Spring Security框架中踢人下线技术探索
1.背景
在某次项目的开发中,使用到了Spring Security权限框架进行后端权限开发的权限校验,底层集成Spring Session组件,非常方便的集成Redis进行分布式Session的会话集群部署。系统正式上线后,各个部署节点能够非常方便的进行集群部署,用户的Session会话信息全部保存在Redis中间件库中,开发者不用关心具体的实现,Spring Session组件已经全部集成好了。
但是在系统的用户管理模块中,提供了对系统用户账号的删除功能以及禁用功能,针对这两个功能,需求方给出的具体要求是:
- 删除:当管理员删除当前用户账号时,如果当前账号已经登录系统,则需要剔除下线,并且不可登录
- 禁用:当管理员对当前账号禁用操作时,如果当前账号已经登录系统,则需要剔除下线,并且登录时,提示当前账号已禁用
2.需求分析
从上面的需求来看,不管是删除还是禁用功能,都需要实现,如果当前账号已经登录系统,则需要剔除下线,而禁用操作只需要再登录时给出提示信息即可,这个在业务登录方法中就可以实现,不必从底层框架进行考虑。
因此,从底层技术测进行考虑时,我们需要探索如何在Spring Security权限框架中实现踢人下线的功能。
既然需求已经明确,从功能的实现可能性方面入手,我们则需要从几个方面进行考虑:
- 1)、在Spring Security框架中,用户登录的Session会话信息存储在哪里?
- 2)、在Spring Security框架中,Session会话如何存储,主要存储哪些信息?
- 3)、如何根据账号收集当前该账号登录的所有Session会话信息?
- 4)、如何在服务端主动销毁Session对象?
1)、在Spring Security框架中,用户登录的Session会话信息存储在哪里?
如果我们不考虑分布式Session会话的情况,单体Spring Boot项目中,服务端Session会话肯定存储在内存中,这样的弊端是如果当前应用需要做负载均衡进行部署时,用户请求服务端接口时,会存在Session会话丢失的情况,因为用户登录的会话信息都存在JVM内存中,没有进程之间的共享互通。
为了解决分布式应用Session会话不丢失的问题,Spring Session组件发布了,该组件提供了基于JDBC\Redis等中间件的方式,将用户端的Session会话存储在中间件中,这样分布式应用获取用户会话时,都会从中间件去获取会话Session,这样也保证了服务可以做负载部署以保证Session会话不丢失。本文主要讨论的也是这种情况,集成Redis中间件用来保存用户会话信息。
2)、在Spring Security框架中,Session会话如何存储,主要存储哪些信息?
由于我们使用了Redis中间件,所以,在Spring Security权限框架中产生的Session会话信息,肯定存储与Redis中,这点毫无疑问,那么存储了哪些信息呢?我会在接下来的源码分析中进行介绍
3)、如何根据账号收集当前该账号登录的所有Session会话信息?
我们从上面的需求分析中已经得知Session会话已经存储在Redis中,那么我们是否可以做这样的假设,我们只需要根据Spring Security中在Redis中存储的键值,找到和登录用户名相关的Redis缓存数据,就可以通过调用Security封装的方法进行获取,得到当前登录账号的会话信息呢?这个我们需要在源码中去找到答案
4)、如何在服务端主动销毁Session对象?
