65、Spark Streaming:数据接收原理剖析与源码分析
一、数据接收原理
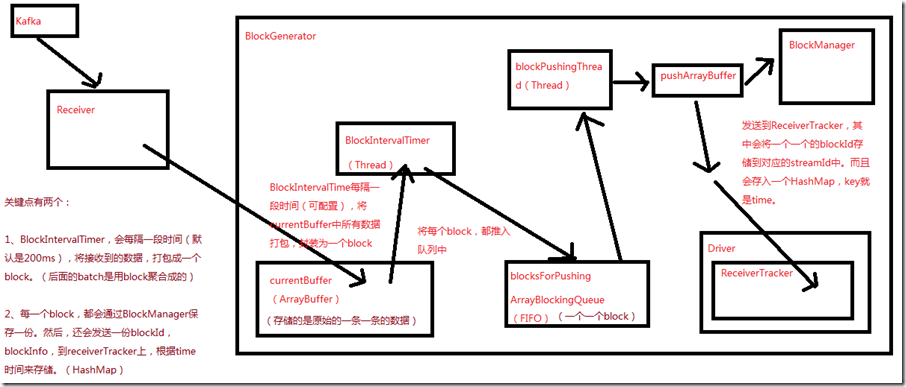
二、源码分析
入口包org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver下ReceiverSupervisorImpl类的onStart()方法
###
override protected def onStart() {
// 这里的blockGenerator很重要,和数据接收有关,其运行在worker的executor端负责数据接收后的一些存取工作,以及配合ReceiverTracker
// 在Executor上,启动Receiver之前,就会先启动这个Receiver相关的一个blockGenerator,该组件,在数据接收中,极其重要
blockGenerator.start()
}
ReceiverSupervisorImpl类的onStart()方法,调用了blockGenerator.start()方法,跟进去看看
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/BlockGenerator.scala
def start() {
// BlockGenerator.start()方法,其实就是启动内部两个关键的后台线程,
// 一个是blockIntervalTimer,负责将currentBuffer中的原始数据,打包成一个个的block
// 另一个是blockPushingThread,负责将blocksForPushing中的block,调用pushArrayBuffer()方法
blockIntervalTimer.start()
blockPushingThread.start()
logInfo("Started BlockGenerator")
}
blockGenerator.start()方法,调用了blockIntervalTimer.start()和blockPushingThread.start()方法
先看看有关变量的定义
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/BlockGenerator.scala
private val blockInterval = conf.getLong("spark.streaming.blockInterval", 200)
// blockInterval,是有一个默认值的,spark.streaming.blockInterval,默认是200ms,每隔200ms,就会调用updateCurrentBuffer函数
private val blockIntervalTimer =
new RecurringTimer(clock, blockInterval, updateCurrentBuffer, "BlockGenerator")
// blocksForPushing队列的长度,可以调节的,spark.streaming.blockQueueSize,默认10个,可大可小
private val blockQueueSize = conf.getInt("spark.streaming.blockQueueSize", 10)
// blocksForPushing队列,
private val blocksForPushing = new ArrayBlockingQueue[Block](blockQueueSize)
// blockPushingThread,后台线程,启动之后,就会调用keepPushingBlocks()方法,这个方法中,就会每隔一段时间,去blocksForPushing队列中取block
private val blockPushingThread = new Thread() { override def run() { keepPushingBlocks() } }
// 这个currentBuffer,就是用于存放原始的数据
@volatile private var currentBuffer = new ArrayBuffer[Any]
blockIntervalTimer.start()就是一个线程,这个方法就不看了
重点看下blockPushingThread.start()方法,这个线程开始运行,会调用keepPushingBlocks()方法,代码如下
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/BlockGenerator.scala
private val blockPushingThread = new Thread() { override def run() { keepPushingBlocks() } }
看keepPushingBlocks()方法
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/BlockGenerator.scala
private def keepPushingBlocks() {
logInfo("Started block pushing thread")
try {
while(!stopped) {
// 从blocksForPushing这个队列中,poll出来当前队列队首的block,对于阻塞队列,默认设置100ms的超时
Option(blocksForPushing.poll(100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) match {
// 如果拿到了block,调用pushBlock去推送block
case Some(block) => pushBlock(block)
case None =>
}
}
// Push out the blocks that are still left
logInfo("Pushing out the last " + blocksForPushing.size() + " blocks")
while (!blocksForPushing.isEmpty) {
logDebug("Getting block ")
val block = blocksForPushing.take()
pushBlock(block)
logInfo("Blocks left to push " + blocksForPushing.size())
}
logInfo("Stopped block pushing thread")
} catch {
case ie: InterruptedException =>
