JAVA笔记26-网络编程(不等于网站编程)
一、网络基础(TCP/IP详解)
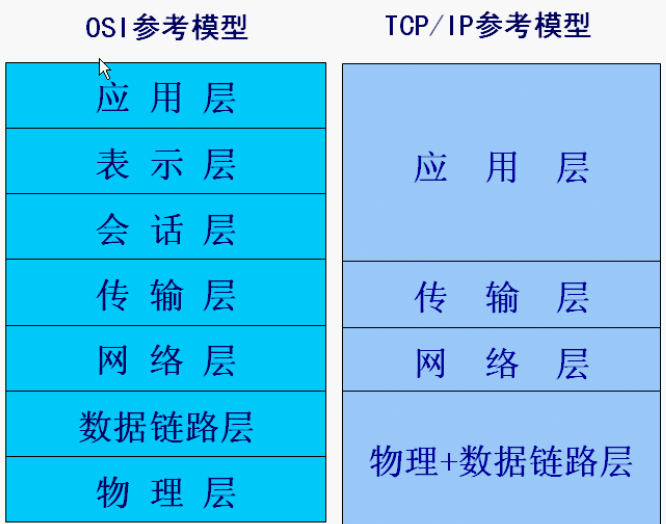
1、IP协议(Internet Protocol):网络层,支持网间数据报通信。无连接数据报传送,数据报路由选择和差错控制。

IPv4 32位(4字节),IPv6 128位(16字节)。P
ping ICMP协议
2、TCP协议、UDP协议
(1)TCP(transmission control protocol 打电话):专门设计用于在不可靠的因特网上提供可靠的、端到端的字节流通信的协议。它是一种面向连接的协议。有三次握手。慢
(2)UDP(user data protocol 寄信):提供了一种发送封装的原始IP数据报的方法、并且发送时无需建立连接,是一种不可靠的连接。快
二、Socket
两个Java应用程序可以通过一个双向的网络通信连接实现数据交换,这个双向链路的一端称为一个Socket。
Socket通常用来实现client-server连接。
java.net包中定义的两个类Socket和ServerSocket,分别用来实现双向连接(TCP连接)的client和server端。
建立连接时所需的寻址信息为远程计算机的IP地址和端口号(Port number)。端口号2字节,可以区分不同的应用程序。端口号又分TCP端口和UDP端口,每个都是65536个端口。
例如:
收邮件 POP3 110
STMP 25
FTP 21
HTTP 80
1、TCP Socket通信模型
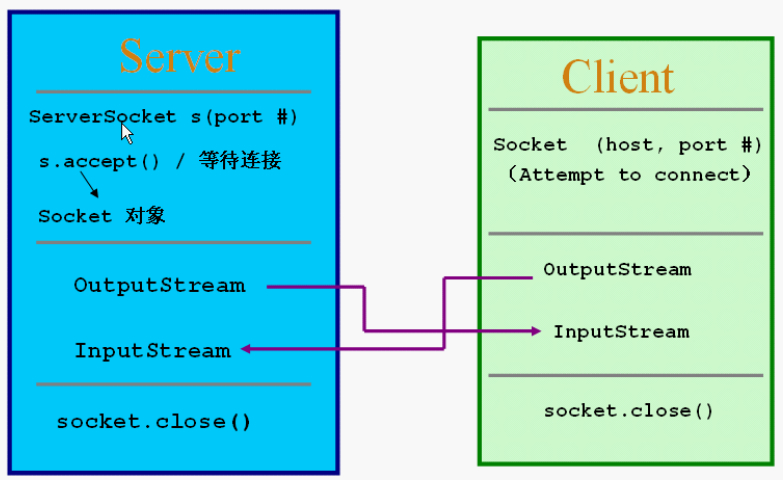
这只是练习,实际上的网络编程都是异步式的。System.in,accept(),readUTF()都是阻塞式的(非重点)
例1
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TCPServer{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(6666);//端口号6666
while(true){
Socket s = ss.accept();
System.out.println("a client connect!");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
dis.close();
s.close();
}
}
}
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TCPClient{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1",6666);
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("hello server!");
dos.flush();
dos.close();
s.close();
}
}
例2
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class TestServer{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
ServerSocket s = new ServerSocket(8888);//服务器端口号8888
while(true){
Socket s1 = s.accept();
OutputStream os = s1.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("Hello,"+s1.getInetAddress()+"port#"+s1.getPort()+" byebye!");//客户端的IP地址和端口号
dos.close();
s1.close();
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TestClient{
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
Socket s1 = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);//服务器地址和端口号
InputStream is = s1.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
dis.close();
s1.close();
}catch(ConnectException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
例3
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class TestServer{
public static void main(String[] args){
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(5888);//设置端口号
Socket s1 = ss.accept();
in = s1.getInputStream();
out = s1.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in);
String s = null;
if((s=dis.readUTF())!=null){
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("from: "+s1.getInetAddress());
System.out.println("Port: "+s1.getPort());
}
dos.writeUTF("hi,hello");
dis.close();
dos.close();
s1.close();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TestClient{
public static void main(String[] args){
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try{
Socket s1 = new Socket("localhost",5888);//服务器地址和端口号
in = s1.getInputStream();
out = s1.getOutputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
dos.writeUTF("hey");
String s = null;
if((s=dis.readUTF())!=null){
System.out.println(s);
}
dos.close();
dis.close();
s1.close();
}catch(UnknownHostException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
练习4:(by myself)
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class TestServer{
public static void main(String[] args){
