Web监听器导图详解
监听器是JAVA Web开发中很重要的内容,其中涉及到的知识,可以参考下面导图:
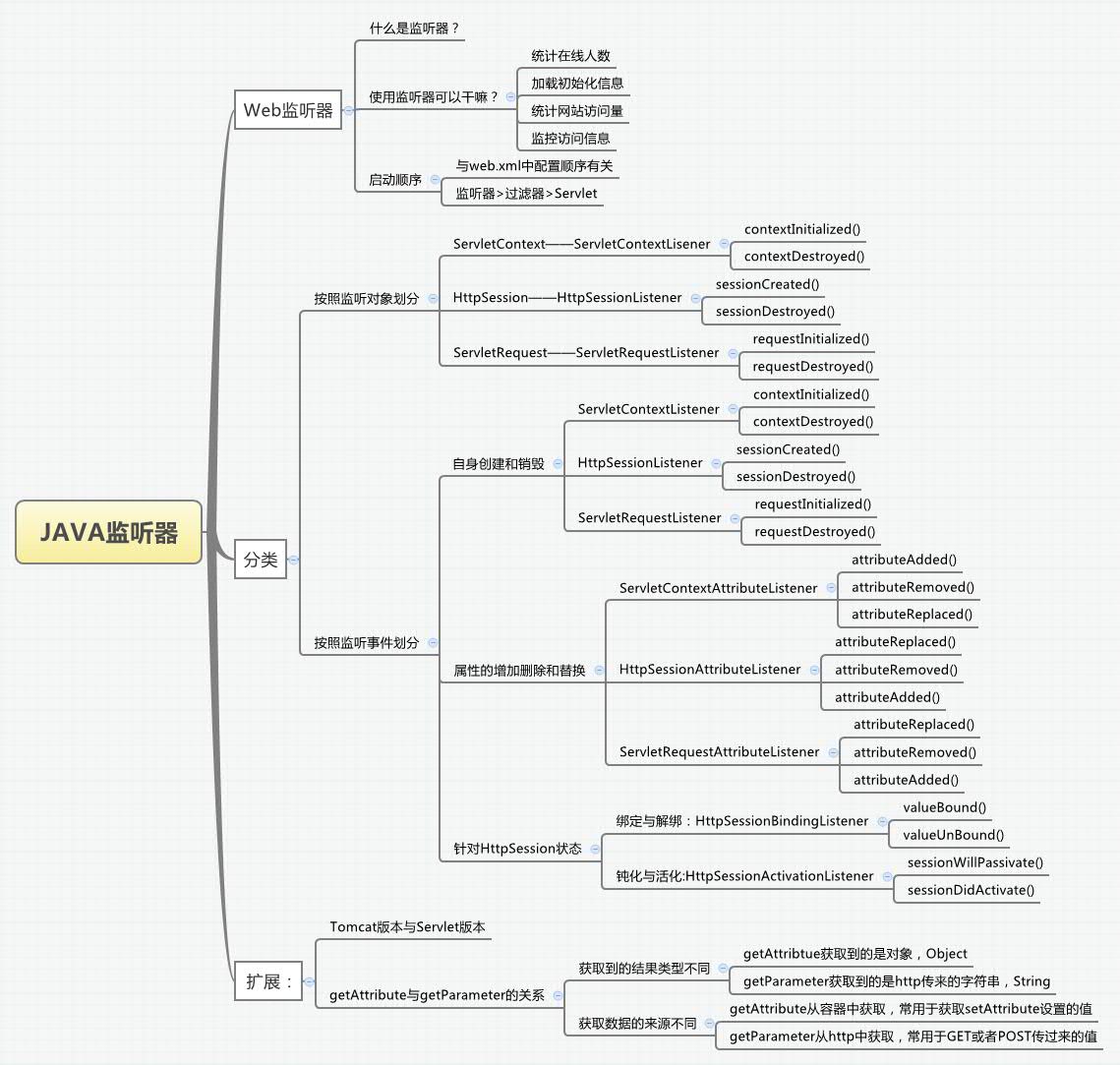
Web监听器
1 什么是web监听器?