logInfo("Block pushing thread was interrupted")
case e: Exception =>
reportError("Error in block pushing thread", e)
}
}
可以看到keepPushingBlocks()方法,如果拿到了block,调用pushBlock()方法
看看pushBlock()方法
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/BlockGenerator.scala
private def pushBlock(block: Block) {
listener.onPushBlock(block.id, block.buffer)
logInfo("Pushed block " + block.id)
}
pushBlock()方法会调用listener.onPushBlock()方法,这个listener是BlockGeneratorListener,onPushBlock()在ReceiverSupervisorImpl类中,
看ReceiverSupervisorImpl类的onPushBlock()方法:
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/ReceiverSupervisorImpl.scala
// onPushBlock就会去调用pushArrayBuffer去推送block
def onPushBlock(blockId: StreamBlockId, arrayBuffer: ArrayBuffer[_]) {
pushArrayBuffer(arrayBuffer, None, Some(blockId))
}
onPushBlock就会去调用pushArrayBuffer()方法
看pushArrayBuffer()方法:
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/ReceiverSupervisorImpl.scala def pushArrayBuffer(
arrayBuffer: ArrayBuffer[_],
metadataOption: Option[Any],
blockIdOption: Option[StreamBlockId]
) {
pushAndReportBlock(ArrayBufferBlock(arrayBuffer), metadataOption, blockIdOption)
}
接着看pushAndReportBlock()方法:
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/ReceiverSupervisorImpl.scala def pushAndReportBlock(
receivedBlock: ReceivedBlock,
metadataOption: Option[Any],
blockIdOption: Option[StreamBlockId]
) {
val blockId = blockIdOption.getOrElse(nextBlockId)
val numRecords = receivedBlock match {
case ArrayBufferBlock(arrayBuffer) => arrayBuffer.size
case _ => -1
} val time = System.currentTimeMillis
// 还用receivedBlockHandler,去调用storeBlock方法,存储block到BlockManager中,这里,也可以看出预写日志的机制
val blockStoreResult = receivedBlockHandler.storeBlock(blockId, receivedBlock)
logDebug(s"Pushed block $blockId in ${(System.currentTimeMillis - time)} ms") // 封装一个ReceiverBlockInfo对象,里面有一个streamId
val blockInfo = ReceivedBlockInfo(streamId, numRecords, blockStoreResult)
// 调用了ReceiverTracker的Acrot的ask方法,发送AddBlock消息
val future = trackerActor.ask(AddBlock(blockInfo))(askTimeout)
Await.result(future, askTimeout)
logDebug(s"Reported block $blockId")
}
这里主要看receivedBlockHandler.storeBlock()方法和trackerActor.ask(AddBlock(blockInfo))(askTimeout)
首先看receivedBlockHandler.storeBlock(),看看receivedBlockHandler是什么
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/ReceiverSupervisorImpl.scala
private val receivedBlockHandler: ReceivedBlockHandler = {
// 如果开启了预写日志机制,spark.streaming.receiver.writeAheadLog.enable,默认false
// 如果为true,那么receivedBlockHandler就是WriteAheadLogBasedBlockHandler
// 如果没有开启预写日志机制,那么receivedBlockHandler就是BlockManagerBasedBlockHandler
if (env.conf.getBoolean("spark.streaming.receiver.writeAheadLog.enable", false)) {
if (checkpointDirOption.isEmpty) {
throw new SparkException(
"Cannot enable receiver write-ahead log without checkpoint directory set. " +
"Please use streamingContext.checkpoint() to set the checkpoint directory. " +
"See documentation for more details.")
