java常用类-StringBuffer,Integer,Character
* StringBuffer:
* 线程安全的可变字符串。
*
* StringBuffer和String的区别?
* 前者长度和内容可变,后者不可变。
* 如果使用前者做字符串的拼接,不会浪费太多的资源。
*
* StringBuffer的构造方法:
* public StringBuffer():无参构造方法
* public StringBuffer(int capacity):指定容量的字符串缓冲区对象
* public StringBuffer(String str):指定字符串内容的字符串缓冲区对象
*
* StringBuffer的方法:
* public int capacity():返回当前容量。 理论值
* public int length():返回长度(字符数)。 实际值
// public StringBuffer():无参构造方法
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println("sb:" + sb);
System.out.println("sb.capacity():" + sb.capacity());
System.out.println("sb.length():" + sb.length());
System.out.println("--------------------------"); // public StringBuffer(int capacity):指定容量的字符串缓冲区对象
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer(50);
System.out.println("sb2:" + sb2);
System.out.println("sb2.capacity():" + sb2.capacity());
System.out.println("sb2.length():" + sb2.length());
System.out.println("--------------------------"); // public StringBuffer(String str):指定字符串内容的字符串缓冲区对象
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("hello");
System.out.println("sb3:" + sb3);
System.out.println("sb3.capacity():" + sb3.capacity());
System.out.println("sb3.length():" + sb3.length());
* StringBuffer的添加功能:
* public StringBuffer append(String str):可以把任意类型数据添加到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符串缓冲区本身
*
* public StringBuffer insert(int offset,String str):在指定位置把任意类型的数据插入到字符串缓冲区里面,并返回字符串缓冲区本身
* StringBuffer的删除功能
* public StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index):删除指定位置的字符,并返回本身
* public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end):删除从指定位置开始指定位置结束的内容,并返回本身
// 需求:我要删除所有的数据
sb.delete(0, sb.length());
* StringBuffer的替换功能:
* public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str):从start开始到end用str替换
* StringBuffer的反转功能:
* public StringBuffer reverse()
* StringBuffer的截取功能:注意返回值类型不再是StringBuffer本身了
* public String substring(int start)
* public String substring(int start,int end)
* String和StringBuffer的相互转换:
// String -- StringBuffer
String s = "hello";
// 注意:不能把字符串的值直接赋值给StringBuffer
// StringBuffer sb = "hello";
// StringBuffer sb = s;
// 方式1:通过构造方法
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(s);
// 方式2:通过append()方法
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer();
sb2.append(s);
System.out.println("sb:" + sb);
System.out.println("sb2:" + sb2);
System.out.println("---------------"); // StringBuffer -- String
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("java");
// String(StringBuffer buffer)
// 方式1:通过构造方法
String str = new String(buffer);
// 方式2:通过toString()方法
String str2 = buffer.toString();
System.out.println("str:" + str);
System.out.println("str2:" + str2);
* 把数组拼接成一个字符串
// 用StringBuffer做拼接的方式
public static String arrayToString2(int[] arr) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); sb.append("[");
for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) {
if (x == arr.length - 1) {
sb.append(arr[x]);
} else {
sb.append(arr[x]).append(", ");
}
}
sb.append("]"); return sb.toString();
}
* 面试题:
* 1:String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder的区别?
* A:String是内容不可变的,而StringBuffer,StringBuilder都是内容可变的。
* B:StringBuffer是同步的,数据安全,效率低;StringBuilder是不同步的,数据不安全,效率高
*
* 2:StringBuffer和数组的区别?