如果是单体的Spring Boot应用,Session信息肯定存储在JVM的内存中,服务端要主动销毁Session对象只需要找到Security权限框架如何存储的就可以进行删除。
在分布式的Spring Boot应用中,我们从上面已经得知Session会话信息以及存储在Redis中间件中,那么我们只需要得到当前登录的Session在Redis中的键值,就可以调用方法进行删除操作,从而主动在服务端销毁Session会话
3.源码分析
在上面的需求分析中,我们已经提出了假设,并且根据假设,做出来技术性的判断,接下来我们需要从Spring Security以及Spring Session组件的源码中,去寻找我们需要的答案。
首先,我们在源码分析前,我们需要找到入口,也就是我们在使用Spring Security框架,并且使用Spring Session组件时,我们如何使用的。
在pom.xml文件中引入组件的依赖是必不可少的,如下:
<!--Spring Security组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Spring针对Redis操作组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Spring Session集成Redis分布式Session会话-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
接下来,我们在Spring Boot项目中,需要添加@EnableRedisHttpSession注解,以开启Redis组件对Session会话的支持,该注解我们需要制定Spring Session在Redis中存储的Redis命名空间,已经Session会话的时效性,示例代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableRedisHttpSession(redisNamespace = "fish-admin:session",maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds = 7200)
public class FishAdminApplication {
static Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger(FishAdminApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
ConfigurableApplicationContext application=SpringApplication.run(FishAdminApplication.class, args);
Environment env = application.getEnvironment();
String host= InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
String port=env.getProperty("server.port");
logger.info("\n----------------------------------------------------------\n\t" +
"Application '{}' is running! Access URLs:\n\t" +
"Local: \t\thttp://localhost:{}\n\t" +
"External: \thttp://{}:{}\n\t"+
"Doc: \thttp://{}:{}/doc.html\n\t"+
"----------------------------------------------------------",
env.getProperty("spring.application.name"),
env.getProperty("server.port"),
host,port,
host,port);
}
在上面的代码中,我们指定Redis的命名空间是fish-admin:session,默认最大失效7200秒。
如果开发者默认不指定这两个属性的话,命名空间默认值是spring:session,默认最大时效则是1800秒
在上面我们已经说过了,既然是看源码,我们需要找到入口,这是看源码最好的方式,我们在使用Spring Session组件时,需要使用@EnableRedisHttpSession注解,那么该注解就是我们需要重点关注的对象,我们需要搞清楚,该注解的作用是什么?
EnableRedisHttpSession.java部分源码如下:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(RedisHttpSessionConfiguration.class)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public @interface EnableRedisHttpSession {
//more property..
}
在该注解中,我们可以看到,最关键的是在该注解之上,使用@Import注解导入了RedisHttpSessionConfiguration.java配置类,如果你经常翻看Spring Boot相关的源码,你会敏锐的察觉到,该配置类就是我们最终要找的类
先来看该类的UML图,如下:
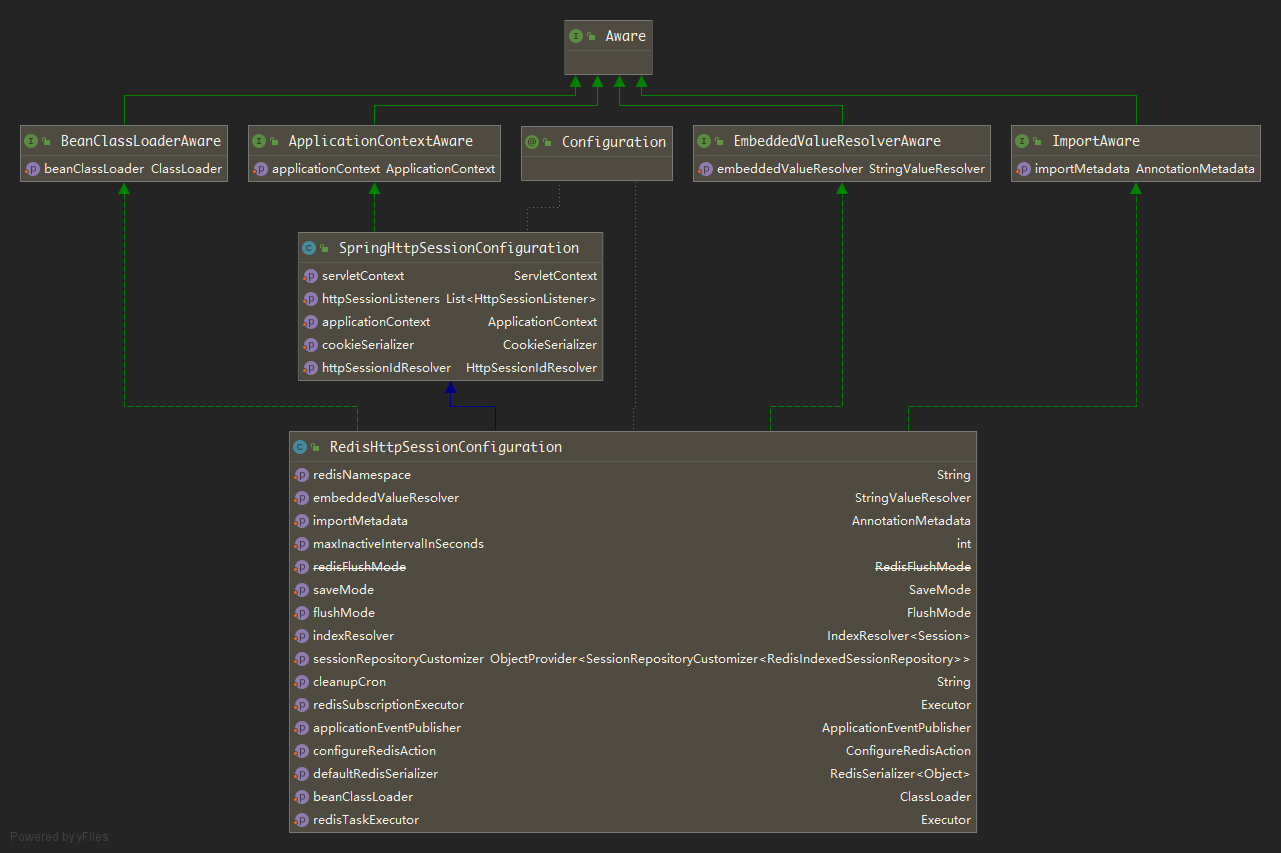
该类实现了Spring框架中很多Aware类型接口,Aware类型的接口我们都知道,Spring容器在启动创建实体Bean后,会调用Aware系列的set方法传参赋值
当然,最核心的,我们从源码中可以看到,是Spring Session组件会向Spring容器中注入两个实体Bean,代码如下:
@Bean
public RedisIndexedSessionRepository sessionRepository() {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = createRedisTemplate();