}
new WriteAheadLogBasedBlockHandler(env.blockManager, receiver.streamId,
receiver.storageLevel, env.conf, hadoopConf, checkpointDirOption.get)
} else {
new BlockManagerBasedBlockHandler(env.blockManager, receiver.storageLevel)
}
接着分别看BlockManagerBasedBlockHandler和WriteAheadLogBasedBlockHandler的storeBlock()方法
先看WriteAheadLogBasedBlockHandler
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/ReceivedBlockHandler.scala
def storeBlock(blockId: StreamBlockId, block: ReceivedBlock): ReceivedBlockStoreResult = {
// Serialize the block so that it can be inserted into both
// 先用BlockManager序列化数据
val serializedBlock = block match {
case ArrayBufferBlock(arrayBuffer) =>
blockManager.dataSerialize(blockId, arrayBuffer.iterator)
case IteratorBlock(iterator) =>
blockManager.dataSerialize(blockId, iterator)
case ByteBufferBlock(byteBuffer) =>
byteBuffer
case _ =>
throw new Exception(s"Could not push $blockId to block manager, unexpected block type")
}
// Store the block in block manager
// 将数据保存到BlockManager中去,默认的持久化策略,StorageLevel,是带_SER,_2的,会序列化,复制一份副本到其他Executor的BlockManager,以供容错
val storeInBlockManagerFuture = Future {
val putResult =
blockManager.putBytes(blockId, serializedBlock, effectiveStorageLevel, tellMaster = true)
if (!putResult.map { _._1 }.contains(blockId)) {
throw new SparkException(
s"Could not store $blockId to block manager with storage level $storageLevel")
}
}
// Store the block in write ahead log
// 将block存入预写日志,通过logManager的writeToLog()方法
val storeInWriteAheadLogFuture = Future {
logManager.writeToLog(serializedBlock)
}
// Combine the futures, wait for both to complete, and return the write ahead log segment
val combinedFuture = storeInBlockManagerFuture.zip(storeInWriteAheadLogFuture).map(_._2)
val segment = Await.result(combinedFuture, blockStoreTimeout)
WriteAheadLogBasedStoreResult(blockId, segment)
}
再看BlockManagerBasedBlockHandler
###org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver/ReceivedBlockHandler.scala // 直接将数据保存到BlockManager中,就可以了
def storeBlock(blockId: StreamBlockId, block: ReceivedBlock): ReceivedBlockStoreResult = {
val putResult: Seq[(BlockId, BlockStatus)] = block match {
case ArrayBufferBlock(arrayBuffer) =>
blockManager.putIterator(blockId, arrayBuffer.iterator, storageLevel, tellMaster = true)
case IteratorBlock(iterator) =>
blockManager.putIterator(blockId, iterator, storageLevel, tellMaster = true)
case ByteBufferBlock(byteBuffer) =>
blockManager.putBytes(blockId, byteBuffer, storageLevel, tellMaster = true)
case o =>
throw new SparkException(
s"Could not store $blockId to block manager, unexpected block type ${o.getClass.getName}")
}
if (!putResult.map { _._1 }.contains(blockId)) {
throw new SparkException(
s"Could not store $blockId to block manager with storage level $storageLevel")
}
BlockManagerBasedStoreResult(blockId)
}
接着看trackerActor.ask(AddBlock(blockInfo))(askTimeout),会发一个AddBlock消息到ReceiverTracker,进入看一下:
###org.apache.spark.streaming.scheduler/ReceiverTracker.scala
private def addBlock(receivedBlockInfo: ReceivedBlockInfo): Boolean = {
receivedBlockTracker.addBlock(receivedBlockInfo)
}
接着看receivedBlockTracker的addBlock方法,除了这个方法之外,还看receivedBlockTracker的几个重要变量,
先看方法:
###org.apache.spark.streaming.scheduler/ReceivedBlockTracker.scala
def addBlock(receivedBlockInfo: ReceivedBlockInfo): Boolean = synchronized {
try {
writeToLog(BlockAdditionEvent(receivedBlockInfo))
getReceivedBlockQueue(receivedBlockInfo.streamId) += receivedBlockInfo
logDebug(s"Stream ${receivedBlockInfo.streamId} received " +
s"block ${receivedBlockInfo.blockStoreResult.blockId}")
true
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
logError(s"Error adding block $receivedBlockInfo", e)
false
}
}
再看变量
###org.apache.spark.streaming.scheduler/ReceivedBlockTracker.scala // 封装了streamId到block的映射
private val streamIdToUnallocatedBlockQueues = new mutable.HashMap[Int, ReceivedBlockQueue]
// 封装了time到block的映射
private val timeToAllocatedBlocks = new mutable.HashMap[Time, AllocatedBlocks]
// 如果开启了预写机制机制,这还有LogManager,ReceiverTracker接收到数据时,也会判断,
// 如果开启了预写日志机制,写一份到预写日志中
private val logManagerOption = createLogManager()
65、Spark Streaming:数据接收原理剖析与源码分析的更多相关文章
- 66、Spark Streaming:数据处理原理剖析与源码分析(block与batch关系透彻解析)
一.数据处理原理剖析 每隔我们设置的batch interval 的time,就去找ReceiverTracker,将其中的,从上次划分batch的时间,到目前为止的这个batch interval ...
