(四)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- 多数据源,JdbcTemplate和JpaRepository
在日常开发中,经常会遇到多个数据源的问题,而SpringBoot也有相关API:Configure Two DataSources:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.4.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#howto-two-datasources
本文SpringBoot版本为2.0(由于2.0之前的版本和之后的版本配置会有些许不同,2.0之前的版本推荐一位大牛的博文:http://blog.didispace.com/springbootmultidatasource/)下面会介绍这两种多数据源的配置方法,希望大家多多指教!
一、JdbcTemplate多数据源配置
1、添加applicaton.properties数据库连接信息,有两个数据源,一个为主,一个为从:
app.datasource.foo.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.121:3306/test
app.datasource.foo.username=root
app.datasource.foo.password=admincss
app.datasource.foo.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver app.datasource.bar.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.121:3306/test2
app.datasource.bar.username=root
app.datasource.bar.password=admincss
app.datasource.bar.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2、创建数据源类:
package com.cn.datasource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import javax.sql.DataSource; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description: 数据源配置类
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-03 14:35
**/ @Configuration
public class JdbcDataSourceConfig { @Primary
@Bean(name = "dataSourcePropertiesFoo")
@Qualifier("dataSourcePropertiesFoo")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="app.datasource.foo")
public DataSourceProperties dataSourcePropertiesFoo() {
return new DataSourceProperties();
} @Primary
@Bean(name = "fooDataSource")
@Qualifier("fooDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="app.datasource.foo")
public DataSource fooDataSource(@Qualifier("dataSourcePropertiesFoo") DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties) {
return dataSourceProperties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
} @Bean(name = "dataSourcePropertiesBar")
@Qualifier("dataSourcePropertiesBar")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="app.datasource.bar")
public DataSourceProperties dataSourcePropertiesBar() {
return new DataSourceProperties();
} @Bean(name = "barDataSource")
@Qualifier("barDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="app.datasource.bar")
public DataSource barDataSource(@Qualifier("dataSourcePropertiesBar") DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties) {
return dataSourceProperties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
} @Bean(name = "fooJdbcTemplate")
@Qualifier("fooJdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate fooJdbcTemplate(@Qualifier("fooDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
} @Bean(name = "barJdbcTemplate")
@Qualifier("barJdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate barJdbcTemplate(@Qualifier("barDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}
3、创建简单的测试bean、controller、service、entityRowMapper:
package com.cn.entity.u; import java.io.Serializable; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description: 用户类
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 09:59
**/
public class User implements Serializable{ private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String address; @Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} public String getAddress() {
return address;
} public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
User.java
package com.cn.controller; import com.cn.entity.u.User;
import com.cn.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 09:58
**/ @RestController
public class JdbcTestController { @Autowired
private UserService userService; @RequestMapping(value = "getUserById/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUserById(@PathVariable int id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
} }
JdbcTestController.java
package com.cn.service; import com.cn.entity.u.User; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 10:02