web监听器是一种Servlet中的特殊的类,它们能帮助开发者监听web中的特定事件,比如ServletContext,HttpSession,ServletRequest的创建和销毁;变量的创建、销毁和修改等。可以在某些动作前后增加处理,实现监控。
2 监听器常用的用途
通常使用Web监听器做以下的内容:
统计在线人数,利用HttpSessionLisener
加载初始化信息:利用ServletContextListener
统计网站访问量
实现访问监控
3 接下里看看一个监听器的创建以及执行过程
首先需要创建一个监听器,实现某种接口,例如我想实现一个对在线人数的监控,可以创建如下的监听器:
public class MyListener implements HttpSessionListener{
private int userNumber = 0;
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent arg0) {
userNumber++;
arg0.getSession().setAttribute("userNumber", userNumber);
}
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent arg0) {
userNumber--;
arg0.getSession().setAttribute("userNumber", userNumber);
}
}
然后在web.xml中配置该监听器,在web-app中添加:
<listener>
<listener-class>com.test.MyListener</listener-class>
</listener>
在JSP中添加访问人数:
<body>
在线人数:<%=session.getAttribute("userNumber") %><br/>
</body>
当我使用我的浏览器访问时,执行结果如下:
当打开另一个浏览器访问时:
由于打开另一个浏览器访问,相当于另一个会话,因此在线人数会增加。
对于3.0版本的Servlet来说,还支持使用注解的方式进行配置。
那么接下来看看都有哪些监听器以及方法吧!
监听器的分类
1 按照监听的对象划分:
按照监听对象的不同可以划分为三种:
ServletContext监控:对应监控application内置对象的创建和销毁。
当web容器开启时,执行contextInitialized方法;当容器关闭或重启时,执行contextDestroyed方法。
实现方式:直接实现ServletContextListener接口:
public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener{
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
}
HttpSession监控:对应监控session内置对象的创建和销毁。
当打开一个新的页面时,开启一个session会话,执行sessionCreated方法;当页面关闭session过期时,或者容器关闭销毁时,执行sessionDestroyed方法。
实现方式:直接实现HttpSessionListener接口:
public class MyHttpSessionListener implements HttpSessionListener{
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent arg0) {
}
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent arg0) {
}
}
ServletRequest监控:对应监控request内置对象的创建和销毁。
当访问某个页面时,出发一个request请求,执行requestInitialized方法;当页面关闭时,执行requestDestroyed方法。
实现方式,直接实现ServletRequestListener接口:
public class MyServletRequestListener implements ServletRequestListener{
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent arg0) {
}
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent arg0) {
}
}
2 按照监听事件划分:
2.1 监听事件自身的创建和销毁:同上面的按对象划分。
2.2 监听属性的新增、删除和修改:
监听属性的新增、删除和修改也是划分成三种,分别针对于ServletContext、HttpSession、ServletRequest对象:
ServletContext,实现ServletContextAttributeListener接口:
通过调用ServletContextAttribtueEvent的getName方法可以得到属性的名称。
public class MyServletContextAttrListener implements ServletContextAttributeListener{
public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In servletContext added :name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In servletContext removed :name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In servletContext replaced :name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
}
HttpSession,实现HttpSessionAttributeListener接口:
public class MyHttpSessionAttrListener implements HttpSessionAttributeListener{