* 二者都可以看出是一个容器,装其他的数据。
* 但是呢,StringBuffer的数据最终是一个字符串数据。
* 而数组可以放置多种数据,但必须是同一种数据类型的。
*
* 3:形式参数问题
* String作为参数传递
* StringBuffer作为参数传递
*
* 形式参数:
* 基本类型:形式参数的改变不影响实际参数
* 引用类型:形式参数的改变直接影响实际参数
*
* 注意:
* String作为参数传递,效果和基本类型作为参数传递是一样的。
冒泡排序图解:

public class BubbleSort {
public static void sort(int[] data) {
for (int i = 0; i < data.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < data.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (data[j] > data[j + 1]) {
SortTest.swap(data, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
}
}
选择排序图解:
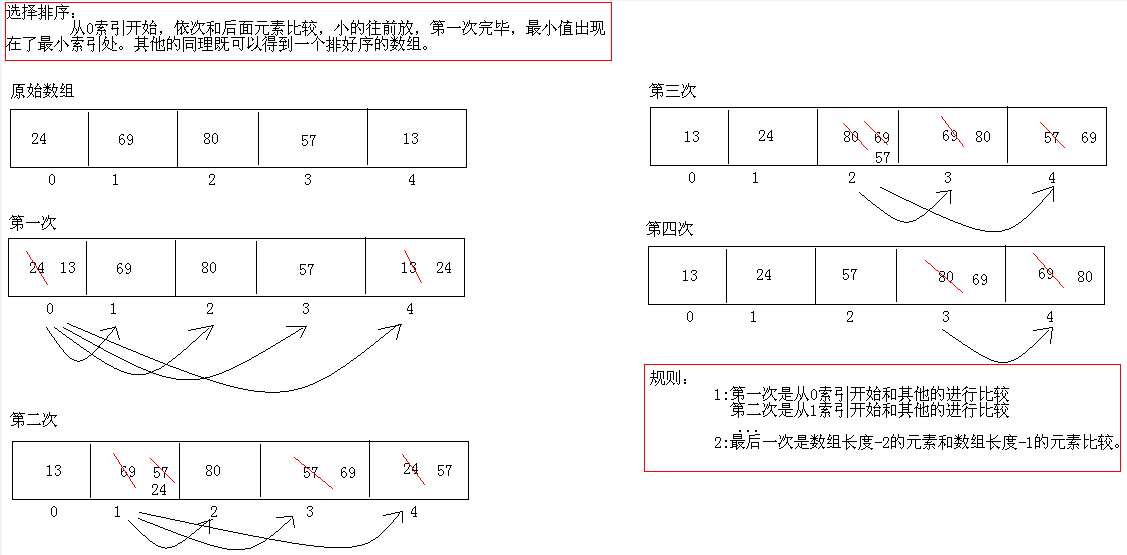
public class SelectionSort {
public static void sort(int[] data) {
for (int x = 0; x < data.length - 1; x++) {
for (int y = x + 1; y < data.length; y++) {
if (data[y] < data[x]) {
SortTest.swap(data, x, y);
}
}
}
}
}
二分查找图解:

// 二分查找
public static int getIndex(int[] arr, int value) {
// 定义最大索引,最小索引
int max = arr.length - 1;
int min = 0; // 计算出中间索引
int mid = (max + min) / 2; // 拿中间索引的值和要查找的值进行比较
while (arr[mid] != value) {
if (arr[mid] > value) {
max = mid - 1;
} else if (arr[mid] < value) {
min = mid + 1;
} // 加入判断
if (min > max) {
return -1;
} mid = (max + min) / 2;
} return mid;
}
* Arrays:针对数组进行操作的工具类。比如说排序和查找。
* 1:public static String toString(int[] a) 把数组转成字符串
* 2:public static void sort(int[] a) 对数组进行排序
* 3:public static int binarySearch(int[] a,int key) 二分查找
Arrays工具类的方法源码解析:
public static String toString(int[] a)
public static void sort(int[] a) 底层是快速排序,知道就可以了。有空看,有问题再问我
public static int binarySearch(int[] a,int key) 开发原则:
只要是对象,我们就要判断该对象是否为null。 int[] arr = { 24, 69, 80, 57, 13 };
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr)); public static String toString(int[] a) {
//a -- arr -- { 24, 69, 80, 57, 13 } if (a == null)
return "null"; //说明数组对象不存在
int iMax = a.length - 1; //iMax=4;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]"; //说明数组存在,但是没有元素。 StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('['); //"["
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]); //"[24, 69, 80, 57, 13"
if (i == iMax)
//"[24, 69, 80, 57, 13]"
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", "); //"[24, 69, 80, 57, "
}
}
----------------------------------------------------- int[] arr = {13, 24, 57, 69, 80};
System.out.println("binarySearch:" + Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 577)); public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) {
//a -- arr -- {13, 24, 57, 69, 80}
//key -- 577
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
} private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
//a -- arr -- {13, 24, 57, 69, 80}
//fromIndex -- 0
//toIndex -- 5
//key -- 577 int low = fromIndex; //low=0
int high = toIndex - 1; //high=4 while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1; //mid=2,mid=3,mid=4
int midVal = a[mid]; //midVal=57,midVal=69,midVal=80 if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1; //low=3,low=4,low=5
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
* 为了对基本数据类型进行更多的操作,更方便的操作,Java就针对每一种基本数据类型提供了对应的类类型。包装类类型。
* byte Byte
* short Short
* int Integer
* long Long
* float Float
