集合之HashMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一、前言
之前的List,讲了ArrayList、LinkedList,反映的是两种思想:
(1)ArrayList以数组形式实现,顺序插入、查找快,插入、删除较慢
(2)LinkedList以链表形式实现,顺序插入、查找较慢,插入、删除方便
那么是否有一种数据结构能够结合上面两种的优点呢?有,答案就是HashMap。
HashMap是一种非常常见、方便和有用的集合,是一种键值对(K-V)形式的存储结构。
四个关注点在HashMap上的答案

二、hashMap数据结构

说明:上图说明了hashMap的数据结构,由数组+链表+红黑树组成,链表为单向链表,桶中的结构可能是链表,也可能是红黑树,红黑树的引用是为了提高效率。
三、hashMap源码分析-属性及构造函数
3.1 类的继承关系
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
可以看到HashMap继承自父类(AbstractMap),实现了Map、Cloneable、Serializable接口。其中,Map接口定义了一组通用的操作;Cloneable接口则表示可以进行拷贝,在HashMap中,实现的是浅层次拷贝,即对拷贝对象的改变会影响被拷贝的对象;Serializable接口表示HashMap实现了序列化,即可以将HashMap对象保存至本地,之后可以恢复状态。
3.2 类的属性
// 序列号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L;
// 默认的初始容量是16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// 最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认的加载因子是0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 当桶(bucket)上的结点数大于这个值时链表会转成红黑树
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// 当桶(bucket)上的结点数小于这个值时红黑树转成链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 桶中结构转化为红黑树对应的table的最小大小
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
// 存储元素的数组,总是2的幂次倍
transient Node<k,v>[] table;
// 存放具体元素的集
transient Set<map.entry<k,v>> entrySet;
// 存放元素的个数,注意这个不等于数组的长度。
transient int size;
// 每次扩容和更改map结构的计数器
transient int modCount;
// 临界值 当实际大小size(容量*加载因子)超过该值时,会进行扩容
int threshold;
// 加载因子
final float loadFactor;
说明:hashMap的属性比较多,这里说一下threshold和loadFactor这两个属性。hashMap的默认初始容量为16,默认加载因子为0.75,那么threshold = 16 * 0.75 = 12,当size > 12时,就会进行扩容。而加载因子越大,threshold越大,那么在扩容之前可以填充的元素就越多,空间利用率提高了,但是相应的就会比较容易造成hash冲突。而加载因子越小,threshold越小,那么在扩容之前可以填充的元素就越少,空间利用降低了,但是相应的就没那么容易造成hash冲突。
3.3 类的构造函数
1.、public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)型
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
tableSizeFor函数返回大于等于initialCapacity最小的二次幂的值
/**
* Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
*/
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
说明:>>> 操作符表示无符号右移,高位取0。
2、public HashMap(int initialCapacity)型
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative.
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
3、public HashMap()型
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
4、public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)型
/**
* Constructs a new <tt>HashMap</tt> with the same mappings as the
* specified <tt>Map</tt>. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with
* default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to
* hold the mappings in the specified <tt>Map</tt>.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
说明:putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict)函数将m的所有元素存入本HashMap实例中。
/**
* Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor
*
* @param m the map
* @param evict false when initially constructing this map, else
* true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion).