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
String si = null;
String so = "";
try{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(5888);//设置端口号
while(true){
Socket s1 = ss.accept();
in = s1.getInputStream();//接收数据
out = s1.getOutputStream();//发送数据
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
//从键盘读入
InputStreamReader isr2 = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br2 = new BufferedReader(isr2);
while(!so.equals("exit")){
if((so=br2.readLine())!=null&&!so.equals("exit")){
System.out.println("Server:"+so);
dos.writeUTF(so);
}
if((si=dis.readUTF())!=null){
System.out.println("Client:"+si);
}
}
dis.close();
br2.close();
dos.close();
s1.close();
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TestClient{
public static void main(String[] args){
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
String si = null;
String so= "";
try{
Socket s1 = new Socket("127.0.0.1",5888);//服务器地址和端口号
in = s1.getInputStream();//接收
out = s1.getOutputStream();//发送
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
//从键盘读入
InputStreamReader isr2 = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br2 = new BufferedReader(isr2);
while(!so.equals("exit")){
if((si=dis.readUTF())!=null){
System.out.println("Server:"+si);
}
if((so=br2.readLine())!=null&&!so.equals("exit")){
System.out.println("Client:"+so);
dos.writeUTF(so);
}
}
dis.close();
br2.close();
dos.close();
s1.close();
}catch(UnknownHostException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2、UDP Socket通信模型
没有server,client的概念,不区分两者的socket。receive()方法也是阻塞式的。
例1
import java.net.*;
public class TestUDPServer{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
byte buf[] = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(5678);
while(true){
ds.receive(dp);
System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, dp.getLength()));
}
}
}
import java.net.*;
public class TestUDPClient{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
byte[] buf = (new String("Hello")).getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 5678));
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
ds.send(dp);
ds.close();
}
}
例2
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TestUDPServer{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
byte buf[] = new byte[1024];
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(buf);//从字节数组读数据
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bais);
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(5678);
while(true){
ds.receive(dp);
long l = dis.readLong();
System.out.println(l);
}
}
}
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class TestUDPClient{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{
long n = 10000L;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos);
dos.writeLong(n);
byte[] buf = baos.toByteArray();
System.out.println(buf.length);
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",5678));
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
ds.send(dp);
ds.close();
}
}
JAVA笔记26-网络编程(不等于网站编程)的更多相关文章
- Java笔记 - Socket编程
两个Java应用程序可以通过一个双向的网络通讯连接实现数据交换,这个双向链路的一端称为一个Socket.java.net包中定义的两个类Socket和ServerSocket,分别用来实现双向链路的c ...
- Java 学习之网络编程案例
网络编程案例 一,概念 1,网络编程不等于网站编程 2,编程只和传输层打交道,即TCP和UDP两个协议 二,案例 1,TCP实现点对点的聊天 Server端:两个输入流:读客户端和控制台,一个输出端: ...