* double Double
* char Character
* boolean Boolean
*
* 用于基本数据类型与字符串之间的转换。
// public static String toBinaryString(int i)
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(100));
// public static String toOctalString(int i)
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(100));
// public static String toHexString(int i)
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(100)); // public static final int MAX_VALUE
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// public static final int MIN_VALUE
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
* Integer的构造方法:
* public Integer(int value)
* public Integer(String s)
* 注意:这个字符串必须是由数字字符组成
String s = "100";
// NumberFormatException
// String s = "abc";
Integer iii = new Integer(s);
System.out.println("iii:" + iii);
* int类型和String类型的相互转换
*
* int -- String
* String.valueOf(number)
*
* String -- int
* Integer.parseInt(s)
// int -- String
int number = 100;
// 方式1
String s1 = "" + number;
System.out.println("s1:" + s1);
// 方式2
String s2 = String.valueOf(number);
System.out.println("s2:" + s2);
// 方式3
// int -- Integer -- String
Integer i = new Integer(number);
String s3 = i.toString();
System.out.println("s3:" + s3);
// 方式4
// public static String toString(int i)
String s4 = Integer.toString(number);
System.out.println("s4:" + s4);
System.out.println("-----------------"); // String -- int
String s = "100";
// 方式1
// String -- Integer -- int
Integer ii = new Integer(s);
// public int intValue()
int x = ii.intValue();
System.out.println("x:" + x);
//方式2
//public static int parseInt(String s)
int y = Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println("y:"+y);
* 常用的基本进制转换
* public static String toBinaryString(int i)
* public static String toOctalString(int i)
* public static String toHexString(int i)
*
* 十进制到其他进制
* public static String toString(int i,int radix)
* 由这个我们也看到了进制的范围:2-36
* 为什么呢?0,...9,a...z
*
* 其他进制到十进制
* public static int parseInt(String s,int radix)
* JDK5的新特性
* 自动装箱:把基本类型转换为包装类类型
* 自动拆箱:把包装类类型转换为基本类型
*
* 注意一个小问题:
* 在使用时,Integer x = null;代码就会出现NullPointerException。
* 建议先判断是否为null,然后再使用。
Integer iii = null;
// NullPointerException
if (iii != null) {
iii += 1000;
System.out.println(iii);
}
* 注意:Integer的数据直接赋值,如果在-128到127之间,会直接从缓冲池里获取数据
Integer i5 = 128;
Integer i6 = 128;
System.out.println(i5 == i6); //false
System.out.println(i5.equals(i6)); //true
System.out.println("-----------"); Integer i7 = 127;
Integer i8 = 127;
System.out.println(i7 == i8); //true
System.out.println(i7.equals(i8)); //true
* Character 类在对象中包装一个基本类型 char 的值
* 此外,该类提供了几种方法,以确定字符的类别(小写字母,数字,等等),并将字符从大写转换成小写,反之亦然
*
* 构造方法:
* Character(char value)
* public static boolean isUpperCase(char ch):判断给定的字符是否是大写字符
* public static boolean isLowerCase(char ch):判断给定的字符是否是小写字符
* public static boolean isDigit(char ch):判断给定的字符是否是数字字符
* public static char toUpperCase(char ch):把给定的字符转换为大写字符
* public static char toLowerCase(char ch):把给定的字符转换为小写字符
java常用类-StringBuffer,Integer,Character的更多相关文章
- Java常用类StringBuffer详解
内容多为最近学习的自我总结,可能有些地方写的不严谨,甚至会有错误的地方,仅供参考,如发现错误敬请指出,谢谢! 灰色字体为补充扩展内容,多为帮助自己理解. StringBuffer概述: 线程安全的可变 ...