*/
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { // pre-size
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
四、hashMap源码分析-核心函数
4.1 增:put和putVal函数----存储元素
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
putVal函数
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
HashMap.Node<K,V>[] tab; HashMap.Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//判断tab是否为空
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//为空,构建tab
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//(n - 1) & hash 按位与运算得到tab的索引值,判断该索引值处是否有元素
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
//该索引值处无元素,构建Node节点放入桶中(桶中的第一个元素,位于数组中),存储key-value
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//该索引值处有元素(对应桶中的第一个元素,位于tab数组中)
HashMap.Node<K,V> e; K k;
//比较桶中的第一个元素(数组中)与要存储的元素的hash值和key值
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//相等(key值相同),将桶中的第一个元素赋值给e
e = p;
//hash值不相等,存储在链表或是红黑树中
else if (p instanceof HashMap.TreeNode)
//存储在红黑树中(此时p所在的桶中的那条链表(Node节点)已经转换成了红黑树(TreeNode节点)了)
e = ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//存储在链表中
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//判断桶中的第一个元素是否有next节点
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//为null,没有next节点,构建Node,赋值给p.next(p关联起来形成链表结构)
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//链表中的节点数量大于阈值,将那条链表转换成红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
//跳出循环
break;
}
//判断链表中的节点的key值与要存储的key值是否相等
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//相等,跳出循环(此时e == p.next)
break;
//用于遍历链表中的节点,和e = p.next结合,可以遍历链表中的所有节点
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
//要存储的key找到了对应的mapping,替换value并返回oldValue
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
//onlyIfAbsent为false或者旧值为null,替换
e.value = value;
//访问后回调
afterNodeAccess(e);
//返回oldValue
return oldValue;
}
}
//结构性修改加一
++modCount;
//map中实际元素的大小大于阈值则进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
//插入后回调
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
//no existing mapping for key,返回null值
return null;
}
说明:HashMap并没有直接提供putVal接口给用户调用,而是提供的put函数,而put函数就是通过putVal来插入元素的。
举例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("zhangsan", "zhangsan");
map.put("lisi", "lisi");
map.put("wangwu", "wangwu");
map.put("zhaoliu", "zhaoliu");
map.put("caocao", "caocao");
map.put("liubei", "liubei");
map.put("sunquan", "sunquan");
map.put("guanyu", "guanyu");
map.put("zhangfei", "zhangfei");
map.put("zhugeliang", "zhugeliang");
map.put("zhubajie", "zhubajie");
map.put("sunwukong", "sunwukong");
map.put("tangseng", "tangseng");
map.put("shaseng", "shaseng");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
结果:
{lisi=lisi, zhangfei=zhangfei, shaseng=shaseng, zhaoliu=zhaoliu, liubei=liubei, tangseng=tangseng, sunquan=sunquan, sanzhang=sanzhang, zhugeliang=zhugeliang, sunwukong=sunwukong, zhubajie=zhubajie, guanyu=guanyu, wangwu=wangwu, caocao=caocao}
说明:可以看到,获取元素的顺序与put的顺序不一致。这里列出key值、hash(key)值和在数组tab中的索引index(i = (n - 1) & hash),并用图示说明上述元素在hashMap中的分布:
key hash(key) index(i = (n - 1) & hash) zhangsan -1432577304 8 lisi 3322017 1 wangwu -795083590 10 zhaoliu -323235449 7 caocao -1367733222 10 liubei -1102508889 7 sunquan -1856616245 11 guanyu -1235148906 6 zhangfei -1432573310 2 zhugeliang 466938860 12 zhubajie -871240751 1 sunwukong -1589103089 15 tangseng -556007510 10 shaseng 2054237254 6
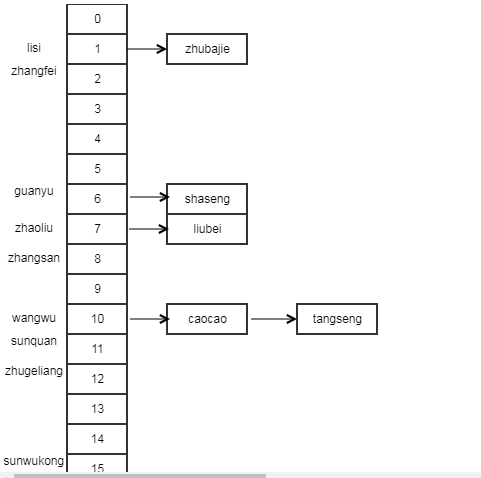
4.2 删:remove和removeNode函数----删除元素
/**
* Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present.