**/ public interface UserService { User getUserById(int id); }
UserService.java
package com.cn.service; import com.cn.entity.u.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 10:07
**/ @Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired
@Qualifier("fooJdbcTemplate")
protected JdbcTemplate fooJdbcTemplate; @Autowired
@Qualifier("barJdbcTemplate")
protected JdbcTemplate barJdbcTemplate; @Override
public User getUserById(int id) {
User user = fooJdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from user where id=?", new Object[]{id},new UserRowMapper());
User user2 = barJdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from user where id=?", new Object[]{id},new UserRowMapper());
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(user2);
return user;
} }
UserServiceImpl.java
package com.cn.service; import com.cn.entity.u.User;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException; class UserRowMapper implements RowMapper<User> { public User mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user.setAge(resultSet.getInt("age"));
user.setAddress(resultSet.getString("address"));
return user;
} }
UserRowMapper.java
4、测试;
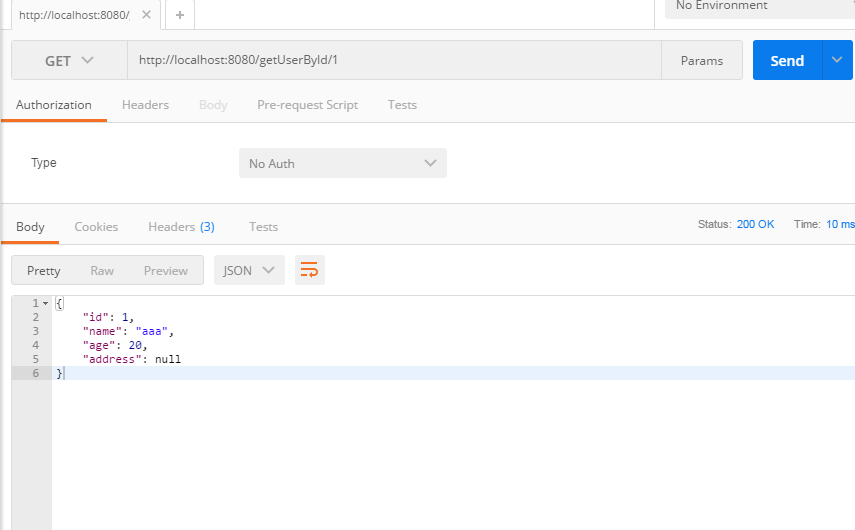
二、JpaRepository多数据源
1、添加数据源信息如上;
2、使用上一个项目的数据源DataSource进行进一步的配置JpaFooConfig、JpaBarConfig:
package com.cn.datasource; import java.util.Map;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateSettings;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-04 10:54
**/ @Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
entityManagerFactoryRef = "entityManagerFactoryFoo",
transactionManagerRef = "transactionManagerFoo",
basePackages = {"com.cn.entity.s"})
public class JpaFooConfig { @Resource
@Qualifier("fooDataSource")
private DataSource fooDataSource; @Primary
@Bean(name = "entityManagerFoo")
public EntityManager entityManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return entityManagerFactoryFoo(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
} @Resource
private JpaProperties jpaProperties; private Map<String, Object> getVendorProperties() {
return jpaProperties.getHibernateProperties(new HibernateSettings());
} /**
* 设置实体类所在位置
*/
@Primary
@Bean(name = "entityManagerFactoryFoo")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryFoo(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder
.dataSource(fooDataSource)
.packages("com.cn.entity.s")
.persistenceUnit("fooPersistenceUnit")
.properties(getVendorProperties())
.build();
} @Primary
@Bean(name = "transactionManagerFoo")
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManagerFoo(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(entityManagerFactoryFoo(builder).getObject());
} }
package com.cn.datasource; import java.util.Map;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateSettings;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-04 10:54
**/ @Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
entityManagerFactoryRef = "entityManagerFactoryBar",
transactionManagerRef = "transactionManagerBar",
basePackages = {"com.cn.entity.t"})//repository的目录
public class JpaBarConfig { @Autowired
@Qualifier("barDataSource")
private DataSource barDataSource; @Bean(name = "entityManagerBar")
public EntityManager entityManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return entityManagerFactoryBar(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
} @Resource
private JpaProperties jpaProperties; private Map<String, Object> getVendorProperties() {
return jpaProperties.getHibernateProperties(new HibernateSettings());
} @Bean(name = "entityManagerFactoryBar")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBar(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder
.dataSource(barDataSource)
.packages("com.cn.entity.t")//实体类的目录
.persistenceUnit("barPersistenceUnit")
.properties(getVendorProperties())
.build();
} @Bean(name = "transactionManagerBar")