public void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In httpsession added:name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
public void attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In httpsession removed:name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
public void attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In httpsession replaced:name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
}
ServletRequest,实现ServletRequestAttributeListener接口:
public class MyServletRequestAttrListener implements ServletRequestAttributeListener{
public void attributeAdded(ServletRequestAttributeEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In servletrequest added :name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
public void attributeRemoved(ServletRequestAttributeEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In servletrequest removed :name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
public void attributeReplaced(ServletRequestAttributeEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("In servletrequest replaced :name = "+hsbe.getName());
}
}
2.3 监听对象的状态:
针对某些POJO类,可以通过实现HttpSessionBindingListener接口,监听POJO类对象的事件。例如:
public class User implements HttpSessionBindingListener,Serializable{
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("valueBound name: "+hsbe.getName());
}
public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("valueUnbound name: "+hsbe.getName());
}
}
Session数据的钝化与活化:
由于session中保存大量访问网站相关的重要信息,因此过多的session数据就会服务器性能的下降,占用过多的内存。因此类似数据库对象的持久化,web容器也会把不常使用的session数据持久化到本地文件或者数据中。这些都是有web容器自己完成,不需要用户设定。
不用的session数据序列化到本地文件中的过程,就是钝化;
当再次访问需要到该session的内容时,就会读取本地文件,再次放入内存中,这个过程就是活化。
类似的,只要实现HttpSeesionActivationListener接口就是实现钝化与活化事件的监听:
public class User implements HttpSessionBindingListener,
HttpSessionActivationListener,Serializable{ private String username;
private String password; public String getUsername() {
return username;
} public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
} public String getPassword() {
return password;
} public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
} public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("valueBound name: "+hsbe.getName());
} public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("valueUnbound name: "+hsbe.getName());
} public void sessionDidActivate(HttpSessionEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("sessionDidActivate name: "+hsbe.getSource());
} public void sessionWillPassivate(HttpSessionEvent hsbe) {
System.out.println("sessionWillPassivate name: "+hsbe.getSource());
} }
Servlet版本与Tomcat版本
首先看一下Tomcat官网给出的匹配:
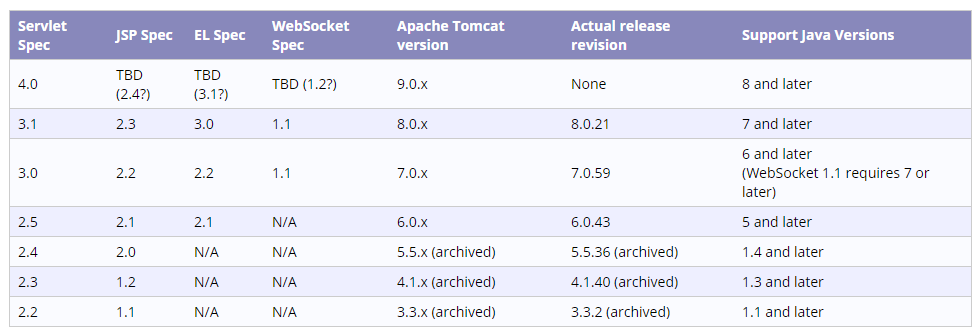
如果版本不匹配,那么tomcat是不能发布该工程的,首先看一下版本不匹配时,会发生什么!
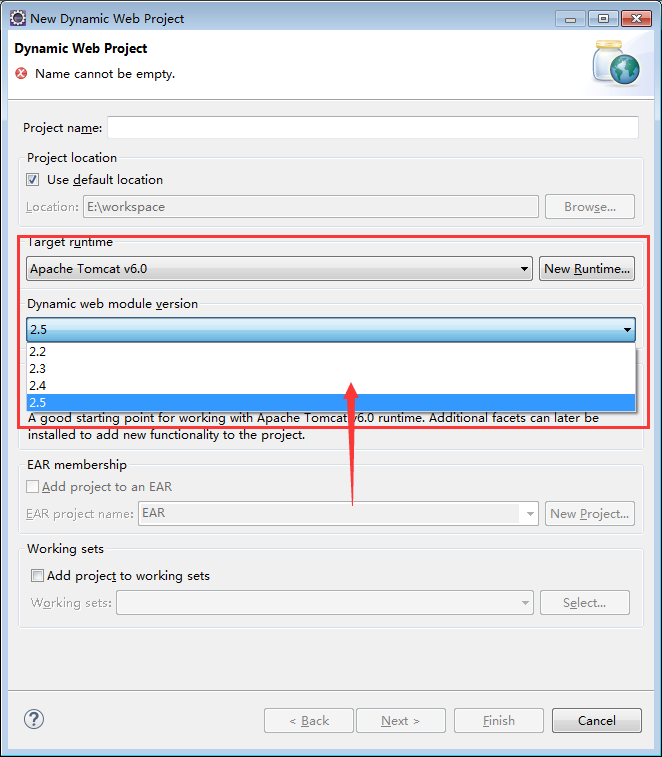
我试图创建一个web工程,并且选取了Servlet3.0版本:

然后我想要在tomcat6中发布,可以看到报错了!
