CSS - 定位(position),难点
元素的定位属性主要包括定位模式和边偏移两部分。
1. 边偏移
| 边偏移属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| top | 顶端偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素上边线的距离 |
| bottom | 底部偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素下边线的距离 |
| left | 左侧偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素左边线的距离 |
| right | 右侧偏移量,定义元素相对于其父元素右边线的距离 |
2. 定位模式(定位的分类)
选择器{position:属性值;}
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| static | 自动定位(默认定位方式) |
| relative | 相对定位,相对于其原文档流的位置进行定位 |
| absolute | 绝对定位,相对于其上一个已经定位的父元素进行定位 |
| fixed | 固定定位,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位 |
3. 静态定位static
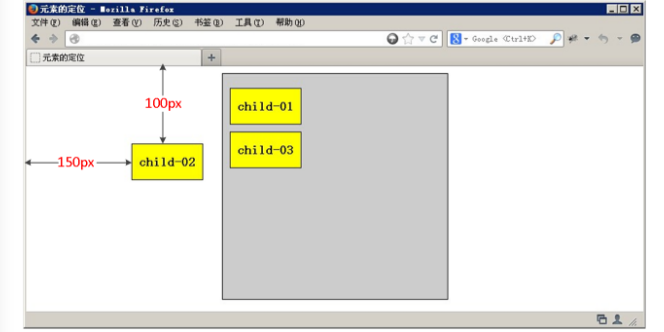
3.1 静态定位是所有元素的默认定位方式,当position属性的取值为static时,可以将元素定位于静态位置。 所谓静态位置就是各个元素在HTML文档流中默认的位置。(标准流特性)
3.2 静态定位状态下,无法通过边偏移属性(top、bottom、left或right)来改变元素的位置。
3.3 静态定位唯一的用处就是取消定位。 position: static;
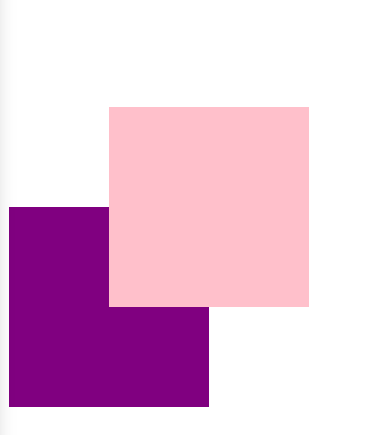
4. 相对定位relative(自恋)
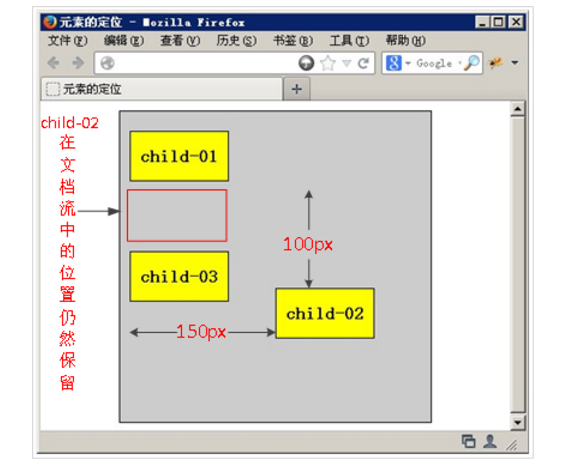
4.1 相对定位是将元素相对于它在标准流中的位置进行定位
4.2 对元素设置相对定位后,可以通过边偏移属性改变元素的位置,但是它在文档流中的位置仍然保留。https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011395218,https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26560303/does-setting-position-to-relative-on-a-div-takes-it-out-of-document-flow。
4.3 相对定位的盒子仍在标准流中,它后面的盒子仍以标准流方式对待它。(相对定位不脱标)
