初试PyOpenGL一 (Python+OpenGL)
很早就一直想学Python,看到一些书都有介绍,不管是做为游戏的脚本语言,还是做为开发项目的主要语言都有提及(最主要的CUDA都开始支持Python,CUDA后面一定要学),做为先熟悉一下Python,本文用PyOpenGL实现一些基本的显示效果,一个网格,一个球体,加一个能切换第一与第三人称的摄像机。
PyOpenGL是一个用Python实现的多平台的OpenGL的API,为了学习Python与PyOpengl,本文也是用的Python,而不是.net版本的IronPython.
先看一下,相关环境的搭建:
首先我们需要下载Python: http://www.python.org/getit/
然后是PyOpenGL库:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/PyOpenGL
和PyOpenGL库常连在一起用的二个库,一个库numpy,提供常用的科学计算包含矩阵运算,数组转换与序列化,还有一个是3D常用的图片处理库:Python Imaging Library (PIL)。
numpy下载:http://sourceforge.net/projects/numpy/files/ 简介:http://sebug.net/paper/books/scipydoc/numpy_intro.html
Python Imaging Library (PIL)下载:http://www.pythonware.com/products/pil/
当上面环境安装完成后,我们先来实现一个基本的球体VBO实现,代码请参考前面的WebGL 利用FBO完成立方体贴图中的球的代码:
#common.py
import math
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.arrays import vbo
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
#import OpenGL.GLUT as glut
import numpy as ny
#Python Imaging Library (PIL)
class common:
bCreate = False #球的实现
class sphere(common):
def __init__(this,rigns,segments,radius):
this.rigns = rigns
this.segments = segments
this.radius = radius
def createVAO(this):
vdata = []
vindex = []
for y in range(this.rigns):
phi = (float(y) / (this.rigns - 1)) * math.pi
for x in range(this.segments):
theta = (float(x) / float(this.segments - 1)) * 2 * math.pi
vdata.append(this.radius * math.sin(phi) * math.cos(theta))
vdata.append(this.radius * math.cos(phi))
vdata.append(this.radius * math.sin(phi) * math.sin(theta))
vdata.append(math.sin(phi) * math.cos(theta))
vdata.append(math.cos(phi))
vdata.append(math.sin(phi) * math.sin(theta))
for y in range(this.rigns - 1):
for x in range(this.segments - 1):
vindex.append((y + 0) * this.segments + x)
vindex.append((y + 1) * this.segments + x)
vindex.append((y + 1) * this.segments + x + 1)
vindex.append((y + 1) * this.segments + x + 1)
vindex.append((y + 0) * this.segments + x + 1)
vindex.append((y + 0) * this.segments + x)
#this.vboID = glGenBuffers(1)
#glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER,this.vboID)
#glBufferData (GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, len(vdata)*4, vdata, GL_STATIC_DRAW)
#this.eboID = glGenBuffers(1)
#glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,this.eboID)
#glBufferData (GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, len(vIndex)*4, vIndex,
#GL_STATIC_DRAW)
this.vbo = vbo.VBO(ny.array(vdata,'f'))
this.ebo = vbo.VBO(ny.array(vindex,'H'),target = GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER)
this.vboLength = this.segments * this.rigns
this.eboLength = len(vindex)
this.bCreate = True
def drawShader(this,vi,ni,ei):
if this.bCreate == False:
this.createVAO()
#glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER,this.vboID)
#glVertexAttribPointer(vi,3,GL_FLOAT,False,24,0)
#glEnableVertexAttribArray(vi)
#glVertexAttribPointer(ni,3,GL_FLOAT,False,24,12)
#glEnableVertexAttribArray(ni)
#glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,this.eboID)
#glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES,this.eboLength,GL_UNSIGNED_INT,0)
this.vbo.bind()
def draw(this):
if this.bCreate == False:
this.createVAO()
#glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER,this.vboID)
#glInterleavedArrays(GL_N3F_V3F,0,None)
#glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,this.eboID)
#glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES,this.eboLength,GL_UNSIGNED_INT,None)
this.vbo.bind()
glInterleavedArrays(GL_N3F_V3F,0,None)
this.ebo.bind()
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES,this.eboLength,GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT,None)
球
这段代码画球,不同于我最开始用的每个三角形分成四个三角形的代码,基本思想是和地球仪上的经纬线一样,画出经纬线的点(顶点位置),然后有顺序的连接在一起(顶点索引)就可以了。
这里先说下python,和我之前接触的语言来看,我发现这个出乎意料的最和F#比较接近,虽然他们一个是动态语言,一个是静态语言,但是他们首先都是强类型语言,并且都支持多范式(对象式,过程式,函数式),同做为强类型语言,默认都不需要声明类型,不知Python是否和F#一样,是用的类型推导,有个比较明显的地方和F#一样的地方就是,在这里def __init__(this,rigns,segments,radius),首先righs,segments,radius开始鼠标移上去都是unknow type,但是在别的地方调用common.sphere(16,16,1)后,他就能推断出righs,segments,radius都为int.并且和F#一样,声明类的方法时,都需要带一个表示自己的参数,且都和C#不一样(限定this)可以自定义这个参数的名称.当然还有最大的共同点,他们都是用缩进来控制语言块(满分),现在写C#代码有些不爽的地方就是缩进。基于以上这些,写python感觉很亲切,也很爽,和F#一样,能写出很简洁的代码,相信一个学习过F#的人来写python,肯定也有此类感觉。当然python做为动态语言,比F#,C#来说,开发效率更高,比如,在上面一段中,this.vboLength = this.segments * this.rigns,这里直接动态声明一个属性vboLength,而不需要和F#与C#一样来先声明一个这样的属性,当然,net4.0中的DLR来说,也是能实现这种效果,但是用起来感觉就不一样了。
大家如果有兴趣了解各编程语言,强烈推荐郑晖大神的冒号课堂系列文章 第一篇冒号课堂§1.1:开班发言
下面是网格的代码,代码也可以参考前面柏林噪声实践(一) 海波,一样是生成网格上所有的x,z点,然后组织索引,看代码:
class plane(common):
def __init__(this,xres,yres,xscale,yscale):
this.xr,this.yr,this.xc,this.yc = xres - 1,yres - 1,xscale,yscale
def createVAO(this):
helfx = this.xr * this.xc * 0.5
helfy = this.yr * this.yc * 0.5
vdata = []
vindex = []
for y in range(this.yr):
for x in range(this.xr):
vdata.append(this.xc * float(x) - helfx)
vdata.append(0.)
vdata.append(this.yc * float(y) - helfy)
for y in range(this.yr - 1):
for x in range(this.xr - 1):
vindex.append((y + 0) * this.xr + x)
vindex.append((y + 1) * this.xr + x)
vindex.append((y + 0) * this.xr + x + 1)
vindex.append((y + 0) * this.xr + x + 1)
vindex.append((y + 1) * this.xr + x)
vindex.append((y + 1) * this.xr + x + 1)
print len(vdata),len(vindex)
this.vbo = vbo.VBO(ny.array(vdata,'f'))
this.ebo = vbo.VBO(ny.array(vindex,'H'),target = GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER)
this.eboLength = len(vindex)
this.bCreate = True
def draw(this):
if this.bCreate == False:
this.createVAO()
this.vbo.bind()
glInterleavedArrays(GL_V3F,0,None)
this.ebo.bind()
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES,this.eboLength,GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT,None)
网络
哈哈,大家发现了,我都是把以前写的javascripe,F#代码拿来改写的,毕竟我也只是一个python新手,把别的语言拿来改写我认为是最快熟悉一门语言的方法。同样,下面第一,第三人称漫游代码也是我前面Opengl绘制我们的小屋(四)第三人称漫游,Opengl绘制我们的小屋(二)第一人称漫游里的代码改写的,具体思路请转至这二篇文章。
class camera:
origin = [0.0,0.0,0.0]
length = 1.
yangle = 0.
zangle = 0.