JDK版本不对....这是在平时开发如果对Servlet不熟悉的web新手,常犯的错误。
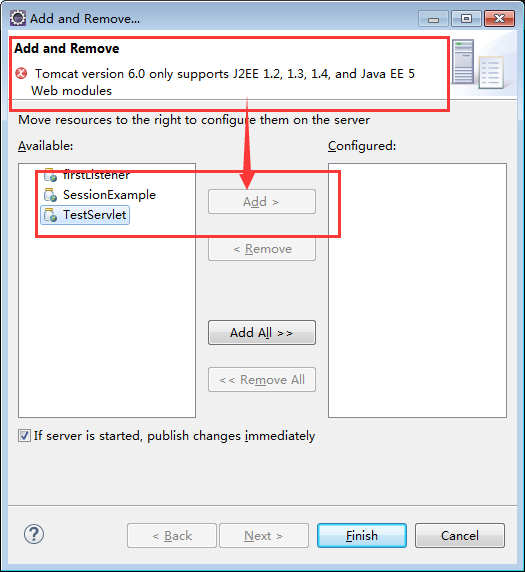
解决方法:
1 在创建时,直接发布到Tomcat容器中,此时Servlet仅仅会列出Tomcat支持的版本:
2 修改工程Servlet版本配置信息,文件为:工作目录\SessionExample\.settings\org.eclipse.wst.common.project.facet.core.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<faceted-project>
<runtime name="Apache Tomcat v6.0"/>
<fixed facet="java"/>
<fixed facet="wst.jsdt.web"/>
<fixed facet="jst.web"/>
<installed facet="java" version="1.7"/>
<installed facet="jst.web" version="2.5"/>
<installed facet="wst.jsdt.web" version="1.0"/>
</faceted-project>
getAttribute与getParameter的区别
这部分是对JSP的扩展,经常在JSP或者Servlet中获取数据,那么getAttribute与getParameter有什么区别呢?
1 从获取到数据的来源来说:
getAttribtue获取到的是web容器中的值,比如:
我们在Servlet中通过setAttribute设定某个值,这个值存在于容器中,就可以通过getAttribute方法获取;
getParameter获取到的是通过http传来的值,比如这样一个http请求:
http:localhost:8080/test/test.html?username=xingoo
还有其他的GET和POST方式,都可以通过getParameter来获取。
2 从获取到的数据类型来说:
getAttribute返回的是一个对象,Object。
getParameter返回的是,前面页面中某个表单或者http后面参数传递的值,是个字符串。
参考
【1】慕课网,监听器:http://www.imooc.com/learn/271
【2】jsp中getAttribute与getParameter的区别:http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=4URJWerrusLTFRviR1sAlTH4BKc7QswiRYsso3xaYs_nZMiTMV-TwCnIIgu31K1N9HbrUhfgO2-jXjpYe1hGZn9RBo3b8HHzY2Dn2-Fcbs7
Web监听器导图详解的更多相关文章
- Web监听器导图详解(转)
阅读目录 Web监听器 监听器的分类 Servlet版本与Tomcat版本 getAttribute与getParameter的区别 参考 监听器是JAVA Web开发中很重要的内容,其中涉及到的知识 ...
- java Web监听器导图详解
监听器是JAVA Web开发中很重要的内容,其中涉及到的知识,可以参考下面导图: Web监听器 1 什么是web监听器? web监听器是一种Servlet中的特殊的类,它们能帮助开发者监听web中的特 ...