RedisIndexedSessionRepository sessionRepository = new RedisIndexedSessionRepository(redisTemplate);
sessionRepository.setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationEventPublisher);
if (this.indexResolver != null) {
sessionRepository.setIndexResolver(this.indexResolver);
}
if (this.defaultRedisSerializer != null) {
sessionRepository.setDefaultSerializer(this.defaultRedisSerializer);
}
sessionRepository.setDefaultMaxInactiveInterval(this.maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.redisNamespace)) {
sessionRepository.setRedisKeyNamespace(this.redisNamespace);
}
sessionRepository.setFlushMode(this.flushMode);
sessionRepository.setSaveMode(this.saveMode);
int database = resolveDatabase();
sessionRepository.setDatabase(database);
this.sessionRepositoryCustomizers
.forEach((sessionRepositoryCustomizer) -> sessionRepositoryCustomizer.customize(sessionRepository));
return sessionRepository;
}
@Bean
public RedisMessageListenerContainer springSessionRedisMessageListenerContainer(
RedisIndexedSessionRepository sessionRepository) {
RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer();
container.setConnectionFactory(this.redisConnectionFactory);
if (this.redisTaskExecutor != null) {
container.setTaskExecutor(this.redisTaskExecutor);
}
if (this.redisSubscriptionExecutor != null) {
container.setSubscriptionExecutor(this.redisSubscriptionExecutor);
}
container.addMessageListener(sessionRepository,
Arrays.asList(new ChannelTopic(sessionRepository.getSessionDeletedChannel()),
new ChannelTopic(sessionRepository.getSessionExpiredChannel())));
container.addMessageListener(sessionRepository,
Collections.singletonList(new PatternTopic(sessionRepository.getSessionCreatedChannelPrefix() + "*")));
return container;
}
RedisIndexedSessionRepository以及RedisMessageListenerContainer的实体Bean
RedisMessageListenerContainer:该类是Redis的消息通知回调机制实体类,Redis提供了针对不同Key的操作回调消息通知,比如常见的删除key、key过期等事件的回调,在Spring Session组件中注入该实体Bean,从代码中也可以看出是用来监听处理Session会话的过期以及删除事件RedisIndexedSessionRepository:该类是Spring Session组件提供基于Redis的针对Session会话一系列操作的具体实现类,是我们接下来源码分析的重点。
先来看RedisIndexedSessionRepository类的UML类图结构,如下图:

RedisIndexedSessionRepository实现了FindByIndexNameSessionRepository接口,而FindByIndexNameSessionRepository接口又继承Spring Security权限框架提供的顶级SessionRepository接口,UML类图中,我们可以得到几个重要的信息:
RedisIndexedSessionRepository拥有创建Session会话、销毁删除Session会话的能力RedisIndexedSessionRepository由于实现自FindByIndexNameSessionRepository接口,而该接口提供了根据PrincipalName查找Session会话的能力- 拥有Redis回调事件的处理消息能力,因为实现了
MessageListener接口
SessionRepository是Spring Security提供的顶级接口,源码如下:
public interface SessionRepository<S extends Session> {
/**
* Creates a new {@link Session} that is capable of being persisted by this
* {@link SessionRepository}.
*
* <p>