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManagerBar(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(entityManagerFactoryBar(builder).getObject());
} }
3、同上创建相关的测试类进行测试(bean、repository、controller、service 注意bean、repository的目录要放在2步骤中配置的位置):
package com.cn.entity.s; import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description: 学生实体类
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 10:47
**/
@Entity
public class Student { @Id
@GeneratedValue
private int id; private String name; private int age; private int grade; public Student() {
} public Student(String name, int age, int grade) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.grade = grade;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", grade=" + grade +
'}';
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} public int getGrade() {
return grade;
} public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
}
Student.java
package com.cn.entity.s; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 11:02
**/
public interface StudentDao extends JpaRepository<Student,Integer> { Student findByName(String name); }
StudentDao.java
package com.cn.entity.t; import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-04 10:38
**/ @Entity
public class Teacher { @Id
@GeneratedValue
private int id;
private String name;
private String age;
private String course; public Teacher() {
} public Teacher(String name, String age, String course) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.course = course;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Teacher{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
", course='" + course + '\'' +
'}';
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
} public String getCourse() {
return course;
} public void setCourse(String course) {
this.course = course;
}
}
Teacher.java
package com.cn.entity.t; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; /**
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 11:02
**/
public interface TeacherDao extends JpaRepository<Teacher,Integer> { Teacher findByName(String name); }
TeacherDao.java
package com.cn.controller; import com.cn.entity.s.Student;
import com.cn.service.JpaService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /*
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 11:15
*/ @RestController
public class JpaTestController { @Autowired
private JpaService jpaService; @RequestMapping("findByName/{name}")
public Student findByName(@PathVariable String name) {
return jpaService.findByName(name);
} }
JpaTestController.java
package com.cn.service; import com.cn.entity.s.Student; /*
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 11:12
*/ public interface JpaService { Student findByName(String name); }
JpaService.java
package com.cn.service; import com.cn.entity.s.StudentDao;
import com.cn.entity.s.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /*
* @program: spring-boot-example
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2018-05-02 11:13
*/ @Service
public class JpaServiceImpl implements JpaService { @Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao; @Override
public Student findByName(String name) {
return studentDao.findByName(name);
} }
JpaServiceImpl.java
4、测试;
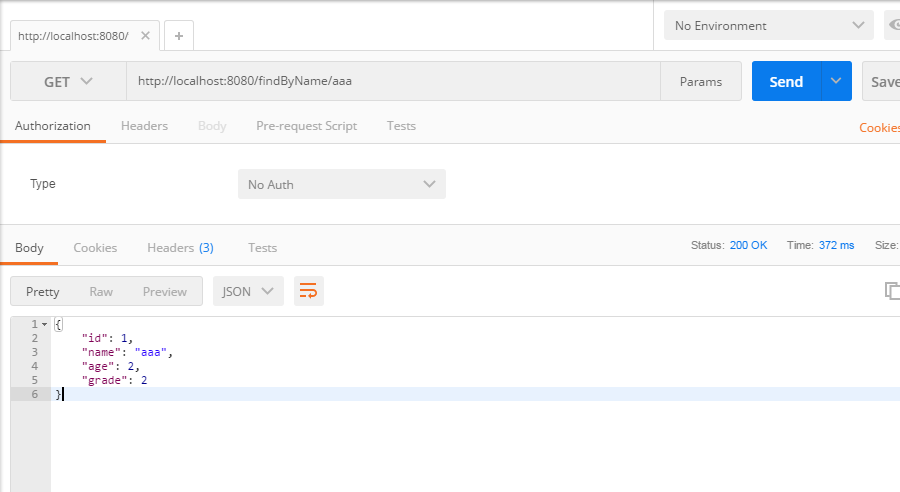
示例代码:https://gitee.com/lfalex/spring-boot-example/tree/dev/spring-boot-datasource
参考官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.4.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#howto-data-access
(四)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- 多数据源,JdbcTemplate和JpaRepository的更多相关文章
- (六)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- Redis整合(JedisCluster集群连接)
一.环境 Redis:4.0.9 SpringBoot:2.0.1 Redis安装:Linux(Redhat)安装Redis 二.SpringBoot整合Redis 1.项目基本搭建: 我们基于(五) ...
- (二)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- 静态资源的访问及Thymeleaf模板引擎的使用
一.描述 在应用系统开发的过程中,不可避免的需要使用静态资源(浏览器看的懂,他可以有变量,例:HTML页面,css样式文件,文本,属性文件,图片等): 并且SpringBoot内置了Thymeleaf ...