*
* @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
removeNode函数
/**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final HashMap.Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
HashMap.Node<K,V>[] tab; HashMap.Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
//判断table表是否为空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
HashMap.Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//得到要移除的元素是桶中的第一个元素(位于数组中)
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof HashMap.TreeNode)
//要移除的元素位于红黑树中
node = ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
//要移除的元素位于链表中
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
//链表中匹配到了要移除的元素
node = e;
break;
}
//p存储链表中要移除节点的前一个节点
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//至此,要移除的元素node已经找到,;判断是根据key移除还是根据key和value移除
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof HashMap.TreeNode)
//node节点为红黑树节点,调用treeNode的方法移除
((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
//node节点是桶中的第一个元素,将node.next变成桶中的第一个元素
tab[index] = node.next;
else
//node节点在链表中,p存储的是要移除节点的前一个节点,将其的next由指向node转为指向node的next
p.next = node.next;
//结构性修改加一
++modCount;
//元素个数减一
--size;
//删除后回调
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
说明:hashMap中并没有直接提供removeNode接口给用户使用,而是通过remove(Object key)函数和remove(Object key,Object value)函数,再调用removeNode来获取元素的。removeNode函数主要完成两方面的事情。一、找到要remove的元素(桶中第一个元素、红黑树中、链表中)。二、根据一中元素所在的位置做相应的移除操作。
举例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("zs1", "zhangsan1");
map.put("zs2", "zhangsan2");
map.put("zs3", "zhangsan3");
map.put("zs4", "zhangsan4");
map.put("zs5", "zhangsan5");
System.out.println("remove之前:=========" + map);
Object value = map.remove("zs1");
System.out.println("所移除元素的value:==========" + value);
System.out.println("remove之后:=========" + map);
}
}
结果:
remove之前:========={zs2=zhangsan2, zs1=zhangsan1, zs4=zhangsan4, zs3=zhangsan3, zs5=zhangsan5}
所移除元素的value:==========zhangsan1
remove之后:========={zs2=zhangsan2, zs4=zhangsan4, zs3=zhangsan3, zs5=zhangsan5}
图示说明remove前后元素在链表中位置:remove zs1(桶中的第一个元素)和remove zs4(链表中的元素)

4.3 改:putVal函数----修改元素
详见4.1,与添加元素是同一个操作
4.4 查:get和getNode函数----获取元素
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
getNode函数
/**
* Implements Map.get and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final HashMap.Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
HashMap.Node<K,V>[] tab; HashMap.Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
//判断table是否为空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//table不为空并将桶中的第一个元素(位于数组中)赋值给first
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//根据hash值和key判断是桶中的第一个元素(位于table数组中)
return first;
//不是桶中的第一个元素
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof HashMap.TreeNode)
//要找的Node节点位于红黑树中
return ((HashMap.TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//位于链表中,将e.next赋值给e,循环获取和key匹配的Node节点
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//table为空,返回null
return null;
}
说明:hashMap中并没有直接提供getNode接口给用户使用,而是通过get函数,再通过get函数调用getNode来获取元素的。
4.5 扩容:reSize函数----hashMap的扩容
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final HashMap.Node<K,V>[] resize() {
//保存原table
HashMap.Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
//获取原table的容量
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
//获取原table的阈值
int oldThr = threshold;
//定义新table的容量和阈值
int newCap, newThr = 0;
//原table容量大于0
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//原table的容量已经达到最大值,不再进行扩容,直接返回原table
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
//原table的容量未达最大值
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
//容量翻倍,使用左移,效率更高
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 阈值翻倍
}
//原table的容量 == 0,再进行原阈值方面的判断
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