4.4 如果说浮动的主要目的是让多个块级元素一行显示,那么定位的主要价值就是移动位置,让盒子到我们想要的位置上去。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.top {
/* 注释这条看看*/
position: relative;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
}
.bottom {
background-color: purple;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</body>
</html>
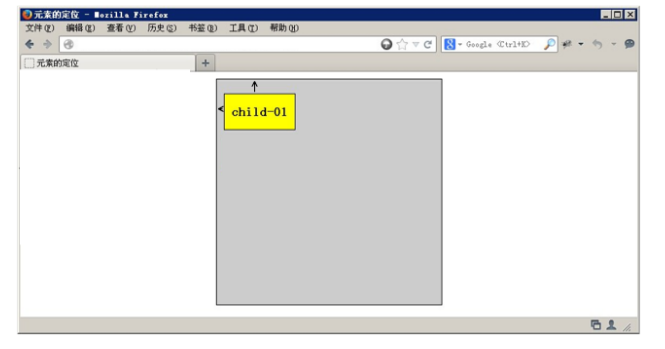
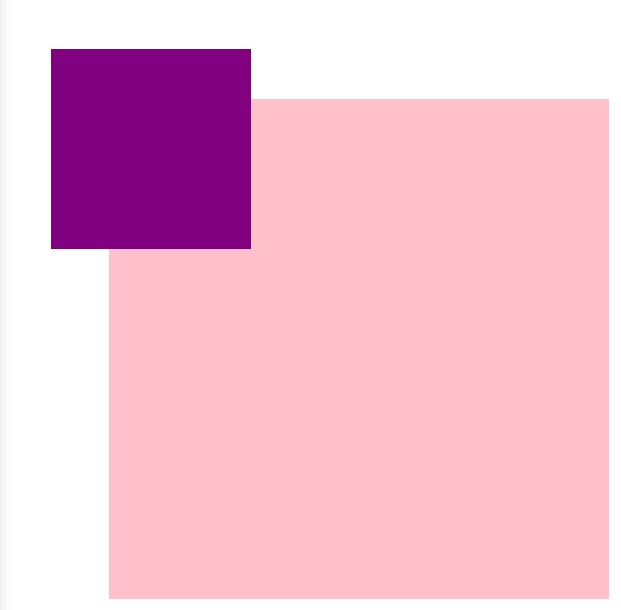
5. 绝对定位absolute(拼爹)
5.1 相对于其上一个已经定位的父元素进行定位
5.2 可以通过边偏移移动位置,但是它完全脱标,完全不占位置。
5.3 若所有父元素都没有定位,以浏览器当前屏幕为准对齐(document文档)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
height: 2000px;
}
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
/*position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;*/
}
.top {
/* 注释看看*/
position: absolute;
/* 脱标,不占位置 跟浮动一样*/
right: 20px;
bottom: 20px;
}
.bottom {
background-color: purple;
width: 110px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</body>
</html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 100px;
/* position: relative;*/
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
/* 注释看看*/
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
/*若所有父元素都没有定位,以浏览器当前屏幕为准对齐(document文档)。*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
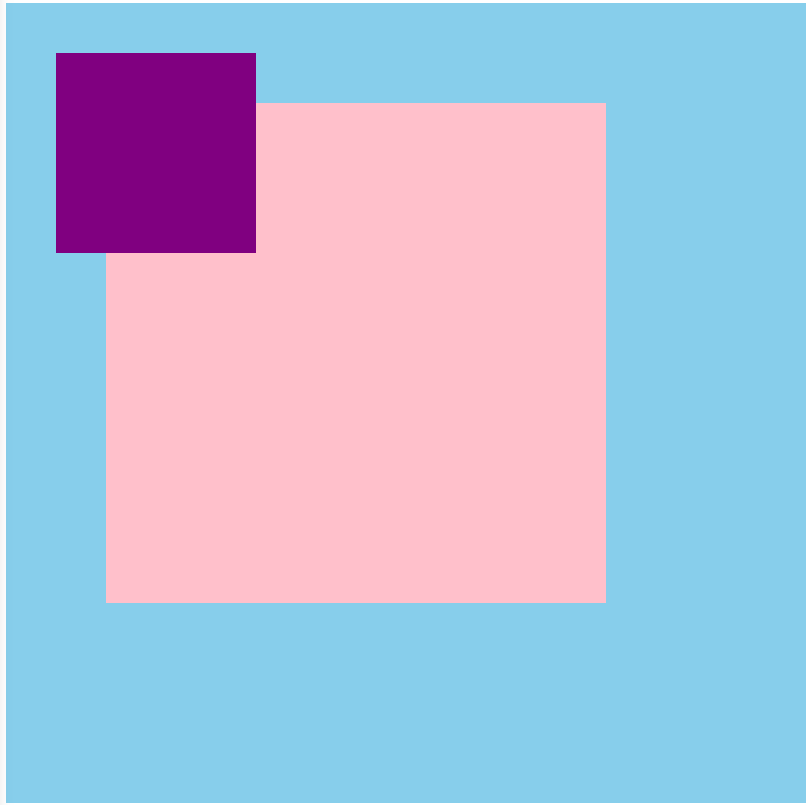
5.4 若父元素都有定位,绝对定位是将元素依据最近的已经定位(绝对、固定或相对定位)的父元素(祖先)进行定位。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.grandfather {