- Java 常用类——StringBuffer&StringBuilder【可变字符序列】
一.字符串拼接问题 由于 String 类的对象内容不可改变,所以每当进行字符串拼接时,总是会在内存中创建一个新的对象. Demo: 1 public class StringDemo { 2 pub ...
- Java基础 —— Java常用类
Java常用类: java.lang包: java.lang.Object类: hashcode()方法:返回一段整型的哈希码,代表地址. toString()方法:返回父类名+"@&quo ...
- Java常用类学习笔记总结
Java常用类 java.lang.String类的使用 1.概述 String:字符串,使用一对""引起来表示. 1.String声明为final的,不可被继承 2.String ...
- Java 常用类总结(SE基础)
本篇博客对java常用类相关知识进行了归纳总结,比较详细,适用于学习和复习. 1. 字符串相关的类 1.1 String String是一个final类,代表不可变的字符序列.不可被继承. Strin ...
- Java常用类的使用
Java常用类 1. Optional 在我们的开发中,NullPointerException可谓是随时随处可见,为了避免空指针异常,我们常常需要进行 一 些防御式的检查,所以在代码中常常可见if( ...
- Java常用类之要点总结
Java常用类之要点总结
- Java常用类:包装类,String,日期类,Math,File,枚举类
Java常用类:包装类,String,日期类,Math,File,枚举类
- Java常用类之String类、Stringbuffer和Random类练习
定义一个StringBuffer类对象, 1)使用append方法向对象中添加26个字母,并倒序遍历输入 2)删除前五个字符 package 第十一章常用类; /** * 定义一个StringBuff ...
随机推荐
- vue父子组件写法,数据传递,顺便封装 element-ui的弹窗组建
父组件如下: <template> <div class="print"> <el-button @click="bbclick" ...
- 初识github之注册和基本概念
通过大量的网络资源,我粗浅了解了GitHub是什么:一个开源的代码存储云平台,它的logo是一只 “章鱼猫(Octocat)”.那么开始学习GitHub第一部分——注册GitHub账号. 首先英文就让 ...
- node.js初识10
post请求 form.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charse ...
- NHibernate之旅系列文章导航
NHibernate之旅系列文章导航 宣传语 NHibernate.NHibernate教程.NHibernate入门.NHibernate下载.NHibernate教程中文版.NHibernate实 ...
- CSS background-image背景图片相关介绍
这里将会介绍如何通过background-image设置背景图片,以及背景图片的平铺.拉伸.偏移.设置大小等操作. 1. 背景图片样式分类 CSS中设置元素背景图片及其背景图片样式的属性主要以下几个: ...
- C# mongodb中内嵌文档数组条件查询
样例数据: { "_id" : "1064621564857", "cNo" : "1064621564857 ...
- Unity shader学习之屏幕后期处理效果之均值模糊
均值模糊,也使用卷积来实现,之不过卷积中每个值均相等,且相加等于1. 代码如下, 子类: using UnityEngine; public class MeanBlurRenderer : Post ...
- 大话设计模式C++ 备忘录模式
备忘录(Memento):在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态.这样以后就可将对象恢复到原先保存的状态. 角色: (1)Originator(发起人):创建盒子, ...
- django admim后台不转义提交的html
autoescape¶ Controls the current auto-escaping behavior. This tag takes either on or off as an argum ...
- CentOS 5 yum源无法使用
在新装的CentOS 5.7系统中,由于CentOS 5.7版本比较旧,yum源无法使用. 尝试多种方法,最终从http://blog.csdn.net/zhuix7788/article/detai ...