//原阈值大于0,新table的容量 == 原阈值
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
//原table的容量 == 0,原阈值 == 0,那么新table的容量和阈值使用默认的容量(16)和阈值(12)
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
//原table的阈值大于0且新table的阈值等于0,定义新table的阈值
//举例:public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)构造hashMap时,适用此种情况
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
//至此,新table的容量和阈值都已经取值完成。
//将新table的阈值赋值给hashMap的属性threshold
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
//初始化table
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
//判断原table是否为空
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)//说明桶中只有一个元素(位于数组中)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;//重新将原数组的值放入新数组中
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)//该桶中的node节点类型是treeNode,红黑树,打乱重新分配
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
//桶中的元素是链表结构,重新rehash链表,即将链表拆分成两条
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
//以e.hash & oldCap是否为零来拆分该链表中的元素
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;//重新指向该node节点中的next节点
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;//重新指向该node节点中的next节点
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
//将rehash后的原链表的最后一个元素loTail的next属性置为null
loTail.next = null;
//原链表在table数组中的索引位置没有改变
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
//将rehash后的新生成的链表的最后一个元素hiTail的next属性置为null
hiTail.next = null;
//将hiHead置于newTab中,形成新的链表结构
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
//返回扩容后的newTab
return newTab;
}
说明:进行扩容,会伴随着一次重新hash分配,并且会遍历hash表中所有的元素,是非常耗时的。在编写程序中,要尽量避免resize。hashMap的扩容函数主要完成两方面的事情。一、生成新table的容量和阈值。二、将原table中的元素置于新生成的table中。
图示说明扩容前后元素的分布:

说明:上图只是针对了数组下标为2的桶中的各个元素在扩容后的分配布局,其他各个桶中的元素布局可以以此类推。
五、总结
5.1再谈HashCode的重要性
前面讲到了,HashMap中对Key的HashCode要做一次rehash,防止一些糟糕的Hash算法生成的糟糕的HashCode,那么为什么要防止糟糕的HashCode?糟糕的HashCode意味着的是Hash冲突,即多个不同的Key可能得到的是同一个HashCode,糟糕的Hash算法意味着的就是Hash冲突的概率增大,这意味着HashMap的性能将下降,表现在两方面:
1、有10个Key,可能6个Key的HashCode都相同,另外四个Key所在的Entry均匀分布在table的位置上,而某一个位置上却连接了6个Entry。这就失去了HashMap的意义,HashMap这种数据结构性高性能的前提是,Entry均匀地分布在table位置上,但现在确是1 1 1 1 6的分布。所以,我们要求HashCode有很强的随机性,这样就尽可能地可以保证了Entry分布的随机性,提升了HashMap的效率。
2、HashMap在一个某个table位置上遍历链表的时候的代码:
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
看到,由于采用了"&&"运算符,因此先比较HashCode,HashCode都不相同就直接pass了,不会再进行equals比较了。HashCode因为是int值,比较速度非常快,而equals方法往往会对比一系列的内容,速度会慢一些。Hash冲突的概率大,意味着equals比较的次数势必增多,必然降低了HashMap的效率了。参考:HashCode的作用。
5.2 hashMap和hashTable的区别
1、Hashtable是线程安全的,Hashtable所有对外提供的方法都使用了synchronized,也就是同步,而HashMap则是线程非安全的。
2、Hashtable不允许空的value,空的value将导致空指针异常,而HashMap则无所谓,没有这方面的限制。
hashTable的put源码:
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
.................
.................
}
参考资料:
Java的位运算符详解实例 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35114086/article/details/70173329#commentBox
https://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/5242233.html#3880042
https://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/5030920.html
集合之HashMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)的更多相关文章
- 集合之LinkedHashSet(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 上篇已经分析了Set接口下HashSet,我们发现其操作都是基于hashMap的,接下来看LinkedHashSet,其底层实现都是基于linkedHashMap的. 二.linkedHas ...
- 集合之HashSet(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 我们已经分析了List接口下的ArrayList和LinkedList,以及Map接口下的HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap,接下来看的是Set接口下HashSet和 ...
- 集合之TreeSet(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 前面分析了Set接口下的hashSet和linkedHashSet,下面接着来看treeSet,treeSet的底层实现是基于treeMap的. 四个关注点在treeSet上的答案 二.tr ...
- 集合之TreeMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 前面所说的hashMap和linkedHashMap都不具备统计的功能,或者说它们的统计性能的时间复杂度都不是很好,要想对两者进行统计,需要遍历所有的entry,时间复杂度比较高,此时,我们 ...