* This allows optimizations and customizations in how the {@link Session} is
* persisted. For example, the implementation returned might keep track of the changes
* ensuring that only the delta needs to be persisted on a save.
* </p>
* @return a new {@link Session} that is capable of being persisted by this
* {@link SessionRepository}
*/
S createSession();
/**
* Ensures the {@link Session} created by
* {@link org.springframework.session.SessionRepository#createSession()} is saved.
*
* <p>
* Some implementations may choose to save as the {@link Session} is updated by
* returning a {@link Session} that immediately persists any changes. In this case,
* this method may not actually do anything.
* </p>
* @param session the {@link Session} to save
*/
void save(S session);
/**
* Gets the {@link Session} by the {@link Session#getId()} or null if no
* {@link Session} is found.
* @param id the {@link org.springframework.session.Session#getId()} to lookup
* @return the {@link Session} by the {@link Session#getId()} or null if no
* {@link Session} is found.
*/
S findById(String id);
/**
* Deletes the {@link Session} with the given {@link Session#getId()} or does nothing
* if the {@link Session} is not found.
* @param id the {@link org.springframework.session.Session#getId()} to delete
*/
void deleteById(String id);
}
该接口提供四个方法:
createSession:创建Session会话save:保存Session会话findById:根据SessionId查找获取Session会话对象信息deleteById:根据SessionId进行删除
FindByIndexNameSessionRepository源码主要是提供根据账号名称进行查询的功能,如下:
public interface FindByIndexNameSessionRepository<S extends Session> extends SessionRepository<S> {
/**
* 当前存储的用户名前缀,使用Redis进行存储时,存储的key值是:redisNamespace+
*/
String PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME = FindByIndexNameSessionRepository.class.getName()
.concat(".PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME");
/**
* Find a {@link Map} of the session id to the {@link Session} of all sessions that
* contain the specified index name index value.
* @param indexName the name of the index (i.e.
* {@link FindByIndexNameSessionRepository#PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME})
* @param indexValue the value of the index to search for.
* @return a {@code Map} (never {@code null}) of the session id to the {@code Session}
* of all sessions that contain the specified index name and index value. If no
* results are found, an empty {@code Map} is returned.
*/
Map<String, S> findByIndexNameAndIndexValue(String indexName, String indexValue);
/**
* Find a {@link Map} of the session id to the {@link Session} of all sessions that
* contain the index with the name
* {@link FindByIndexNameSessionRepository#PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME} and the
* specified principal name.