- Vue基础开发入门之简单语法知识梳理(思维导图详解)
基于个人写的以下关于Vue框架基础学习的三篇随笔,在此基础上,做一个阶段性的知识总结,以此来检验自己对Vue这一段时间学习的成果,内容不多,但很值得一看.(思维导图详解)
- (转)CAS (4) —— CAS浏览器SSO访问顺序图详解(CAS Web Flow Diagram by Example)
CAS (4) —— CAS浏览器SSO访问顺序图详解(CAS Web Flow Diagram by Example) tomcat版本: tomcat-8.0.29 jdk版本: jdk1.8.0 ...
- CAS (4) —— CAS浏览器SSO访问顺序图详解(CAS Web Flow Diagram by Example)
CAS (4) -- CAS浏览器SSO访问顺序图详解(CAS Web Flow Diagram by Example) tomcat版本: tomcat-8.0.29 jdk版本: jdk1.8.0 ...
- CAS (6) —— Nginx代理模式下浏览器访问CAS服务器网络顺序图详解
CAS (6) -- Nginx代理模式下浏览器访问CAS服务器网络顺序图详解 tomcat版本: tomcat-8.0.29 jdk版本: jdk1.8.0_65 nginx版本: nginx-1. ...
- web.xml常用配置详解
web.xml常用配置详解 context-param 指定 ServletContext(上下文) 配置文件路径,基本配置一般是Spring配置文件,或者是spring-security的配置文件. ...
- SPI总线协议及SPI时序图详解
SPI,是英语Serial Peripheral Interface的缩写,顾名思义就是串行外围设备接口.SPI,是一种高速的,全双工,同步的通信总线,并且在芯片的管脚上只占用四根线,节约了芯片的管脚 ...
- SPI总线协议及SPI时序图详解【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/adylee/p/5399742.html SPI,是英语Serial Peripheral Interface的缩写,顾名思义就是串行外围设备接 ...
随机推荐
- Java Nio Socket通讯
Server端: #############服务器端连接请求处理############### public class MultiplexerServer implements Runnable { ...
- 实时视频直播客户端技术盘点:Native、HTML5、WebRTC、微信小程序
1.前言 2017 年 12 月,微信小程序向开发者开放了实时音视频能力,给业内带来广阔的想象空间.连麦互动视频直播技术在 2016 年直播风口中成为视频直播的标配,然而只有在原生的 APP 上才能保 ...
- mysql 严格模式取消 group by 和 date zore
取消单个库的时间严格模式 set global sql_mode=(select replace(@@sql_mode,'NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE',''));
- ES6 对象转Map
使用Object.entries const obj = { foo: 'bar', baz: 42 }; const map = new Map(Object.entries(obj)); map ...
- cookie、localStorage和sessionStorage区别
三者区别见下表: 说明: cookie的处理过程为: 服务器向客户端发送cookie 浏览器将cookie保存 之后每次http请求浏览器都会将cookie发送给服务器端 对于 cookie,我们还需 ...
- 单元测试JUnit 4(二)——keeps the bar green to keeps the code clean
1.Failure和Error Failure是指测试失败 Error是指测试程序本身出错 (int a=10/0) 2.JUnit常用注解 2.1 @RunWith: 可以更改测试运行器(继承o ...
- c++对象模型介绍
http://www.cnblogs.com/skynet/p/3343726.html
- 修改配置nginx,限制无良爬虫频率
配置如下: #全局配置 limit_req_zone $anti_spider zone=anti_spider:10m rate=15r/m; #某个server中 limit_req zone=a ...
- VSCode开发工具下载
VSCode集成多语言和插件,方便开发和代码管理. 请到此处下载:https://code.visualstudio.com/Download
- pandas DataFrame 数据处理常用操作
Xgboost调参: https://wuhuhu800.github.io/2018/02/28/XGboost_param_share/ https://blog.csdn.net/hx2017/ ...