__bthree = False
def __init__(this):
this.mouselocation = [0.0,0.0]
this.offest = 0.01
this.zangle = 0. if not this.__bthree else math.pi
def setthree(this,value):
this.__bthree = value
this.zangle = this.zangle + math.pi
this.yangle = -this.yangle
def eye(this):
return this.origin if not this.__bthree else this.direction()
def target(this):
return this.origin if this.__bthree else this.direction()
def direction(this):
if this.zangle > math.pi * 2.0 :
this.zangle < - this.zangle - math.pi * 2.0
elif this.zangle < 0. :
this.zangle < - this.zangle + math.pi * 2.0
len = 1. if not this.__bthree else this.length if 0. else 1.
xy = math.cos(this.yangle) * len
x = this.origin[0] + xy * math.sin(this.zangle)
y = this.origin[1] + len * math.sin(this.yangle)
z = this.origin[2] + xy * math.cos(this.zangle)
return [x,y,z]
def move(this,x,y,z):
sinz,cosz = math.sin(this.zangle),math.cos(this.zangle)
xstep,zstep = x * cosz + z * sinz,z * cosz - x * sinz
if this.__bthree :
xstep = -xstep
zstep = -zstep
this.origin = [this.origin[0] + xstep,this.origin[1] + y,this.origin[2] + zstep]
def rotate(this,z,y):
this.zangle,this.yangle = this.zangle - z,this.yangle + y if not this.__bthree else -y
def setLookat(this):
ve,vt = this.eye(),this.target()
#print ve,vt
glLoadIdentity()
gluLookAt(ve[0],ve[1],ve[2],vt[0],vt[1],vt[2],0.0,1.0,0.0)
def keypress(this,key, x, y):
if key in ('e', 'E'):
this.move(0.,0.,1 * this.offest)
if key in ('f', 'F'):
this.move(1 * this.offest,0.,0.)
if key in ('s', 'S'):
this.move(-1 * this.offest,0.,0.)
if key in ('d', 'D'):
this.move(0.,0.,-1 * this.offest)
if key in ('w', 'W'):
this.move(0.,1 * this.offest,0.)
if key in ('r', 'R'):
this.move(0.,-1 * this.offest,0.)
if key in ('v', 'V'):
#this.__bthree = not this.__bthree
this.setthree(not this.__bthree)
if key == GLUT_KEY_UP:
this.offest = this.offest + 0.1
if key == GLUT_KEY_DOWN:
this.offest = this.offest - 0.1
def mouse(this,x,y):
rx = (x - this.mouselocation[0]) * this.offest * 0.1
ry = (y - this.mouselocation[1]) * this.offest * -0.1
this.rotate(rx,ry)
print x,y
this.mouselocation = [x,y]
摄像机漫游
代码很简单,当然,做为一个类来说,其实setLookat,keypress,mouse这三个方法应该分离出去的,不过用了使用方便,也便于放在一起理解。其中keypress与mouse实现键盘启用常用的基本漫游,其中EDSF前后左右移动,WR分别向上与向下,鼠标右键加移动鼠标控制方向,V切换第一人称与第三人称。UP与DOWN切换前面操作的移动幅度。其中len = 1. if not this.__bthree else this.length if 0. else 1.这个解释下,在不是第三人称漫游下,长度为1,否则在第三人称漫游下,长度取length的长度,如果length为0,则取1的长度.其实就是相当二个三元运算符,但是感觉理解起来更方便.