* @param principalName the principal name
* @return a {@code Map} (never {@code null}) of the session id to the {@code Session}
* of all sessions that contain the specified principal name. If no results are found,
* an empty {@code Map} is returned.
* @since 2.1.0
*/
default Map<String, S> findByPrincipalName(String principalName) {
return findByIndexNameAndIndexValue(PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME, principalName);
}
}
该接口最核心的功能是提供了根据用户名查找获取Session会话的接口,这对我们后面实现踢人功能很有帮助。
通过查看SessionRepository接口以及FindByIndexNameSessionRepository接口的源码我们得知:
- Redis的实现最终实现了这两个接口,因此获得了基于Redis中间件创建及销毁Session会话的能力
- 根据账号去查找当前的所有登录会话Session符合我们最终需要服务端主动踢人下线的功能需求。
接下来我们只需要关注RedisIndexedSessionRepository的实现即可。首先来看findByPrincipalName方法,源码如下:
@Override
public Map<String, RedisSession> findByIndexNameAndIndexValue(String indexName, String indexValue) {
//如果名称不匹配,则直接反馈空集合Map
if (!PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME.equals(indexName)) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
//获取拼装的Key值
String principalKey = getPrincipalKey(indexValue);
//从Redis中获取该Key值的成员数
Set<Object> sessionIds = this.sessionRedisOperations.boundSetOps(principalKey).members();
//初始化Map集合
Map<String, RedisSession> sessions = new HashMap<>(sessionIds.size());
//循环遍历
for (Object id : sessionIds) {
//根据id查找Session会话
RedisSession session = findById((String) id);
if (session != null) {
sessions.put(session.getId(), session);
}
}
return sessions;
}
String getPrincipalKey(String principalName) {
return this.namespace + "index:" + FindByIndexNameSessionRepository.PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME + ":"
+ principalName;
}
接下来我们看删除Session会话的方法实现:
@Override
public void deleteById(String sessionId) {
//根据sessionId获取Session会话
RedisSession session = getSession(sessionId, true);
if (session == null) {
return;
}
//从Redis中移除所有存储的针对principal的key值
cleanupPrincipalIndex(session);
//Redis中删除SessionId所对应的key值
this.expirationPolicy.onDelete(session);
//移除Session会话创建时,存储的过期key值
String expireKey = getExpiredKey(session.getId());
this.sessionRedisOperations.delete(expireKey);
//设置当前session会话最大存活时间为0
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(Duration.ZERO);
//执行save方法
save(session);
}
从上面的代码中,我们已经知道了Spring Session组件对于Session相关的处理方法,其实我们基于上面的两个核心方法,我们已经获得了踢人下线的能力,但是,既然RedisIndexedSessionRepository实现了MessageListener接口,我们需要继续跟踪一下该接口的具体实现方法,我们直接来看onMessage方法,代码如下:
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) {
byte[] messageChannel = message.getChannel();
byte[] messageBody = message.getBody();
String channel = new String(messageChannel);
if (channel.startsWith(this.sessionCreatedChannelPrefix)) {
// TODO: is this thread safe?