width: 800px;
height: 800px;
background-color: skyblue;
position: absolute;
}
.father {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 100px;
/* position: absolute;*/
}
.son {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
/*若所有父元素都没有定位,以浏览器当前屏幕为准对齐(document文档)。*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="grandfather">
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
6. 子绝父相,最合适的搭配(相对定位不脱标,绝对定位脱标)
6.1 子级是绝对定位的话, 父级要用相对定位。
6.2 看上面的5.4,子级是绝对定位,父亲只要是定位即可(不管父亲是绝对定位还是相对定位,甚至是固定定位都可以),就是说, 子绝父绝,子绝父相都是正确的。
6.3 因为子级是绝对定位,不会占有位置,可以放到父盒子里面的任何一个地方。父盒子布局时,需要占有位置,因此父亲只能是相对定位(不脱标)。这就是子绝父相的由来。
这两个箭头(左移动,右移动)是子绝。
可以实现,小黄色块可以在图片上移动
左右箭头压住图片
hot 在盒子外面多出一块
7. 绝对定位是完全脱标,浮动是半脱标
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.top {
/* float不是完全脱标,文字,图片还可以看*/
float: left;
/* position: absolute;*/
/*绝对定位是完全脱标,看不到文字,图片*/
}
.bottom {
background-color: purple;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="top">123123</div>
<div class="bottom">adsfadfasdfasdfasdf</div>
</body>
</html>
浮动,能看到文字
绝对定位,看不到文字
8. 绝对定位水平居中
8.1 普通的盒子是左右margin 改为 auto就可, 但是对于绝对定位就无效了
8.2 定位的盒子也可以水平或者垂直居中,算法如下
8.3 首先left 50% 父盒子的一半大小
8.4 外边距margin设置为自己盒子大小的负一半 margin-left
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
/* margin: 100px auto;*/
/* float: left;*/
position: absolute;
/*加了定位 浮动的的盒子 margin 0 auto 失效了*/
