[python] RRT快速拓展随机树
"""
version1.1,2018-05-09
《基于智能优化与RRT算法的无人机任务规划方法研究》博士论文
《基于改进人工势场法的路径规划算法研究》硕士论文 """ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import math
import copy show_animation = True class Node(object):
"""
RRT Node
""" def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.parent = None class RRT(object):
"""
Class for RRT Planning
""" def __init__(self, start, goal, obstacle_list, rand_area):
"""
Setting Parameter start:Start Position [x,y]
goal:Goal Position [x,y]
obstacleList:obstacle Positions [[x,y,size],...]
randArea:random sampling Area [min,max] """
self.start = Node(start[0], start[1])
self.end = Node(goal[0], goal[1])
self.min_rand = rand_area[0]
self.max_rand = rand_area[1]
self.expandDis = 1.0
self.goalSampleRate = 0.05 # 选择终点的概率是0.05
self.maxIter = 500
self.obstacleList = obstacle_list
self.nodeList = [self.start] def random_node(self):
"""
产生随机节点
:return:
"""
node_x = random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand)
node_y = random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand)
node = [node_x, node_y] return node @staticmethod
def get_nearest_list_index(node_list, rnd):
"""
:param node_list:
:param rnd:
:return:
"""
d_list = [(node.x - rnd[0]) ** 2 + (node.y - rnd[1]) ** 2 for node in node_list]
min_index = d_list.index(min(d_list))
return min_index @staticmethod
def collision_check(new_node, obstacle_list):
a = 1
for (ox, oy, size) in obstacle_list:
dx = ox - new_node.x
dy = oy - new_node.y
d = math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)
if d <= size:
a = 0 # collision return a # safe def planning(self):
"""
Path planning animation: flag for animation on or off
""" while True:
# Random Sampling
if random.random() > self.goalSampleRate:
rnd = self.random_node()
else:
rnd = [self.end.x, self.end.y] # Find nearest node
min_index = self.get_nearest_list_index(self.nodeList, rnd)
# print(min_index) # expand tree
nearest_node = self.nodeList[min_index] # 返回弧度制
theta = math.atan2(rnd[1] - nearest_node.y, rnd[0] - nearest_node.x) new_node = copy.deepcopy(nearest_node)
new_node.x += self.expandDis * math.cos(theta)
new_node.y += self.expandDis * math.sin(theta)
new_node.parent = min_index if not self.collision_check(new_node, self.obstacleList):
continue self.nodeList.append(new_node) # check goal
dx = new_node.x - self.end.x
dy = new_node.y - self.end.y
d = math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)
if d <= self.expandDis:
print("Goal!!")
break if True:
self.draw_graph(rnd) path = [[self.end.x, self.end.y]]
last_index = len(self.nodeList) - 1
while self.nodeList[last_index].parent is not None:
node = self.nodeList[last_index]
path.append([node.x, node.y])
last_index = node.parent
path.append([self.start.x, self.start.y]) return path def draw_graph(self, rnd=None):
"""
Draw Graph
"""
print('aaa')
plt.clf() # 清除上次画的图
if rnd is not None:
plt.plot(rnd[0], rnd[1], "^g")
for node in self.nodeList:
if node.parent is not None:
plt.plot([node.x, self.nodeList[node.parent].x], [
node.y, self.nodeList[node.parent].y], "-g") for (ox, oy, size) in self.obstacleList:
plt.plot(ox, oy, "sk", ms=10*size) plt.plot(self.start.x, self.start.y, "^r")
plt.plot(self.end.x, self.end.y, "^b")
plt.axis([self.min_rand, self.max_rand, self.min_rand, self.max_rand])
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.01) def draw_static(self, path):
"""
画出静态图像
:return:
"""
plt.clf() # 清除上次画的图 for node in self.nodeList:
if node.parent is not None:
