matplotlib 进阶之origin and extent in imshow
matplotlib教程学习笔记
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
def index_to_coordinate(index, extent, origin):
"""Return the pixel center of an index."""
left, right, bottom, top = extent
hshift = 0.5 * np.sign(right - left)
left, right = left + hshift, right - hshift
vshift = 0.5 * np.sign(top - bottom)
bottom, top = bottom + vshift, top - vshift
if origin == 'upper':
bottom, top = top, bottom
return {
"[0, 0]": (left, bottom),
"[M', 0]": (left, top),
"[0, N']": (right, bottom),
"[M', N']": (right, top),
}[index]
def get_index_label_pos(index, extent, origin, inverted_xindex):
"""
Return the desired position and horizontal alignment of an index label.
"""
if extent is None:
extent = lookup_extent(origin)
left, right, bottom, top = extent
x, y = index_to_coordinate(index, extent, origin)
is_x0 = index[-2:] == "0]"
halign = 'left' if is_x0 ^ inverted_xindex else 'right'
hshift = 0.5 * np.sign(left - right)
x += hshift * (1 if is_x0 else -1)
return x, y, halign
def get_color(index, data, cmap):
"""Return the data color of an index."""
val = {
"[0, 0]": data[0, 0],
"[0, N']": data[0, -1],
"[M', 0]": data[-1, 0],
"[M', N']": data[-1, -1],
}[index]
return cmap(val / data.max())
def lookup_extent(origin):
"""Return extent for label positioning when not given explicitly."""
if origin == 'lower':
return (-0.5, 6.5, -0.5, 5.5)
else:
return (-0.5, 6.5, 5.5, -0.5)
def set_extent_None_text(ax):
ax.text(3, 2.5, 'equals\nextent=None', size='large',
ha='center', va='center', color='w')
def plot_imshow_with_labels(ax, data, extent, origin, xlim, ylim):
"""Actually run ``imshow()`` and add extent and index labels."""
im = ax.imshow(data, origin=origin, extent=extent)
# extent labels (left, right, bottom, top)
left, right, bottom, top = im.get_extent()
if xlim is None or top > bottom:
upper_string, lower_string = 'top', 'bottom'
else:
upper_string, lower_string = 'bottom', 'top'
if ylim is None or left < right:
port_string, starboard_string = 'left', 'right'
inverted_xindex = False
else:
port_string, starboard_string = 'right', 'left'
inverted_xindex = True
bbox_kwargs = {'fc': 'w', 'alpha': .75, 'boxstyle': "round4"}
ann_kwargs = {'xycoords': 'axes fraction',
'textcoords': 'offset points',
'bbox': bbox_kwargs}
ax.annotate(upper_string, xy=(.5, 1), xytext=(0, -1),
ha='center', va='top', **ann_kwargs)
ax.annotate(lower_string, xy=(.5, 0), xytext=(0, 1),
ha='center', va='bottom', **ann_kwargs)
ax.annotate(port_string, xy=(0, .5), xytext=(1, 0),
ha='left', va='center', rotation=90,