left: 50%;
margin-left: -100px;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
9. 固定定位fixed
9.1 固定定位的元素跟父亲没有任何关系,只认浏览器。
9.2 固定定位完全脱标,不占有位置,不随着滚动条滚动。
10. 叠放次序(z-index)
10.1 要想调整重叠定位元素的堆叠顺序,可以对定位元素应用z-index层叠等级属性,其取值可为正整数、负整数和0。例如 z-index: 3; font-weight: 700
10.2 z-index的默认属性值是0,取值越大,定位元素在层叠元素中越居上。
10.3 如果取值相同,则根据书写顺序,后来居上。
10.4 后面数字一定不能加单位。
10.5 只有相对定位,绝对定位,固定定位有此属性,其余标准流,浮动,静态定位都无此属性,亦不可指定此属性。
例子1.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
/* z-index: 0; 只有定位的盒子才有*/
}
.red {
z-index: 1;
}
.blue {
background-color: blue;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
z-index: 2;
}
.green {
background-color: green;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
z-index: 999;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="red"></div>
<div class="blue"></div>
<div class="green"></div>
</body>
</html>
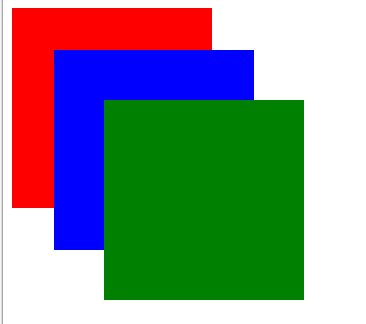
例子2. 因为先float(使多个元素显示在同一行),然后margin-left左移1,右边div的左边压着左边的div的右边,所以hover左边的div时显示不出左边div的右边。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 250px;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
float: left;
/* margin-left: -1px消除边框重叠*/
margin-left: -1px;
/* position: relative;*/
/*z-index: 0;*/
}
div:hover {
border: 1px solid #f40;
/*position: relative; 相对定位比标准流高一级 浮在上面的*/
/* z-index: 1;*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