plt.plot([node.x, self.nodeList[node.parent].x], [
node.y, self.nodeList[node.parent].y], "-g") for (ox, oy, size) in self.obstacleList:
plt.plot(ox, oy, "sk", ms=10*size) plt.plot(self.start.x, self.start.y, "^r")
plt.plot(self.end.x, self.end.y, "^b")
plt.axis([self.min_rand, self.max_rand, self.min_rand, self.max_rand]) plt.plot([data[0] for data in path], [data[1] for data in path], '-r')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show() def main():
print("start RRT path planning") obstacle_list = [
(5, 1, 1),
(3, 6, 2),
(3, 8, 2),
(1, 1, 2),
(3, 5, 2),
(9, 5, 2)] # Set Initial parameters
rrt = RRT(start=[0, 0], goal=[8, 9], rand_area=[-2, 10], obstacle_list=obstacle_list)
path = rrt.planning()
print(path) # Draw final path
if show_animation:
plt.close()
rrt.draw_static(path) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
RRT快速拓展随机树 python实现
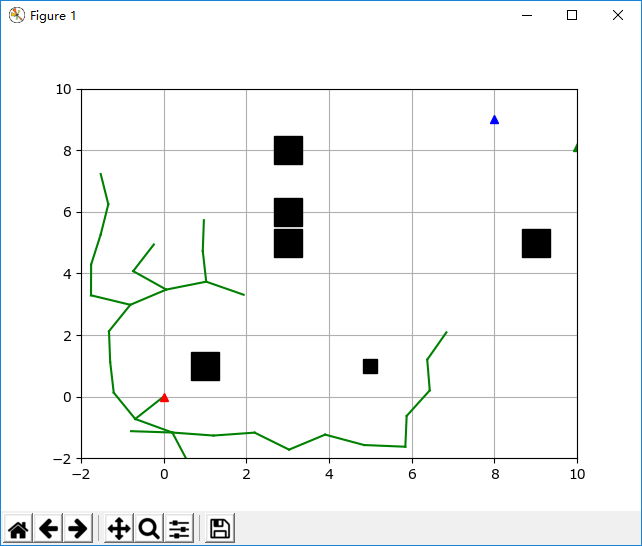
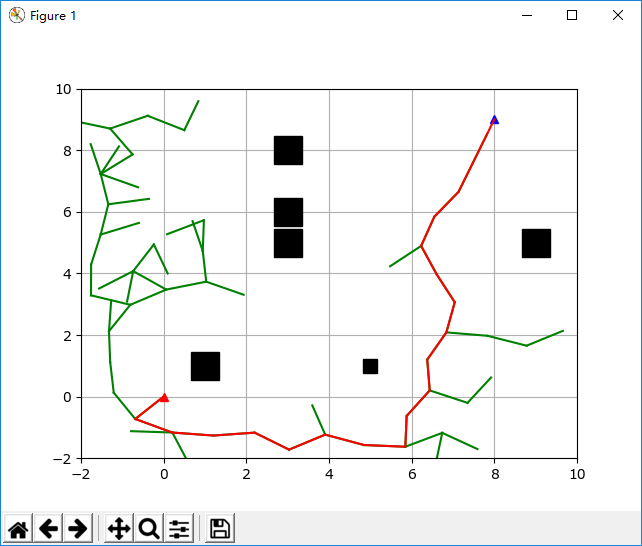
[python] RRT快速拓展随机树的更多相关文章
- matlab练习程序(快速搜索随机树RRT)
RRT快速搜索随机树英文全称Rapid-exploration Random Tree,和PRM类似,也是一种路径规划算法. 和PRM类似,算法也需要随机撒点,不过不同的是,该算法不是全局随机撒点,而 ...
- [matlab] 7.快速搜索随机树(RRT---Rapidly-exploring Random Trees) 路径规划
RRT是一种多维空间中有效率的规划方法.它以一个初始点作为根节点,通过随机采样增加叶子节点的方式,生成一个随机扩展树,当随机树中的叶子节点包含了目标点或进入了目标区域,便可以在随机树中找到一条由从初始 ...
- LSH︱python实现局部敏感随机投影森林——LSHForest/sklearn(一)
关于局部敏感哈希算法.之前用R语言实现过,可是由于在R中效能太低.于是放弃用LSH来做类似性检索.学了python发现非常多模块都能实现,并且通过随机投影森林让查询数据更快.觉得能够试试大规模应用在数 ...
- (数据科学学习手札114)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——上传下载篇
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- P3830 [SHOI2012]随机树 题解
P3830 随机树 坑题,别人的题解我看了一个下午没一个看得懂的,我还是太弱了. 题目链接 P3830 [SHOI2012]随机树 题目描述 输入输出格式 输入格式: 输入仅有一行,包含两个正整数 q ...
- (数据科学学习手札102)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——基础概念篇
本文示例代码与数据已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的新系列教程Python+Dash快 ...
- (数据科学学习手札103)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——页面布局篇
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札104)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——回调交互篇(上)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札109)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——静态部件篇(中)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
随机推荐
- LINUX sed grep awk之间比较整理
正则表达式基础 在最简单的情况下,一个正则表达式看上去就是一个普通的查找串.例如,正则表达式"testing"中没有包含任何元字符,,它可以匹配"testing" ...
- Retrofit2 原理解析
Retrofit是什么 官网介绍是A type-safe HTTP client for Android and Java,是一个 RESTful 的 HTTP 网络请求框架的封装,但网络请求不是Re ...
- 清除float影响
条件: 父元素中有子元素float的话,可能就会影响父元素的高度,从而影响布局: 解决方案: 1.直接给父元素定高: 弊端:必须知道父元素的高: 2. 父元素使用overflow属性值为hidden解 ...
- Fundebug能够捕获这些BUG
摘要:Fundebug的JavaScript监控插件更新至0.1.0,可以监控3种不同类型的前端BUG:JavaScript执行错误.资源加载错误.HTTP请求错误. 从简单的onerror开始,Fu ...
- hash 和pushState,replaceState
hash 要点: 1.不会向后台发请求:#是用来指导浏览器动作的,对服务器端完全无用. 2.用来跳转到页面的指定位置: 为网页位置指定标识符,有两个方法.一是使用锚点,比如<a name=& ...
- C#DataTable复制、C#DataTable列复制、C#DataTable字段复制
try { //获取满足条件的数据 DataTable Mdr = datable.Select().ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " ...
- 【20190220】JavaScript-知识点整理:对象创建方式、原型、闭包
一.对象创建方式 1. 工厂模式 这种模式抽象了创建具体对象的过程,用函数来封装以特定接口创建对象的细节.存在的问题是无法通过 instanceof 识别一个对象的类型. function creat ...
- Android为TV端助力 apk静默安装
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/47803149 之前有很多朋友都问过我,在Android系统中怎样才能实现静默安装呢 ...
- 初学ubuntu命令
将我第一天学的内容做个笔记 ,方便日后查看 命令的使用: ls ls -a 显示所有文件 ls -l 显示文件的所有信息 cp 注意命令格式 /home/../temp/a /ho ...
- C#委托(转载)
C#委托的介绍(delegate.Action.Func.predicate) from:http://www.cnblogs.com/akwwl/p/3232679.html 委托是一个类,它定义了 ...