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<Object, Object> loaded = (Map<Object, Object>) this.defaultSerializer.deserialize(message.getBody());
handleCreated(loaded, channel);
return;
}
String body = new String(messageBody);
if (!body.startsWith(getExpiredKeyPrefix())) {
return;
}
boolean isDeleted = channel.equals(this.sessionDeletedChannel);
if (isDeleted || channel.equals(this.sessionExpiredChannel)) {
int beginIndex = body.lastIndexOf(":") + 1;
int endIndex = body.length();
String sessionId = body.substring(beginIndex, endIndex);
RedisSession session = getSession(sessionId, true);
if (session == null) {
logger.warn("Unable to publish SessionDestroyedEvent for session " + sessionId);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Publishing SessionDestroyedEvent for session " + sessionId);
}
cleanupPrincipalIndex(session);
if (isDeleted) {
handleDeleted(session);
}
else {
handleExpired(session);
}
}
}
private void handleDeleted(RedisSession session) {
publishEvent(new SessionDeletedEvent(this, session));
}
private void handleExpired(RedisSession session) {
publishEvent(new SessionExpiredEvent(this, session));
}
private void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.error("Error publishing " + event + ".", ex);
}
}
在onMessage方法中,最核心的是最后一个判断,分别执行handleDeleted和handleExpired方法,从源码中我们可以看到,当当前Session会话被删除或者失效时,Spring Session会通过ApplicationEventPublisher广播一个事件,分别处理SessionExpiredEvent和SessionDeletedEvent事件
这是Spring Session组件为开发者预留的针对Session会话的Event事件,如果开发者对于当前的Sesssion会话的删除或者失效有特殊的处理需求,则可以通过监听该事件进行处理。
例如,开发者针对Session会话的操作都需要做业务操作,记录日志保存到DB数据库中,此时,开发者只需要使用Spring提供的EventListener实现就可以很轻松的实现,示例代码如下:
@Component
public class SecuritySessionEventListener {
@EventListener
public void sessionDestroyed(SessionDestroyedEvent event) {
//session销毁事件处理方法...
}
@EventListener
public void sessionCreated(SessionCreatedEvent event) {
//session创建会话事件处理方法...
}
@EventListener
public void sessionExired(SessionExpiredEvent event) {
//session会话过期事件处理方法...
}
}
4.解决方案
我们分析了Spring Session针对Session基于Redis的实现,接下来,我们从源码中已经知道了该如何查找Session会话以及销毁会话的方法,此时,我们可以来改造我们的框架代码了
创建SessionService接口,代码如下:
public interface SessionService {
/**
*
* @param account
* @return
*/
boolean hasLogin(String account);
/**
* 根據账号查找当前session会话
* @param account 账号
* @return
*/
Map<String, ? extends Session> loadByAccount(String account);
/**
* 销毁当前session会话
* @param account
*/
void destroySession(String account);
}
声明该接口主要包含3个方法:
- hasLogin:通过传递登录账号,判断该账号是否已经登录过,该方法是一个业务的延伸,比如我们对当前账号判断是否已经登录过,如果登录则提示需要退出才能继续登录的操作等
- loadByAccount:根据登录账号获取当前已经登录的Session会话Map集合
- destroySession:根据登录账号销毁当前所有该账号的Session会话信息,此接口和产品经理要求的踢人下线操作一致
接下来就是实现类,由于我们是基于Redis来处理,因此,我们需要将源码分析中的RedisIndexedSessionRepository实体Bean进行引入,借助该类实现该接口方法
RedisSessionService方法实现如下:
/**
* SpringSession集成底层Redis实现,如果底层分布式会话保持方式不是基于Redis,则该类无法正常使用
* @author <a href="mailto:xiaoymin@foxmail.com">xiaoymin@foxmail.com</a>
* 2021/04/20 16:23
* @since:fish 1.0
*/
public class RedisSessionService implements SessionService {
Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisSessionService.class);
final RedisIndexedSessionRepository redisIndexedSessionRepository;
final ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
public RedisSessionService(RedisIndexedSessionRepository redisIndexedSessionRepository, ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.redisIndexedSessionRepository = redisIndexedSessionRepository;
