am335x system upgrade kernel uart(七)
1 Scope of Document
This document describes UART hardware design, uart driver porting
2 Requiremen
2.1 Function Requirement
Uboot enable uart0 for debug, Kernel enable uart0 uart1 uart2 uart3.
2.2 Performance Requirement
Support common uart rx tx function.
3 Hardware Overview
uart interface,pin map:
// uart 0
AM335X_UART0_RXD
AM335X_UART0_TXD
// uart 1
AM335X_UART1_RXD
AM335X_UART1_TXD
// uart 2
AM335X_UART2_RXD
AM335X_UART2_TXD
// uart 3
AM335X_UART3_RXD
AM335X_UART3_TXD

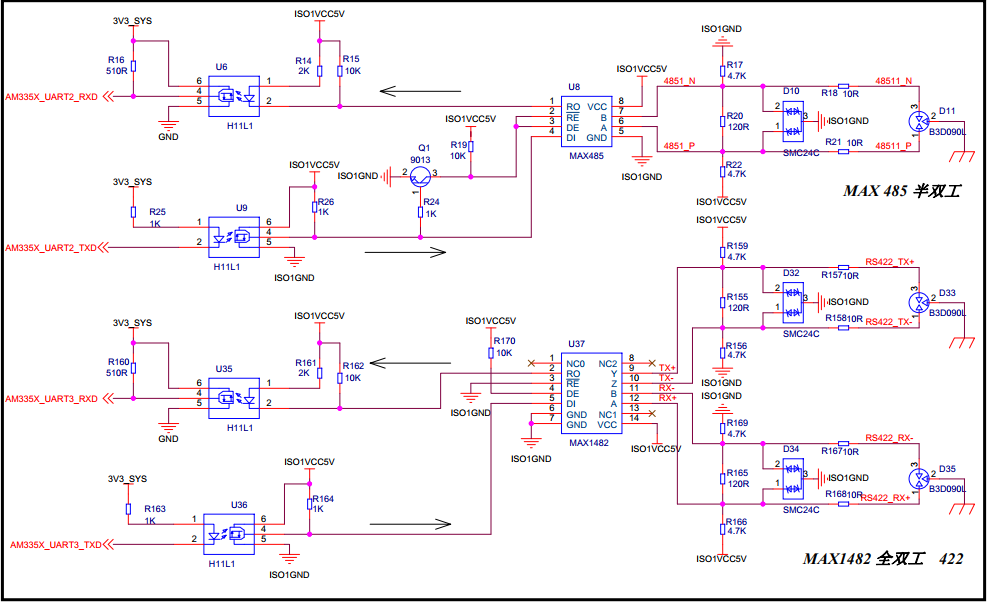
Figure 1 uart interface block diagram
4 Functional Description
4.1 UART DRIVER Overview
The UART Driver enables the UART’s available on the device. The driver configures the UART hardware and interfaces with a number of standard linux tools (ex. stty, minicom, etc.) to enable the configuration and usage of the hardware. The H/W UARTs available will vary by SoC and system configuration.
4.2 UART
4.2.1 Overview
The UART driver can be used to send/receive raw ASCII characters from the User Interface as shown by the below diagram..
4.2.1 User Layer
The UART driver leverages the TTY framework within Linux. This framework uses typical file I/O operations to interact with the UART. This interface allows userspace modules to easily be developed to read/write the /dev/ttyxx to exchange data over the UART. Since this is a very common Linux framework, there are many standard tools that can be used to interact with it. These tools, like stty, minicom, picocom, and many others, can easily be used to exercise a UART for data exchange.

Features
- Exposes UART to User Space via /dev/tty*
- Supports multiple baud rates and UART capabilities
- Hardware Flow Control
5 Porting
5.1 Uboot porting
In uboot default enable debug uart, so do not need to modify.