- 集合之LinkedHashMap(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 大多数的情况下,只要不涉及线程安全问题,map都可以使用hashMap,不过hashMap有一个问题,hashMap的迭代顺序不是hashMap的存储顺序,即hashMap中的元素是无序的. ...
- 集合之LinkedList(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.前言 LinkedList是基于链表实现的,所以先讲解一下什么是链表.链表原先是C/C++的概念,是一种线性的存储结构,意思是将要存储的数据存在一个存储单元里面,这个存储单元里面除了存放有待存储的 ...
- 集合之ArrayList(含JDK1.8源码分析)
一.ArrayList的数据结构 ArrayList底层的数据结构就是数组,数组元素类型为Object类型,即可以存放所有类型数据.我们对ArrayList类的实例的所有的操作(增删改查等),其底层都 ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之HashMap(一) 转载
[集合框架]JDK1.8源码分析之HashMap(一) 一.前言 在分析jdk1.8后的HashMap源码时,发现网上好多分析都是基于之前的jdk,而Java8的HashMap对之前做了较大的优化 ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析HashSet && LinkedHashSet(八)
一.前言 分析完了List的两个主要类之后,我们来分析Set接口下的类,HashSet和LinkedHashSet,其实,在分析完HashMap与LinkedHashMap之后,再来分析HashSet ...
随机推荐
- 【转】vmware的macos中apple ID一直登陆不上解决 ---(伪造smbios设备信息)
伪造smbios设备信息 原文网址:http://www.insanelymac.com/forum/topic/292170-how-to-spoof-real-mac-in-vmware/page ...
- VM虚拟机ubantu自适应屏幕大小
1.菜单栏安装VMware-Tool sudo ./wmware-install.pl 2.sudo apt-get install open-vm-tools装完这两个就可以,有些人只安装了第一个, ...
- Flask-SQLAlchemy常用操作
一.SQLAlchemy介绍 SQLAlchemy是一个基于Python实现的ORM框架.该框架建立在 DB API之上,使用关系对象映射进行数据库操作,简言之便是:将类和对象转换成SQL,然后使用数 ...
- 异常:NoNodeAvailableException
现象 1.启动时候出现 node null not part of the cluster Cluster [********], ignoring... 2.启动时正常,但是请求时出现 NoNode ...
- P3374 【模板】树状数组 1--洛谷luogu
题目描述 如题,已知一个数列,你需要进行下面两种操作: 1.将某一个数加上x 2.求出某区间每一个数的和 输入输出格式 输入格式: 第一行包含两个整数N.M,分别表示该数列数字的个数和操作的总个数. ...
- OpenCV3计算机视觉Python语言实现笔记(二)
1. 图像与原始字节之间的转换 从概念上讲,一个字节能表示0到255的整数.目前,对于多有的实时图像应用而言,虽然有其他的表示形式,但一个像素通常由每个通道的一个字节表示. 一个OpenCV图像是.a ...
- face detection[Face R-FCN]
本文来自<Detecting Faces Using Region-based Fully Convolutional Networks>,又是腾讯ai实验室的作品.时间线为2017年9月 ...
- Feature Extractor[googlenet v1]
1 - V1 google团队在模型上,更多考虑的是实用性,也就是如何能让强大的深度学习模型能够用在嵌入式或者移动设备上.传统的想增强模型的方法无非就是深度和宽度,而如果简单的增加深度和宽度,那么带来 ...
- Generative Adversarial Nets[CAAE]
本文来自<Age Progression/Regression by Conditional Adversarial Autoencoder>,时间线为2017年2月. 该文很有意思,是如 ...
- Git-命令行-使用 Tag 标记你的代码
前言 正文开始之前,我想我们需要弄明白几个问题: 1.tag 是什么? 2.使用tag 的好处? 3.tag 和 branch 的区别以及使用场景? tag 是什么? tag , 翻译过来是标签的意思 ...