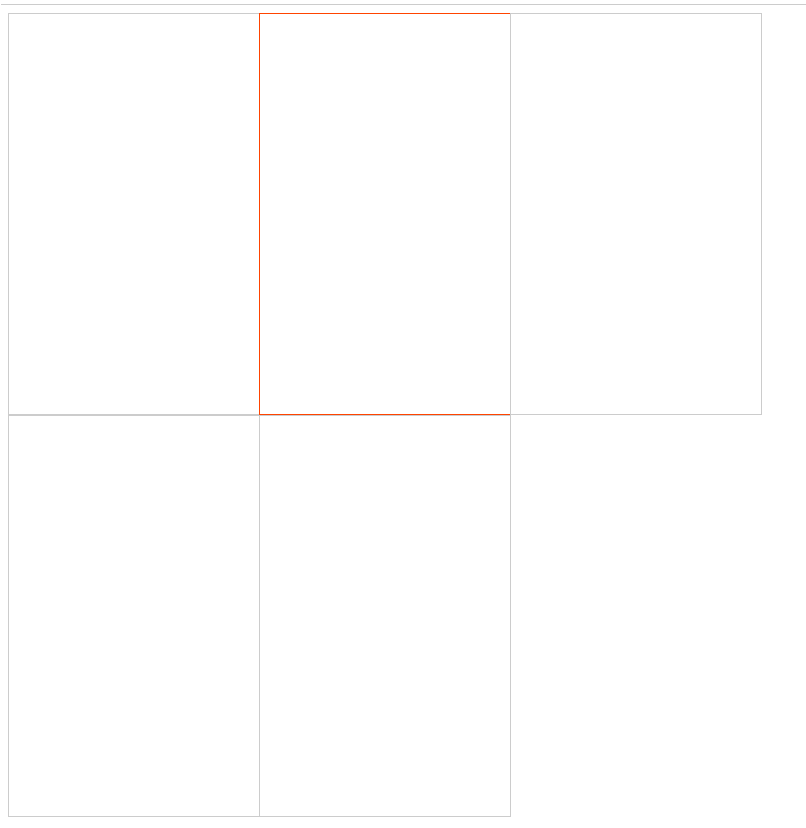
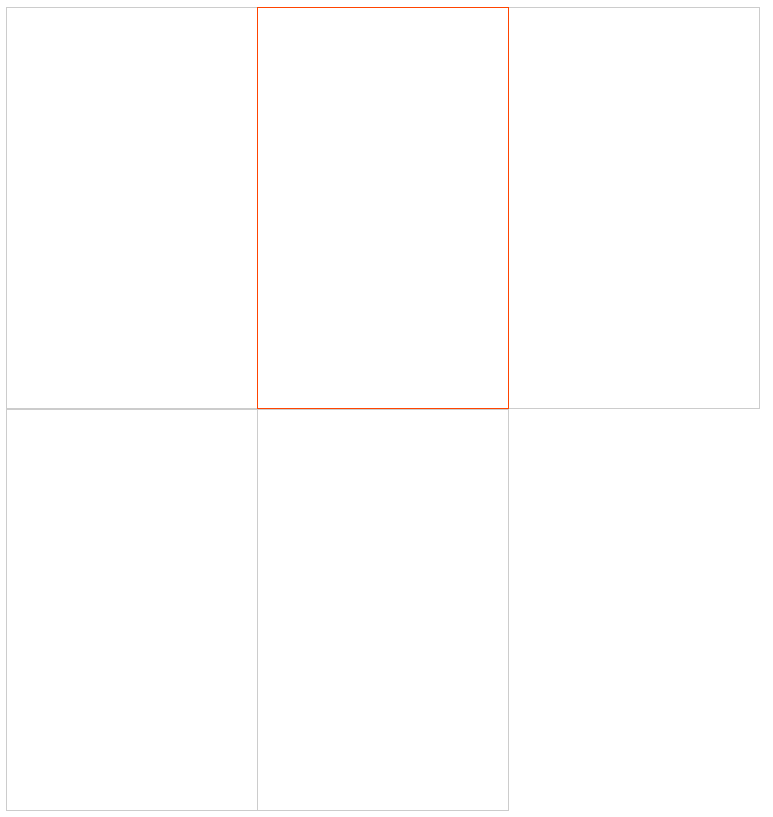
解决方法为设置z-index,使用z-index的前提先设置position
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
width: 250px;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
float: left;
/* margin-left: -1px消除边框重叠*/
margin-left: -1px;
/* position: relative;*/
/*z-index: 0;*/
}
div:hover {
border: 1px solid #f40;
position: relative; 相对定位比标准流高一级 浮在上面的
z-index: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
11. 定位模式转换
跟浮动一样,元素添加了绝对定位和固定定位之后, 元素模式也会发生转换,都转换为行内块(inline-block)模式
因此,行内元素如果添加了绝对定位或者固定定位后(或者浮动后),可以不用转换模式,直接设置width和height
12. 四种定位总结
| 定位模式 | 是否脱标占有位置 | 是否可以使用边偏移 | 移动位置基准 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 静态static | 不脱标,正常模式 | 不可以 | 正常模式 |
| 相对定位relative | 不脱标,占有位置 | 可以 | 相对自身位置移动(自恋型) |
| 绝对定位absolute | 完全脱标,不占有位置 | 可以 | 相对于定位父级移动位置(拼爹型) |
| 固定定位fixed | 完全脱标,不占有位置 | 可以 | 相对于浏览器移动位置(认死型) |
CSS - 定位(position),难点的更多相关文章
- div+css定位position详解
div+css定位position详解 1.div+css中的定位position 最主要的两个属性:属性 absolute(绝对定位) relative(相对定位),有他们才造就了div+css布局 ...
- 《css定位 position》课程笔记
这是我学习课程css定位 position时做的笔记! 本节内容 html的三种布局方式 position可选参数 z-index 盒子模型和定位的区别 侧边栏导航跟随实例 html的三种布局方式 三 ...
- web前端css定位position和浮动float
最近做了几个项目:配资公司,ecmal商城等,客户对前台要求都很高.所以,今天来谈谈css的基础,以及核心,定位问题. div.h1或p元素常常被称为块级元素.这意味着这些元素显示为一块内容,即“块框 ...
