IfcAxis2Placement3D IFC构件的位置和方向
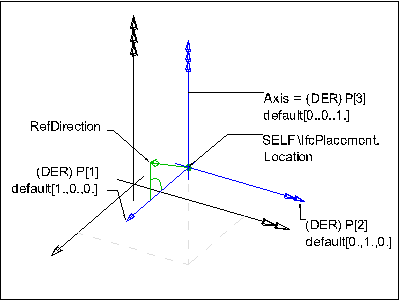
IfcAxis2Placement3D定义了三维空间中物体的位置和方向,由三部分组成:
The attribute Axis defines the Z direction, RefDirection the X direction. The Y direction is derived.
注:Y轴方向由X轴和Z轴方向通过外积计算获得。
当Axis和RefDirection未定义时,X轴为P[1] ,默认值 [1.,0.,0.]。Y轴为P[2],默认值为[0.,1.,0.]。Z轴为P[3] ,默认值为[0.,0.,1.]。
属性定义
| # | Attribute | Type | Cardinality | Description | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Axis | IfcDirection | [0:1] | The exact direction of the local Z Axis. | X |
| 3 | RefDirection | IfcDirection | [0:1] | The direction used to determine the direction of the local X Axis. If necessary an adjustment is made to maintain orthogonality to the Axis direction. If Axis and/or RefDirection is omitted, these directions are taken from the geometric coordinate system. | X |
| P :=IfcBuildAxes(Axis, RefDirection) |
IfcDirection | L[3:3] | The normalized directions of the placement X Axis (P[1]) and the placement Y Axis (P[2]) and the placement Z Axis (P[3]). | X |
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
| LocationIs3D | The dimensionality of the placement location shall be 3. |
| AxisIs3D | The Axis when given should only reference a three-dimensional IfcDirection. |
| RefDirIs3D | The RefDirection when given should only reference a three-dimensional IfcDirection. |
| AxisToRefDirPosition | The Axis and RefDirection shall not be parallel or anti-parallel. |
| AxisAndRefDirProvision | Either both, Axis and RefDirection are not given and therefore defaulted, or both shall be given. |
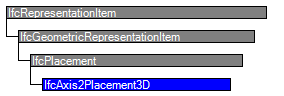
继承关系:
属性
| # | Attribute | Type | Cardinality | Description | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IfcRepresentationItem | |||||
| LayerAssignment | IfcPresentationLayerAssignment @AssignedItems |
S[0:1] | Assignment of the representation item to a single or multiple layer(s). The LayerAssignments can override a LayerAssignments of the IfcRepresentation it is used within the list of Items. | X | |
| StyledByItem | IfcStyledItem @Item |
S[0:1] | Reference to the IfcStyledItem that provides presentation information to the representation, e.g. a curve style, including colour and thickness to a geometric curve. | X | |
| IfcGeometricRepresentationItem | |||||
| IfcPlacement | |||||
| 1 | Location | IfcCartesianPoint | [1:1] | The geometric position of a reference point, such as the center of a circle, of the item to be located. | X |
| Dim :=Location.Dim |
IfcDimensionCount | [1:1] | The space dimensionality of this class, derived from the dimensionality of the location. | X | |
| IfcAxis2Placement3D | |||||
| 2 | Axis | IfcDirection | [0:1] | The exact direction of the local Z Axis. | X |
| 3 | RefDirection | IfcDirection | [0:1] | The direction used to determine the direction of the local X Axis. If necessary an adjustment is made to maintain orthogonality to the Axis direction. If Axis and/or RefDirection is omitted, these directions are taken from the geometric coordinate system. | X |
| P :=IfcBuildAxes(Axis, RefDirection) |