- (三)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- 持久层,jdbcTemplate和JpaRespository
一.介绍 SpringBoot框架为使用SQL数据库提供了广泛的支持,从使用JdbcTemplate的直接JDBC访问到完整的“对象关系映射”技术(如Hibernate).Spring-data-jp ...
- (五)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- Mybatis与插件生成代码
SpringBoot与Mybatis合并 一.创建SpringBoot项目,引入相关依赖包: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8 ...
- (一)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- 介绍及HelloWorld初体验
1.SpringBoot介绍: 根据官方SpringBoot文档描述,BUILD ANYTHING WITH SPRING BOOT (用SPRING BOOT构建任何东西,很牛X呀!),下面是官方文 ...
- (七)SpringBoot2.0基础篇- application.properties属性文件的解析及获取
默认访问的属性文件为application.properties文件,可在启动项目参数中指定spring.config.location的参数: java -jar myproject.jar --s ...
- SpringBoot2.0 基础案例(12):基于转账案例,演示事务管理操作
本文源码 GitHub地址:知了一笑 https://github.com/cicadasmile/spring-boot-base 一.事务管理简介 1.事务基本概念 一组业务操作ABCD,要么全部 ...
- 【转】WF4.0 (基础篇)
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/foundation/category/215023.html 作者:WXWinter —— 兰竹菊梅★春夏秋冬☆ —— wxwinter@16 ...
- iOS开发swift语法0基础篇—————(swift技术交流群:361513739)
iOS开发之swift语法0基础篇:点击打开链接 swift技术交流QQ群361513739
随机推荐
- Linux IPC实践(13) --System V IPC综合实践
实践:实现一个先进先出的共享内存shmfifo 使用消息队列即可实现消息的先进先出(FIFO), 但是使用共享内存实现消息的先进先出则更加快速; 我们首先完成C语言版本的shmfifo(基于过程调用) ...
- (五十一)KVC与KVO详解
KVC的全称为key value coding,它是一种使用字符串间接更改对象属性的方法. 假设有一个Person类和一个Student类,其中Person类有age.name两个属性,Student ...
- python3爬虫 - cookie登录实战
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/47948065 实战1:使用cookie登录哈工大ACM网站 获取网站登录地址 http://acm.h ...
- centos vsftpd 553 Could not create file解决方法
centos vsftpd 553 Could not create file解决方法 问题由于selinux引起的,问题解决办法: www.2cto.com 输入:getsebool - ...
- python模块 - 常用模块推荐
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/47185795 python常用模块 压缩字符 当谈起压缩时我们通常想到文件,比如ZIP结构.在Pyth ...
- Leetcode_48_Rotate Image
本文是在学习中的总结,欢迎转载但请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/pistolove/article/details/44216867 You are given an n x n ...
- 苹果IOS与谷歌 android系统的UI设计原则
一.苹果为IOS的界面设计提出了六大原则: 1.整体美学 整体美学指的是一个应用的表现和行为与它的功能完美集成,传达连贯的信息. 人们关心一个应用是否提供它承诺的功能,但他们也被应用的外观和行为强烈影 ...
- URL 多线程下载
该资源来源于李刚老师的疯狂JAVA讲义 InutStream openStream():打开与此URL链接,并返回一个用于读取该URL资源的InputStream. 提供的openStream()可以 ...
- “《编程珠玑》(第2版)第2章”:B题(向量旋转)
B题是这样子的: 将一个n元一维向量向左旋转(即循环移位)i个位置.例如,当n=8且i=3时,向量abcdefgh旋转为defghabc.简单的代码使用一个n元的中间向量在n步内完成该工作.你能否仅使 ...
- Android高级控件(四)——VideoView 实现引导页播放视频欢迎效果,超级简单却十分的炫酷
Android高级控件(四)--VideoView 实现引导页播放视频欢迎效果,超级简单却十分的炫酷 是不是感觉QQ空间什么的每次新版本更新那炫炫的引导页就特别的激动,哈哈,其实他实现起来真的很简单很 ...