**ann_kwargs)
ax.annotate(starboard_string, xy=(1, .5), xytext=(-1, 0),
ha='right', va='center', rotation=-90,
**ann_kwargs)
ax.set_title('origin: {origin}'.format(origin=origin))
# index labels
for index in ["[0, 0]", "[0, N']", "[M', 0]", "[M', N']"]:
tx, ty, halign = get_index_label_pos(index, extent, origin,
inverted_xindex)
facecolor = get_color(index, data, im.get_cmap())
ax.text(tx, ty, index, color='white', ha=halign, va='center',
bbox={'boxstyle': 'square', 'facecolor': facecolor})
if xlim:
ax.set_xlim(*xlim)
if ylim:
ax.set_ylim(*ylim)
def generate_imshow_demo_grid(extents, xlim=None, ylim=None):
N = len(extents)
fig = plt.figure(tight_layout=True)
fig.set_size_inches(6, N * (11.25) / 5)
gs = GridSpec(N, 5, figure=fig)
columns = {'label': [fig.add_subplot(gs[j, 0]) for j in range(N)],
'upper': [fig.add_subplot(gs[j, 1:3]) for j in range(N)],
'lower': [fig.add_subplot(gs[j, 3:5]) for j in range(N)]}
x, y = np.ogrid[0:6, 0:7]
data = x + y
for origin in ['upper', 'lower']:
for ax, extent in zip(columns[origin], extents):
plot_imshow_with_labels(ax, data, extent, origin, xlim, ylim)
for ax, extent in zip(columns['label'], extents):
text_kwargs = {'ha': 'right',
'va': 'center',
'xycoords': 'axes fraction',
'xy': (1, .5)}
if extent is None:
ax.annotate('None', **text_kwargs)
ax.set_title('extent=')
else:
left, right, bottom, top = extent
text = ('left: {left:0.1f}\nright: {right:0.1f}\n' +
'bottom: {bottom:0.1f}\ntop: {top:0.1f}\n').format(
left=left, right=right, bottom=bottom, top=top)
ax.annotate(text, **text_kwargs)
ax.axis('off')
return columns
generate_imshow_demo_grid(extents=[None]);

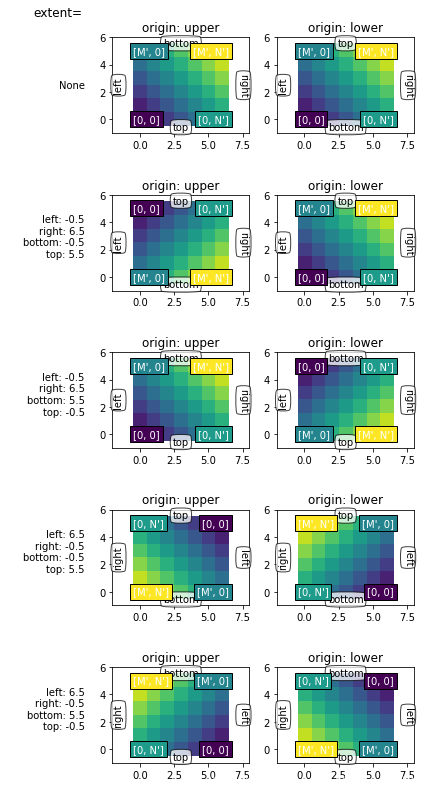
通常来说,对于shape(M, N)来讲,M是沿着竖直方向的,而N是沿着水平方向的。
origin参数觉得了其实位置:
对于 origin="lower":
[0, 0] 在 (left, bottom)位置
[M, 0] 在 (left, upper)位置
[0, N] 在 (right, bottom)位置
[M, N] 在 (right, top) 位置
实际上就是,从左下角往右上角发展
而对于orgin="upper",则是从左上角往右下角发展
显示的extent
extent是控制图片的坐标轴的工具,为(left, right, bottom, top)
就是控制x轴为: left -> right
y轴为: bottom -> top
extents = [(-0.5, 6.5, -0.5, 5.5),
(-0.5, 6.5, 5.5, -0.5),
(6.5, -0.5, -0.5, 5.5),
(6.5, -0.5, 5.5, -0.5)]
columns = generate_imshow_demo_grid(extents)
set_extent_None_text(columns['upper'][1])
set_extent_None_text(columns['lower'][0])

Explicit extent and axes limits
搞不懂了啊,为什么加了limits之后,可以随便转来转去了啊不知道,就这样吧
generate_imshow_demo_grid(extents=[None] + extents,
xlim=(-2, 8), ylim=(-1, 6));
matplotlib 进阶之origin and extent in imshow的更多相关文章
- matplotlib 进阶之Tight Layout guide
目录 简单的例子 Use with GridSpec Legend and Annotations Use with AxesGrid1 Colorbar 函数链接 matplotlib教程学习笔记 ...