IfcDirection | L[3:3] | The normalized directions of the placement X Axis (P[1]) and the placement Y Axis (P[2]) and the placement Z Axis (P[3]). | X | |
ENTITY IfcAxis2Placement3D
SUBTYPE OF (IfcPlacement);
Axis : OPTIONAL IfcDirection;
RefDirection : OPTIONAL IfcDirection;
DERIVE
P : LIST [:] OF IfcDirection := IfcBuildAxes(Axis, RefDirection);
WHERE
LocationIs3D : SELF\IfcPlacement.Location.Dim = ;
AxisIs3D : (NOT (EXISTS (Axis))) OR (Axis.Dim = );
RefDirIs3D : (NOT (EXISTS (RefDirection))) OR (RefDirection.Dim = );
AxisToRefDirPosition : (NOT (EXISTS (Axis))) OR (NOT (EXISTS (RefDirection))) OR (IfcCrossProduct(Axis,RefDirection).Magnitude > 0.0);
AxisAndRefDirProvision : NOT ((EXISTS (Axis)) XOR (EXISTS (RefDirection)));
END_ENTITY;
DATA;
#= IFCORGANIZATION($,'Autodesk Revit 2015 (CHS)',$,$,$);
#= IFCAPPLICATION(#,'','Autodesk Revit 2015 (CHS)','Revit');
#= IFCCARTESIANPOINT((.,.,.));
#= IFCCARTESIANPOINT((.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((-.,.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,-.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,.,-.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((-.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,.));
#= IFCDIRECTION((.,-.)); #= IFCAXIS2PLACEMENT3D(#,$,$);
#= IFCAXIS2PLACEMENT3D(#,$,$);
#= IFCLOCALPLACEMENT($,#);
#= IFCLOCALPLACEMENT(#,#); #= IFCAXIS2PLACEMENT3D(#,$,$);
#= IFCLOCALPLACEMENT(#,#); #= IFCCARTESIANTRANSFORMATIONOPERATOR3D($,$,#,.,$);
#= IFCSHAPEREPRESENTATION(#,'Body','SweptSolid',(#));
#= IFCAXIS2PLACEMENT3D(#,$,$);
#= IFCREPRESENTATIONMAP(#,#); #= IFCMAPPEDITEM(#,#);
#= IFCSHAPEREPRESENTATION(#,'Body','MappedRepresentation',(#));
#= IFCPRODUCTDEFINITIONSHAPE($,$,(#)); #= IFCCARTESIANPOINT((1325.86888709244,31631.0676658748,.));
#= IFCAXIS2PLACEMENT3D(#,$,$);
#= IFCLOCALPLACEMENT(#,#);
#= IFCCOLUMN('2ILfSTle57UhpKxVJ8Mj7L',#,'\X2\7EFC5408697C\X0\-\X2\6DF751DD571F77E95F6267F1\X0\:450 x 600 mm:365232',$,'450 x 600 mm',#,#,'');
计算构件y轴方向
# = IfcDirection((0.,.,.)); //z轴
# = IfcDirection((.,.,.)); //x轴
# = IfcAxis2Placement3D($,#,#); //叉积计算出y轴 (0 ,1, 0)
# = IfcLocalPlacement($,#);
# = IfcDirection((.,.,.)); //z轴
# = IfcDirection((.,.,.)); //x轴
# = IfcAxis2Placement3D($,#,#); //叉积计算出y轴(1, 0, -1)
# = IfcLocalPlacement(#,#); //矩阵相乘(注意顺序)结果:x轴(0,0,1)y轴(1,0,0)z轴(0,1,0)
向量叉积计算
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Vec {
double x;
double y;
double z;
};
Vec ThreeCross(const Vec& a, const Vec& b)
{
Vec C;
C.x = a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y;
C.y = a.z * b.x - a.x * b.z;
C.z = a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
return C;
}
int main()
{
Vec v1;
v1.x = ;
v1.y = ;
v1.z = ;
Vec v2;
v2.x = ;
v2.y = ;
v2.z = ;
Vec v3 = ThreeCross(v1,v2);
cout << v3.x << " " << v3.y << " " << v3.z << endl;
system("pause");
return ;
}
向量叉积计算公式:
a=(X1,Y1,Z1),b=(X2,Y2,Z2),
a×b=(Y1Z2 - Y2Z1,Z1X2 - Z2X1,X1Y2 - X2Y1)
V1(1,2,3)
V2(4,5,6)
V1 * V2=(12-15,12-6,5-8)=(-3,6,-3)

参考:https://blog.csdn.net/liyazhen2011/article/details/82347074
IfcAxis2Placement3D IFC构件的位置和方向的更多相关文章
- 获取IFC构件的位置数据、方向数据
获取IFC构件的位置数据.方向数据 std::map<int, shared_ptr<BuildingEntity>> map_buildingEntity = b_model ...