下面来看具体调用并显示的代码:
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
from OpenGL.GLU import * import common
import sys window = 0
sph = common.sphere(16,16,1)
camera = common.camera()
plane = common.plane(12,12,1.,1.)
def InitGL(width,height):
glClearColor(0.1,0.1,0.5,0.1)
glClearDepth(1.0)
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE)
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)
glLoadIdentity()
gluPerspective(45.0,float(width)/float(height),0.1,100.0)
camera.move(0.0,3.0,-5) def DrawGLScene():
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
camera.setLookat()
plane.draw()
glTranslatef(-1.5,0.0,0.0)
glBegin(GL_QUADS)
glVertex3f(-1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
glVertex3f(1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
glVertex3f(1.0, -1.0, 0.0)
glVertex3f(-1.0, -1.0, 0.0)
glEnd()
glTranslatef(3.0, 0.0, 0.0)
sph.draw()
glutSwapBuffers() def mouseButton( button, mode, x, y ):
if button == GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON:
camera.mouselocation = [x,y] def ReSizeGLScene(Width, Height):
glViewport(0, 0, Width, Height)
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)
glLoadIdentity()
gluPerspective(45.0, float(Width)/float(Height), 0.1, 100.0)
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW) def main():
global window
glutInit(sys.argv)
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGBA | GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_DEPTH)
glutInitWindowSize(640,400)
glutInitWindowPosition(800,400)
window = glutCreateWindow("opengl")
glutDisplayFunc(DrawGLScene)
glutIdleFunc(DrawGLScene)
glutReshapeFunc(ReSizeGLScene)
glutMouseFunc( mouseButton )
glutMotionFunc(camera.mouse)
glutKeyboardFunc(camera.keypress)
glutSpecialFunc(camera.keypress)
InitGL(640, 480)
glutMainLoop() main()
显示效果
代码很简单,把球,网络,漫游摄像机应用进去。注意glutMouseFunc( mouseButton )与glutMotionFunc(camera.mouse)组合用才能达到原来OpenTK提供的鼠标检测功能,因为glutmousefunc只检测鼠标的按下等动作,意思你一直按下移动他是不会引用的,在这引用的是glutmotionfunc,这个大家可以自己去试验。
下面放出效果图:
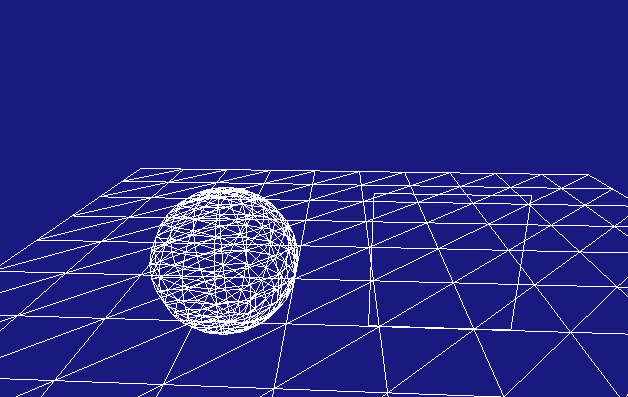
效果很简单,主要是为了下文先做一个基本的效果,同时也是用pyOpengl对前面的一点总结。
代码下载:代码 和上面说的一样,其中EDSF前后左右移动,WR分别向上与向下,鼠标右键加移动鼠标控制方向,V切换第一人称与第三人称。UP与DOWN切换前面操作的移动幅度。
初试PyOpenGL一 (Python+OpenGL)的更多相关文章
- 初试PyOpenGL四 (Python+OpenGL)GPU粒子系统与基本碰撞
这篇相当于是对前三篇的总结,基本效果如下: 在初试PyOpenGL一 (Python+OpenGL)讲解Pyopengl环境搭建,网格,球体,第一与第三人称摄像机的实现.在初试PyOpenGL二 (P ...
- 初试PyOpenGL二 (Python+OpenGL)基本地形生成与高度检测
在上文中,讲述了PyOpenGL的基本配置,以及网格,球形的生成,以及基本的漫游.现在利用上一篇的内容,来利用高程图实现一个基本的地形,并且,利用上文中的第三人称漫游,以小球为视角,来在地形上前后左右 ...