- 【python】matplotlib进阶
参考文章:https://liam0205.me/2014/09/11/matplotlib-tutorial-zh-cn/ 几个重要对象:图像.子图.坐标轴.记号 figure:图像, subplo ...
- matplotlib 进阶之Constrained Layout Guide
目录 简单的例子 Colorbars Suptitle Legends Padding and Spacing spacing with colobars rcParams Use with Grid ...
- matplotlib 进阶之Customizing Figure Layouts Using GridSpec and Other Functions
目录 对Gridspec的一些精细的调整 利用SubplotSpec fig.add_grdispec; gs.subgridspec 一个利用Subplotspec的复杂例子 函数链接 matplo ...
- matplotlib 进阶之Legend guide
目录 matplotlib.pyplot.legend 方法1自动检测 方法2为现有的Artist添加 方3显示添加图例 控制图例的输入 为一类Artist设置图例 Legend 的位置 loc, b ...
- matplotlib 进阶之Artist tutorial(如何操作Atrist和定制)
目录 基本 plt.figure() fig.add_axes() ax.lines set_xlabel 一个完整的例子 定制你的对象 obj.set(alpha=0.5, zorder=2), o ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 热图imshow
热图: Display an image on the axes. 可以用来比较两个矩阵的相似程度 mp.imshow(z, cmap=颜色映射,origin=垂直轴向) imshow( X, cma ...
- 『Python』matplotlib的imshow用法
热力图是一种数据的图形化表示,具体而言,就是将二维数组中的元素用颜色表示.热力图之所以非常有用,是因为它能够从整体视角上展示数据,更确切的说是数值型数据. 使用imshow()函数可以非常容易地制作热 ...
- matplotlib 入门之Sample plots in Matplotlib
文章目录 Line Plot One figure, a set of subplots Image 展示图片 展示二元正态分布 A sample image Interpolating images ...
随机推荐
- 自然语言式parsing
got NUM(1) Is NUM(1) an expr? Is NUM(1) a term? Is NUM(1) a number? is_term got -(-) -(-) was back i ...
- A Child's History of England.32
And so, in darkness and in prison, many years, he thought of all his past life, of the time he had w ...
- Scala(三)【函数式编程】
目录 一.方法和函数 1.方法 1)基本语法 2)简化原则 3)方法参数 2.函数 3.方法和函数的区别 二.高阶函数 三.匿名函数 四.柯里化 五.闭包 一.方法和函数 1.方法 1)基本语法 de ...
- maven的lifecycle
1.maven clean. 清理项目的target目录 2.maven compile 编译项目 3.maven test 编译项目后,再执行Junit测试方法 4.maven package 编译 ...
- 基于docker 操作mysql5.7
1. 安装好 docker 2. 拉取 mysql5.7 镜像: docker pull mysql:5.7 其他版本 mysql:https://hub.docker.com/_/mysql?tab ...
- 【Linux】【Shell】【text】Vim
文本编辑器: 文本:纯文本,ASCII text:Unicode: 文本编辑种类: 行编辑器:sed 全屏编辑器:nano, vi vi: Visual Interface vim: Vi IMpro ...
- JQuery 和 CSS 等选择器:
JQuery 选择器: CSS 选择器:
- 通过js禁用浏览器的回退事件
js代码: <script> history.pushState(null, null, document.URL); window.addEventListener('popstate' ...
- 使用JSP实现输出
一.在JSP页面添加java代码,实现输出,java代码写在<% %>中. 代码示例1: <body> <!-- HTML注释 --> <%-- JSP注释 ...
- java中的++i是线程安全的吗?
java中的++i是线程安全的吗?为什么?怎么使它线程安全呢? 先说答案: 非线程安全 先说下为什么是非线程安全的? 从Java内存模型说起 Java内存模型规定了所有的便利都存储在主内存中,每个线程 ...