- IFC构件位置数据与revit模型中对应构件位置数据对比
IFC构件位置数据与revit模型中对应构件位置数据对比
- iOS使用位置和方向服务(来自苹果apple官方)
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 目录(?)[+] 本文章来自苹果官方文档,特此声明--------禚 Core Location框架为定位用户当前位置和方向(Headin ...
- Unity 中动态修改碰撞框(位置,大小,方向)
在Unity中,玩家处于不同的状态,要求的碰撞框的 位置/大小/方向 会有所改变,怎么动态的修改碰撞框呢? 下面是Capsure Collider(胶囊体)的修改: CapsuleCollider.d ...
- 不规则形状的Ifc构件顶点坐标获取
不规则形状的Ifc构件顶点坐标获取 今天有人问我,ifc构件的顶点坐标怎么获取,自己前年的时候写过类似的程序,但有点记不清了,最近一直用C++解析ifc,慎重起见,还是重新再写一次,java版本的获取 ...
- IFC构件位置信息—ObjectPlacement
在IFC标准中,采用相对坐标系对构件定位.如柱(IfcColumn)的定位信息(局部坐标系及参考坐标系)由ObjectPlacement描述.ObjectPlacement由两部分组成: (1)Pla ...
- ios的位置和方向(来自苹果官方文档,仅供简单参考)
取得用户的当前位置 Core Location框架使您可以定位设备的当前位置,并将这个信息应用到程序中.该框架利用设备内置的硬件,在已有信号的基础上通过三角测量得到固定位置,然后将它报告给您的代码.在 ...
- 不规则的Ifc构件顶点提取方法
BIM模型中有很多不规则的构件,在IFC中这些不规则的构件一般用顶点的形式表示,顶点坐标提取路径: IfcObject->IfcProductDefinitionShape->IfcSh ...
- ifc构件加载到树形控件中
void IfcTreeWidget::setParentCheckState(QTreeWidgetItem *item) { if(!item) return; ; int childCount ...
随机推荐
- 软件测试_Loadrunner_性能测试_脚本录制_录制多server请求脚本
之前我们写过使用Loadrunner录制APP脚本的基本流程:软件测试_Loadrunner_APP测试_性能测试_脚本录制_基本操作流程,但是只能用于请求单一服务器端口适用 这次主要是写的多serv ...
- 链表实现队列(python)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from collections import deque class Node(object): def __init__(self, value=N ...
- LRU(最近最少使用)(python实现)
""" python3 only LRU cache """ from collections import OrderedDict fro ...
- 大数据之路week06--day07(Hadoop常用命令)
一.前述 分享一篇hadoop的常用命令的总结,将常用的Hadoop命令总结如下. 二.具体 1.启动hadoop所有进程start-all.sh等价于start-dfs.sh + start-yar ...
- 0018SpringBoot连接docker中的mysql并使用druid数据源
由于druid数据源自带监控功能,所以引用druid数据源 1.centos7中安装并启动docker 2.docker安装并启动mysql 3.pom.xml中引入druid依赖 4.applica ...
- webpack 配置react脚手架(四):路由配置
1. 由于 react-router 是集成了 react-router-dom 和 react-router-native的一起的,所以这里要使用的是 react-router-dom, 2. 安装 ...
- 1~n中数字0~9出现的次数
题意:rt 分析: 当然不可能去遍历,应该寻找统计的方法. 如计算 78501 中 "5" 出现的次数. 我们可以枚举“5”出现的位置, 如当“5”位于倒数第2位时,写成 xxx5 ...
- sql server 变量和select 赋值的联合使用demo
) ) select @cltcode=cltcode,@brand=brand from prosamplehd CREATE table #t ( cltcode ), brand ) ) INS ...
- 064_将 Linux 系统中 UID 大于等于 1000 的普通用户都删除
#!/bin/bash#先用 awk 提取所有 uid 大于等于 1000 的普通用户名称#再使用 for 循环逐个将每个用户删除即可 user=$(awk -F: '$3>=1000{prin ...
- Cogs 461. [网络流24题] 餐巾(费用流)
[网络流24题] 餐巾 ★★★ 输入文件:napkin.in 输出文件:napkin.out 简单对比 时间限制:5 s 内存限制:128 MB [问题描述] 一个餐厅在相继的N天里,第i天需要Ri块 ...