5.2 Kernel porting
Index: am335x-evm.dts
uart1_pins: pinmux_uart1_pins {
pinctrl-single,pins = <
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x980, PIN_INPUT_PULLUP | MUX_MODE1) /* uart1_rxd.uart1_rxd */
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x984, PIN_OUTPUT_PULLDOWN | MUX_MODE1) /* uart1_txd.uart1_txd */
>;
};
uart2_pins: pinmux_uart2_pins {
pinctrl-single,pins = <
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x92c, PIN_INPUT_PULLUP | MUX_MODE1) /* mii1_txclk.uart2_rxd */
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x930, PIN_OUTPUT_PULLDOWN | MUX_MODE1) /* mii1_rxclk.uart2_txd */
>;
};
uart3_pins: pinmux_uart3_pins {
pinctrl-single,pins = <
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x934, PIN_INPUT_PULLUP | MUX_MODE1) /* mii1_rxd3.uart3_rxd */
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x938, PIN_OUTPUT_PULLDOWN | MUX_MODE1) /* mii1_rxd2.uart3_txd */
>;
};
&uart1 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&uart1_pins>;
status = "okay";
};
&uart2 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&uart2_pins>;
status = "okay";
};
&uart3 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&uart3_pins>;
status = "okay";
};
6 Follow-up
Uart loop test code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define FALSE 1
#define TRUE 0
int fd=-1;
char buff[512];
int speed_arr[] = { B115200, B57600, B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800,
B2400, B1200};
int name_arr[] = {115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200};
#define debugnum(data,len,prefix) \
{ \
unsigned int i; \
for (i = 0;i < len;i++) { \
if(prefix) \
printf("0x%02x ",data[i]); \
else \
printf("%02x ",data[i]); \
} \
}
void set_speed(int fd, int speed)
{
int i;
int status;
struct termios Opt;
tcgetattr(fd, &Opt);
for ( i= 0; i < sizeof(speed_arr) / sizeof(int); i++)
{
if (speed == name_arr[i])
{
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);
cfsetispeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
cfsetospeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
status = tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &Opt);
if (status != 0)
perror("tcsetattr fd1");
return;
}
tcflush(fd,TCIOFLUSH);
}
}
int set_Parity(int fd,int databits,int stopbits,int parity)
{
struct termios options;
if ( tcgetattr( fd,&options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return(FALSE);
}
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch (databits)
{
case 7:
options.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
options.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported data size\n");
return (FALSE);
}
switch (parity)
{
case 'n':
case 'N':
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
options.c_iflag &= ~INPCK;
break;
case 'o':
case 'O':
options.c_cflag |= (PARODD | PARENB);
options.c_iflag |= INPCK;
break;
case 'e':
case 'E':
options.c_cflag |= PARENB;
options.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
options.c_iflag |= INPCK;
break;
case 'S':
case 's':
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported parity\n");
return (FALSE);
}
switch (stopbits)
{
case 1:
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
case 2:
options.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported stop bits\n");
return (FALSE);
}
options.c_iflag &= ~(IGNBRK|BRKINT|PARMRK|ISTRIP|INLCR|IGNCR|ICRNL|IXON);
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
options.c_lflag &= ~(ECHO|ECHONL|ICANON|ISIG|IEXTEN);
/* Set input parity option */
if (parity != 'n')
options.c_iflag |= INPCK;
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 150; // 15 seconds
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH); /* Update the options and do it NOW */
if (tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 3");
return (FALSE);
}
return (TRUE);