- 64、Spark Streaming:StreamingContext初始化与Receiver启动原理剖析与源码分析
一.StreamingContext源码分析 ###入口 org.apache.spark.streaming/StreamingContext.scala /** * 在创建和完成StreamCon ...
- 22、BlockManager原理剖析与源码分析
一.原理 1.图解 Driver上,有BlockManagerMaster,它的功能,就是负责对各个节点上的BlockManager内部管理的数据的元数据进行维护, 比如Block的增删改等操作,都会 ...
- 21、Shuffle原理剖析与源码分析
一.普通shuffle原理 1.图解 假设有一个节点上面运行了4个 ShuffleMapTask,然后这个节点上只有2个 cpu core.假如有另外一台节点,上面也运行了4个ResultTask,现 ...
- 20、Task原理剖析与源码分析
一.Task原理 1.图解 二.源码分析 1. ###org.apache.spark.executor/Executor.scala /** * 从TaskRunner开始,来看Task的运行的工作 ...
- 18、TaskScheduler原理剖析与源码分析
一.源码分析 ###入口 ###org.apache.spark.scheduler/DAGScheduler.scala // 最后,针对stage的task,创建TaskSet对象,调用taskS ...
- 23、CacheManager原理剖析与源码分析
一.图解 二.源码分析 ###org.apache.spark.rdd/RDD.scalal ###入口 final def iterator(split: Partition, context: T ...
- 19、Executor原理剖析与源码分析
一.原理图解 二.源码分析 1.Executor注册机制 worker中为Application启动的executor,实际上是启动了这个CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend进程: ...
- 16、job触发流程原理剖析与源码分析
一.以Wordcount为例来分析 1.Wordcount val lines = sc.textFile() val words = lines.flatMap(line => line.sp ...
随机推荐
- linux 文件夹分享
1.在 linux 安装 samba,安装好之后 配置文件在 /etc/samba/smb.conf 目录下. yum install samba samba-client(yum install s ...
- ChineseNumber 转换
中文数字转换 /** * <html> * <body> * <P> Copyright 1994 JsonInternational</p> * &l ...
- 4.将验证添加到 ASP.NET Core Razor 页面
向 Movie 模型添加了验证逻辑. 每当用户创建或编辑电影时,都会强制执行验证规则. 1.打开Movie.cs文件.DataAnnotations命名空间提供了一组内置的验证属性,这些属性以声明方式 ...
- Golang_小程序学golang
1 前置条件 Golang基本情况自行baidu/google 1.1 环境与工具 IDE:liteide (windows ).mingw-w64 (gcc) DB:SQL Server 2008 ...
- 2019年Amazon AWS-Solutions-Architect-Professional考试最新题库(AWS SAP题库)带考试模拟器
大家好,由于最近自己备考Amazon AWS-Solutions-Architect-Professional考试,购买了以下链接的题库,并通过了考试 https://www.kaoguti.gq/A ...
- selenium自动化测试框架之PO设计模式
面向对象的特性:封装.继承.多态.在自动化中一样适用,Selenium自动化测试中有一个名字常常被提及PageObject(思想与面向对象的特性相同),通过PO模式可以大大提高测试用例的维护效率. 传 ...
- Spring通过注解@Autowired/@Resource获取bean实例时为什么可以直接获取接口而不是注入的类
问: 这个问题困扰了我好久,一直疑问这个接口的bean是怎么注入进去的?因为只看到使用@Service注入了实现类serviceImpl,使用时怎么却获取的接口,而且还能调用到实现类的方法,难道这个接 ...
- python SqlServer操作
python连接微软的sql server数据库用的第三方模块叫做pymssql(document:http://www.pymssql.org/en/stable/index.html).在官方文档 ...
- centos7 ipython安装
##下载yum源(Centos 7 为例)[root@localhost ~]# wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/extras/x86_64/Packag ...
- video基础介绍&封装react-video基础组件,ES6
好几个月没有写博客了,人都赖了,今天抽了一点时间把最近项目react中video整理了一下(感觉这个以后用的活比较多) 1.前三部部分详细归纳了video的基础知识,属性和功能: 2.第四部分是封装了 ...