- css定位position认识
1.绝对定位(position: absolute) 2.相对定位(position: relative) 3.固定定位(position: fixed) 绝对定位 设置position:absolu ...
- CSS定位position
position选项来定义元素的定位属性,选项有5个可选值:static.relative.absolute.fixed.inherit 属性值为relative.absolute.fixed时top ...
- css 定位position总结
在CSS中,Position 属性经常会用到,主要是绝对定位和相对定位,简单的使用都没有问题,尤其嵌套起来,就会有些混乱,今记录总结一下,防止久而忘之. CSS position 属性值: absol ...
- css定位position属性深究
1.static:对象遵循常规流.此时4个定位偏移属性不会被应用. 2.relative:对象遵循常规流,并且参照自身在常规流中的位置通过top,right,bottom,left这4个定位偏移属性进 ...
- 【前段开发】10步掌握CSS定位: position static relative absolute float
希望能帮到须要的人,转自:http://www.see-design.com.tw/i/css_position.html 1. position:static 元素的 position 屬性默認值為 ...
- css定位-position
前言 定位的目的就是把元素摆放到指定的位置. 定位上下文:定位元素的大小,位置都是相对于定位上下文的. position属性值有5个值 static:所有有元素定位默认的初始值都是static.就是不 ...
随机推荐
- ACM-ICPC实验室20.2.19测试-图论
B.Harborfan的新年拜访Ⅱ 就是一道tarjan缩点的裸题. 建图比较麻烦 以后遇到这种建图,先用循环把样例实现出来,再对着循环写建图公式 #include<bits/stdc++.h& ...
- Go之第三方日志库logrus使用
文章引用自 第三方日志库logrus使用 日志是程序中必不可少的一个环节,由于Go语言内置的日志库功能比较简洁,我们在实际开发中通常会选择使用第三方的日志库来进行开发.本文介绍了logrus这个日志库 ...
- SpringBoot Profiles特性
今天我们了解SpringBoot Profiles特性 一.外部化配置 配置分为编译时和运行时,而Spring采用后者,在工作中有时也会两者一起使用. 何为"外部化配置"官方没 ...
- Java7任务并行执行神器:Fork&Join框架
原 Java7任务并行执行神器:Fork&Join框架 2018年01月12日 17:25:03 Java技术栈 阅读数:426 标签: JAVAFORKJOIN 更多 个人分类: Java ...
- Sqlmap 工具用法详解
Sqlmap 工具用法详解 sqlmap是一款自动化的sql注入工具. 1.主要功能:扫描.发现.利用给定的url的sql注入漏 ...
- C语言函数不能返回数组,但可以返回结构体
为什么C语言函数可以返回结构体,却不可以返回数组?有这样的问题并不奇怪,因为C语言数组和结构体本质上都是管理一块内存,那为何编译器要区别对待二者呢? C语言函数为什么不能返回数组? 在C语言程序开发中 ...
- 搭建一个ssm框架的maven项目需要配置的文件
单独功能需要的配置文件: 1,mybatis配置文件 mybatis-config.xml2,spring配置文件 spring-context.xml ......3,we ...
- ➡️➡️➡️IELTS Listening
目录 src numbers and letters src https://ielts-simon.com/ielts-help-and-english-pr/ielts-listening/ nu ...
- Laravel 6.X + Vue.js 2.X + Element UI 开发知乎流程
本流程参照:CODECASTS的Laravel Vuejs 实战:开发知乎 视频教程 1项目环境配置和用户表设计 2Laravel 开发知乎:用户注册 3Laravel 开发知乎:用户登录 4Lara ...
- LPWAN
典型LPWA技术: 1 Sigfox技术由同名的法国Sigfox公司设计研发,成立于2010年,因为Sigfox网络由Sigfox公司为主导进行全球部署,这样能最大程度保证网络服务质量的统一性和稳定性 ...