- 初试PyOpenGL三 (Python+OpenGL)GPGPU基本运算与乒乓技术
这篇GPGPU 概念1: 数组= 纹理 - 文档文章提出的数组与纹理相等让人打开新的眼界与思维,本文在这文基础上,尝试把这部分思想拿来用在VBO粒子系统上. 在前面的文章中,我们把CPU的数据传到GP ...
- (Python OpenGL)【5】平移 PyOpenGL
(Python OpenGL) 原文:http://ogldev.atspace.co.uk/www/tutorial06/tutorial06.html (英文) 下面是我翻译过来的: 背景 在本 ...
- (Python OpenGL)【4】Uniform变量 PyOpenGL
(Python OpenGL) 原文:http://ogldev.atspace.co.uk/www/tutorial05/tutorial05.html(英文) __author__ = " ...
- (Python OpenGL)【3】着色器 PyOpenGL
(Python OpenGL)现在开始我们使用着色器来进行渲染.着色器是目前做3D图形最流行的方式. OpenGL的渲染管线流程: 数据传输到OpenGL—>顶点处理器—>细分着色—> ...
- 【Python OpenGL】【2】第一个三角形(Pyopengl)
根据顶点缓存来生成图元(Python OpenGL) 原文(英文链接)http://ogldev.atspace.co.uk/www/tutorial03/tutorial03.html __auth ...
- (Python OpenGL)【1】你好顶点 PyOpenGL
原文链接(C语言环境)(Python OpenGL) 我用python实现的代码: __author__ = "WSX" from OpenGL.GLUT.freeglut imp ...
- (Python OpenGL)【 0】关于VAO和VBO以及OpenGL新特性
(Python OpenGL)关于新版OpenGL需要了解的: 随着OpenGL状态和固定管线模式的移除,我们不在用任何glEnable函数调用,而且也不会有glVertex.glColor等函数调用 ...
随机推荐
- NLP资料
https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-get-started-in-nlp-6a62aa4eaeff?source=rss-299377188126------3
- [Windows Azure] Development Considerations in Windows Azure SQL Database
Development Considerations in Windows Azure SQL Database 3 out of 5 rated this helpful - Rate this t ...
- Tornado使用-队列Queue
1.tornado队列的特点 和python标准队列queue相比,tornado的队列Queue支持异步 2.Queue常用方法 Queue.get() 会暂停,直到queue中有元素 Queue. ...
- DIOCP3-关于TIOCPConsole和编码解码器
TIOCPConsole是继承至TIocpTcpServer,做了管理和调用编码和解码器器的功能.可以通过向他注册编码和解码器可以忽略粘包的问题. 这样如果TIOCPConsole客户端必须按照一 ...
- 记一次金士顿DT100 G3 32G修复
修复方法参考原文:http://bbs.mydigit.cn/read.php?tid=2291146 故障描述:某天在使用时突然要求格式化,但里面有重要数据,于是想通过DG恢复出来,没想到经过这样的 ...
- img的src不连接本地地址实现输出一个图片(使用base64)
<img alt="100%x180" data-src="holder.js/100%x180" style="height: 180px; ...
- SqlServer select * into 对应 Oracle语法
创建新表,并插入旧表值 Sql Server select * into new_emp from emp; Oracle create table new_emp as select * from ...
- Android线程通信
摘要 andriod提供了 Handler 和 Looper 来满足线程间的通信.例如一个子线程从网络上下载了一副图片,当它下载完成后会发送消息给主线程,这个消息是通过绑定在主线程的Handler来传 ...
- Notepad++的右键菜单
这种方法可以重复利用,如果下次它又消失了,你可以再导入一次就OK了.比如我们创建一个叫 notepad++.reg的文件,将下面的内容拷贝进去保存 Windows Registry Editor Ve ...
- Maven 统一指定jar包版本的方法
在看别人的源码的过程中,会遇到这种情况,就是很多jar包没有指定版本,却能够下载下来. 在后来的研究中发现,有这样一个配置. <parent> <groupId>org.spr ...
