐
- 我的2018:OCR、实习和秋招
真的是光阴似箭,好像昨天还沉浸在考研成功的喜悦,今天却要即将步入2019年,即将硕士毕业.老规矩,还是在每一年的最后一天总结今年以及展望明年.回首2018,经历的东西特别多,视野也开阔了不少,可以说, ...
- 数据仓库:Mysql大量数据快速导出
背景 写这篇文章主要是介绍一下我做数据仓库ETL同步的过程中遇到的一些有意思的内容和提升程序运行效率的过程. 关系型数据库: 项目初期:游戏的运营数据比较轻量,相关的运营数据是通过Java后台程序聚合 ...
- Linux常用的基础组件
Linux服务器(新机器) yum install gcc gcc-c++ glibc-devel make ncurses-devel openssl-devel autoconf git yum ...
- UITableView 自定义多选
前言 在上一篇文章中介绍了UITableView的多选操作,有提到将 return UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete | UITableViewCellEditing ...
- tensorflow冻结变量方法(tensorflow freeze variable)
最近由于项目需要,要对tensorflow构造的模型中部分变量冻结,然后继续训练,因此研究了一下tf中冻结变量的方法,目前找到三种,各有优缺点,记录如下: 1.名词解释 冻结变量,指的是在训练模型时, ...
- xib view frame 大小调整
1.IOS - xib(Interface Builder,view) - can't change view size(view不能改变大小问题) 很多时候,我们自定义tableview.colle ...
- Python的安装以及编译器的安装
首先要想写python语言,要安装并配置python的环境,点击python下载即可,当然需要看下自己电脑适合下载的版本,64位还是32位的即可. 安装一般情况安装在C盘即可,选择添加变量的配置,完成 ...
- 异常处理与MiniDump 用于投放市场c++异常捕获
最近一段时间,新上线的软件在外场偶尔会出现异常崩溃的情况.由于试用范围比较分散,很难一一前往现场定位问题.而传统的log日志方法,在崩溃的情况下,并不能比较准确的表示出问题位置,这使得软件调试进程缓慢 ...
- http://www.rehack.cn/techshare/webbe/php/3391.html
首先配置好本地PHPstudy环境: 默认在D:\phpStudy\php\php-7.0.12-nts\ext目录下有php_pdo_sqlsrv_7_nts_x86.dll.php_sqlsrv_ ...
- C#俄罗斯方块小游戏程序设计与简单实现
C#俄罗斯方块小游戏程序设计与简单实现 相信90后或者80后都玩过这款小游戏,一直想干一票,琢磨一下,但又不太懂,于是网上搜集修改就有了以下效果!bug较多,多多包涵! 1.效果展示 2.实现方法 参 ...