this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
@Override
public boolean hasLogin(String account) {
return CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(loadByAccount(account));
}
@Override
public Map<String, ? extends Session> loadByAccount(String account) {
logger.info("收集当前登录会话session,账号:{}",account);
return redisIndexedSessionRepository.findByIndexNameAndIndexValue(FindByIndexNameSessionRepository.PRINCIPAL_NAME_INDEX_NAME,account);
}
@Override
public void destroySession(String account) {
logger.info("销毁当前登录session会话,账号:{}",account);
Map<String,? extends Session> sessionMap=loadByAccount(account);
if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(sessionMap)){
logger.info("当前登录会话size:{}",sessionMap.size());
for (Map.Entry<String,? extends Session> sessionEntry:sessionMap.entrySet()){
String key=sessionEntry.getKey();
Session session=sessionEntry.getValue();
logger.info("destroy session key:{}",key);
//删除
redisIndexedSessionRepository.deleteById(session.getId());
//广播Session会话销毁事件
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new SessionDestroyedEvent(redisIndexedSessionRepository,session));
}
}
}
}
在destroySession方法实现中,首先根据账号获取当前所有登录会话信息,如果会话不为空,则遍历会话Map集合,执行删除会话操作,并且通过applicationEventPublisher广播一个会话被销毁的事件。该广播事件非必须,但是从代码的全局进行考虑,还是需要加上
接下来,我们就可以将该类注入到Spring的容器中的,注入实体Bean代码如下:
@Bean
public RedisSessionService sessionService(RedisIndexedSessionRepository redisIndexedSessionRepository, ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher){
return new RedisSessionService(redisIndexedSessionRepository,applicationEventPublisher);
}
PS:我们为什么需要创建接口而不是直接创建class的方式通过
@Service等注解进行注入,而是通过抽象接口实现类的方式,最终通过JavaConfig的方式进行注入呢?从代码的耦合度上来看,由于Spring Session提供处理基于Redis的能力处理Session会话之外,还提供了诸如JDBC\mongo等多元化的扩展方式,因此,为了代码解耦,通过抽象接口的方式是更合理的。
接下来,我们在我们的用户管理的业务Service方法中就可以进行操作了
删除用户的业务Service方法
/**
* 根据主键id删除用户管理
* @param id 主键id
* @return 是否删除成功
*/
@Override
public RestfulMessage<String> delete(Integer id) {
logger.info("根据主键id删除用户管理,id:{}",id);
FishUserInfo fishUserInfo=fishUserInfoMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
assertArgumentNotEmpty(fishUserInfo,"请求数据非法");
int ret=fishUserInfoMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);
//删除成功,如果该角色在线,则强制剔除下线
if (ret>0){
logger.info("用户会话剔除下线");
sessionService.destroySession(fishUserInfo.getAccount());
}
return ret>0?RestfulMessage.success("删除成功"):RestfulMessage.error("删除失败");
}
禁用用户
禁用用户其实操作方法和删除一样,区别在于禁用操作只是将用户在数据库中的状态进行变更,而删除则是将该用户的数据从数据库DB中进行删除。更新库的用户状态后,调用destroySession删除该账号的所有Session会话操作即可
Spring Security框架中踢人下线技术探索的更多相关文章
- Spring Security框架进阶、自定义登录
1.Spring Security框架进阶 1.1 Spring Security简介 Spring Security是一个能够为基于Spring的企业应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案的安 ...
- Spring Security框架入门
1.Spring Security框架入门 1.1 Spring Security简介 Spring Security是一个能够为基于Spring的企业应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案的安全框 ...
- spring security 3中的10个典型用法小结
spring security 3比较庞大,但功能很强,下面小结下spring security 3中值得 注意的10个典型用法 1)多个authentication-provide可以同时使用 &l ...
- Spring Security 5中的默认密码编码器
1.概述 在Spring Security 4中,可以使用内存中身份验证以纯文本格式存储密码. 对版本5中的密码管理过程进行了重大改进,为密码编码和解码引入了更安全的默认机制.这意味着如果您的Spri ...
- Spring Security框架下实现两周内自动登录"记住我"功能
本文是Spring Security系列中的一篇.在上一篇文章中,我们通过实现UserDetailsService和UserDetails接口,实现了动态的从数据库加载用户.角色.权限相关信息,从而实 ...
- Spring Security 5中 PasswordEncoder的使用
在最新的 Spring Security 5发布版本中, 出于安全性的考虑调整了PasswordEncoder的实现与使用策略. 1.以前常用的实现 StandardPasswordEncoder, ...