- 大数据学习笔记——Java篇之网络编程基础
Java网络编程学习笔记 1. 网络编程基础知识 1.1 网络分层图 网络分层分为两种模型:OSI模型以及TCP/IP网络模型,前者模型分为7层,是一个理论的,参考的模型:后者为实际应用的模型,具体对 ...
- JAVA自学笔记26
JAVA自学笔记26 1.网络编程 1)用来实现网络互联的不同计算机上运行的程序可以进行数据交换 2)网络模型一般泛指 OSI:(Open System Interconnection)开放系统互联参 ...
- Java学习之网络编程实例
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/springcsc/archive/2009/12/03/1616413.html 多谢分享 网络编程 网络编程对于很多的初学者来说,都是很向往的一 ...
- Java进阶之网络编程
网络编程 网络编程对于很多的初学者来说,都是很向往的一种编程技能,但是很多的初学者却因为很长一段时间无法进入网络编程的大门而放弃了对于该部分技术的学习. 在 学习网络编程以前,很多初学者可能觉得网络编 ...
- java第九节 网络编程的基础知识
/** * * 网络编程的基础知识 * 网络协议与TCP/IP * IP地址和Port(端口号) * 本地回路的IP地址:127.0.0.1 * 端口号的范围为0-65535之间,0-1023之间的端 ...
- 20165324 Java实验五 网络编程与安全
20165324 Java实验五 网络编程与安全 一.实验报告封面 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1653班 姓名:何春江 学号:20165324 指导教师:娄嘉鹏 实验日期:2018年5月28日 实 ...
- Java网络编程 -- NIO非阻塞网络编程
从Java1.4开始,为了替代Java IO和网络相关的API,提高程序的运行速度,Java提供了新的IO操作非阻塞的API即Java NIO.NIO中有三大核心组件:Buffer(缓冲区),Chan ...
随机推荐
- epoll 性能分析(解决占用CPU 过高问题)2
针对服务器框架Engine,在工作线程中发现该线程占用CPU过高,分析之后发现问题出在死循环那里 void cServerBase::OnProcess() { printf("cServe ...
- HTML DOM Document对象 元素对象 属性对象 事件对象
DOM Document对象 DOM 元素 对象 DOM 属性 对象 DOM 事件 菜鸟教程上 总结挺全的,就不多废话,链接点进去即可.. 后期对经常用到的会在此更新一些总结..... 开学了...自 ...
- python学习之迭代器
4.5 迭代器 4.5.1 可迭代对象 **字面意思分析**:可以重复的迭代的实实在在的东西. list,dict(keys(),values(),items()),tuple,str,set,ran ...
- 20191209 Linux就该这么学(5)
5. 用户身份与文件权限 5.1 用户的身份和能力 Linux 系统的管理员之所以是 root,并不是因为它的名字叫 root,而是因为该用户的身份号码即 UID( User IDentificati ...
- python 并发编程 多线程 GIL与Lock
GIL与Lock Python已经有一个GIL来保证同一时间只能有一个线程来执行了,为什么这里还需要互斥锁lock? 锁的目的是为了保护共享的数据,同一时间只能有一个线程来修改共享的数据 GIT保证了 ...
- MAS多媒体的整个存储架构是怎样的?
MAS多媒体的整个存储架构是怎样的?
- UML类图知识点整理
引用源:https://www.cnblogs.com/me115/p/4092632.html 从一个示例开始 请看以下这个类图,类之间的关系是我们需要关注的: 车的类图结构为<<abs ...
- 【6.24校内test】T3 棠梨煎雪
[题目背景] 岁岁花藻檐下共将棠梨煎雪. 自总角至你我某日辗转天边. 天淡天青,宿雨沾襟. 一年一会信笺却只见寥寥数言. ——银临<棠梨煎雪> [问题描述] 扶苏正在听<棠梨煎雪&g ...
- svn下载项目的时候出现 Path to certificate
svn关联的时候出现这种情况,并且有svn的账号的时候,可以找setting中Version Control 中的Subversion中celar 一下即可,然后再重新下载就会让你重新输入用户名和密码 ...
- Tomcat 调优的技巧 (转)
描述 最近在补充自己的短板,刚好整理到Tomcat调优这块,基本上面试必问,于是就花了点时间去搜集一下tomcat调优都调了些什么,先记录一下调优手段,更多详细的原理和实现以后用到时候再来补充记录,下 ...