}
void receivethread(void)
{
int nread;
while(1)
{
if((nread = read(fd,buff,100))>0) //接收数据
{
printf("[RECEIVE] Len is %d,content is :\n",nread);
buff[nread]='\0';
printf("%s\n",buff);
}
usleep(100/**1000*/);
}
return;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char str[500];
pthread_t receiveid;
int c, ctrlbits;
/*
参数个数小于1则返回,按如下方式执行:
./uart_test /dev/ttyAT1
*/
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Useage: %s dev\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
printf("test\n");
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0){
printf("open device %s faild\n", argv[1]);
exit(0);
}
set_speed(fd,115200); //设置串口波特率
set_Parity(fd,8,1,'N'); //设置8位数据位,1位停止位,无校验等其他设置。
pthread_create(&receiveid,NULL,(void*)receivethread,NULL);//创建接收线程
while(1)
{
printf("Please Input string to send to %s\n:",argv[1]);
scanf("%s", str);
if(strlen(str)>0){
//发送数据
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
write(fd, "\n", strlen("\n"));
usleep(200*1000);
}
}
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
am335x system upgrade kernel uart(七)的更多相关文章
- am335x system upgrade kernel tf(五)
1 Scope of Document This document describes TF hardware design 2 Requiremen 2.1 Functi ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel ethernet(四)
1 Scope of Document This document describes ethernet hardware design and porting KZS8081 to ubo ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel gpio(九)
1 Hardware Overview gpio interface,pin map: AM335X_I2C0_W_C----------------------MCASP0_AXR1 /* ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel can(八)
1 Scope of Document This document describes can bus hardware design and can bus driver developm ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel i2c rtc eeprom(六)
1 Scope of Document This document describes i2c bus hardware design and support i2c-devices: ee ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel ec20 simcom7600ce(十一)
1 Scope of Document This document describes 4G hardware design, support quectel ec20 4G module/ ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel usb stroage(十)
1 Scope of Document This document describes USB hardware design, support stardard usb2.0 port o ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel f-ram fm25l16b(十六)
1 Scope of Document This document describes SPI F-RAM hardware design 2 Requiremen 2.1 ...
- am335x system upgrade kernel emmc(十八)
1 Scope of Document This document describes EMMC hardware design 2 Requiremen 2.1 Func ...
随机推荐
- python MySQL 插入Elasticsearch
一.需求分析 注意: 本环境使用 elasticsearch 7.0版本开发,切勿低于此版本 mysql 表结构 有一张表,记录的数据特别的多,需要将7天前的记录,插入到Elasticsearch中, ...
- docker 入坑1
本文是记录一下学习docker的过程,希望可以帮助到入门的朋友. 系统:ubuntu16.04 docker:18.09 打开官网:https://docs.docker.com/install/li ...
- 空间数据索引RTree(R树)完全解析及Java实现
第一部分 空间数据的背景介绍 空间数据的建模 基于实体的模型(基于对象)Entity-based models (or object based) 常用的空间数据查询方式 空间数据获取的方法 R树 简 ...
- ① Python3.0基础语法
稍微了解一下py2.0和py3.0的区别,Py3.0在设计的时候,为了不带入过多的累赘,没有考虑向下兼容低版本的Py2.0.而在低版本中Py2.6作为过渡版,基本使用Py2.x的语法和库,同时考虑Py ...
- Java调用WebService方法总结(8)--soap.jar调用WebService
Apache的soap.jar是一种历史很久远的WebService技术,大概是2001年左右的技术,所需soap.jar可以在http://archive.apache.org/dist/ws/so ...
- CSS标签选择器&类选择器
基本选择器包括标签选择器.类选择器和ID选择器三类,其他选择器都是在这三类选择器的基础上组合形成 ##标签选择器 示例: <style type="text/css"> ...
- Android数据存储原理分析
Android上常见的数据存储方式为: SharedPreferences是 Android 中比较常用的存储方法,本篇将从源码角度带大家分析一下Android中常用的轻量级数据存储工具SharedP ...
- 社交类app开发( 仿陌陌 客户端+服务器端)
一.开发所需要的技术 手机端需要Android/iOS开发人员,服务器端需要php/数据库开发人员, 如果再做网页版的话,WEB开发也是要的. 即时通讯 GPS地图 群聊 差不多 对 http so ...
- SpringBoot中LocalDatetime作为参数和返回值的序列化问题
欢迎访问我的个人网站 https://www.zhoutao123.com 本文原文地址 https://www.zhoutao123.com/#/blog/article/59 LocalDatet ...
- VIM的配置以及插件管理
VIM的配置详细说明参考:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2018/09/vimrc.html 此外VIM的插件管理比如 Vundle可以参考这个博客: https:// ...