- 一文搞懂Java/Spring/Dubbo框架中的SPI机制
几天前和一位前辈聊起了Spring技术,大佬突然说了SPI,作为一个熟练使用Spring的民工,心中一紧,咱也不敢说不懂,而是在聊完之后赶紧打开了浏览器,开始的学习之路,所以也就有了这篇文章.废话不多 ...
- Spring+MyBatis框架中sql语句的书写,数据集的传递以及多表关联查询
在很多Java EE项目中,Spring+MyBatis框架经常被用到,项目搭建在这里不再赘述,现在要将的是如何在项目中书写,增删改查的语句,如何操作数据库,以及后台如何获取数据,如何进行关联查询,以 ...
- Spring Security框架下Restful Token的验证方案
项目使用Restful的规范,权限内容的访问,考虑使用Token验证的权限解决方案. 验证方案(简要概括): 首先,用户需要登陆,成功登陆后返回一个Token串: 然后用户访问有权限的内容时需要上传T ...
随机推荐
- 【SVM】kaggle之澳大利亚天气预测
项目目标 由于大气运动极为复杂,影响天气的因素较多,而人们认识大气本身运动的能力极为有限,因此天气预报水平较低,预报员在预报实践中,每次预报的过程都极为复杂,需要综合分析,并预报各气象要素,比如温度. ...
- Anno&Viper -分布式锁服务端怎么实现
1.Anno简介 Anno是一个微服务框架引擎.入门简单.安全.稳定.高可用.全平台可监控.依赖第三方框架少.底层通讯RPC(Remote Procedure Call)采用稳定可靠经过无数成功项目验 ...
- 大数据开发-Spark-Streaming处理数据到mysql
前面一篇讲到streamin读取kafka数据加工处理后写到kafka数据,大数据开发-Spark-开发Streaming处理数据 && 写入Kafka是针对比如推荐领域,实时标签等场 ...
- [源码解析] 消息队列 Kombu 之 基本架构
[源码解析] 消息队列 Kombu 之 基本架构 目录 [源码解析] 消息队列 Kombu 之 基本架构 0x00 摘要 0x01 AMQP 1.1 基本概念 1.2 工作过程 0x02 Poll系列 ...
- pytorch(05)计算图
张量的一系列操作,增多,导致可能出现多个操作之间的串行并行,协同不同的底层之间的协作,避免操作的冗余.计算图就是为了解决这些问题产生的. 计算图与动态图机制 1. 计算图 计算图用来描述运算的有向无环 ...
- mysql内一些可以报错注入的查询语句
一.exp() 取反参数 该函数简单来说就是,以e为底的对数,在当传递一个大于709的值时,函数exp()就会引起一个溢出错误,取反则可以导致很小的数值变得很大,比如说0 这样既可配合使用,e ...
- NumPy 将停止支持 Python 2
NumPy 项目宣布将停止支持 Python 2.Python 核心团队已经决定在 2020 年停止支持 Python 2,而 NumPy 项目自 2010 年以来同时支持 Python 2 和 Py ...
- VSCode添加用户代码片段,自定义用户代码片段
在使用VScode开发中经常会有一些重复使用的代码块,复制粘贴也很麻烦,这时可以在VScode中添加用户代码片段,输入简写即可快捷输入. VScode中添加用户自定义代码片段很简单. 1.在VScod ...
- Python开发环境从零搭建-03-安装Python解释器并配置
想要从零开始搭建一个Python的开发环境说容易也容易 说难也能难倒一片开发人员,在接下来的一系列视频中,会详细的讲解如何一步步搭建python的开发环境 本文章是搭建环境的第3篇 讲解的内容是:安装 ...
- 1.mysql读写
一.数据库读取(mysql) 参数 接受 作用 默认 sql or table_name string 读取的表名,或sql语句 无 con 数据库连接 数据库连接信息 无 index_col Int ...
