spark 笔记 15: ShuffleManager,shuffle map两端的stage/task的桥梁
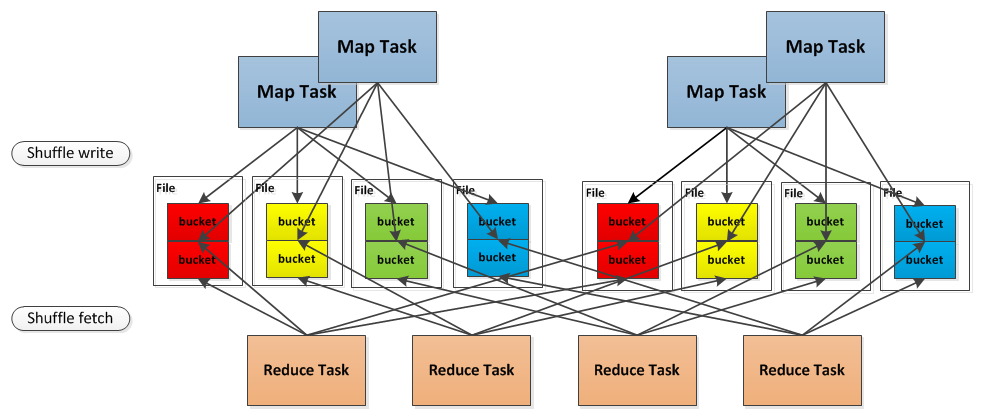
无论是Hadoop还是spark,shuffle操作都是决定其性能的重要因素。在不能减少shuffle的情况下,使用一个好的shuffle管理器也是优化性能的重要手段。
* A ShuffleManager using hashing, that creates one output file per reduce partition on each
* mapper (possibly reusing these across waves of tasks).
/**
* Pluggable interface for shuffle systems. A ShuffleManager is created in SparkEnv on both the
* driver and executors, based on the spark.shuffle.manager setting. The driver registers shuffles
* with it, and executors (or tasks running locally in the driver) can ask to read and write data.
*
* NOTE: this will be instantiated by SparkEnv so its constructor can take a SparkConf and
* boolean isDriver as parameters.
*/
private[spark] trait ShuffleManager {
/**
* Register a shuffle with the manager and obtain a handle for it to pass to tasks.
*/
def registerShuffle[K, V, C](
shuffleId: Int,
numMaps: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]): ShuffleHandle
/** Get a writer for a given partition. Called on executors by map tasks. */
def getWriter[K, V](handle: ShuffleHandle, mapId: Int, context: TaskContext): ShuffleWriter[K, V]
/**
* Get a reader for a range of reduce partitions (startPartition to endPartition-1, inclusive).
* Called on executors by reduce tasks.
*/
def getReader[K, C](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
startPartition: Int,
endPartition: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleReader[K, C]
/** Remove a shuffle's metadata from the ShuffleManager. */
def unregisterShuffle(shuffleId: Int)
/** Shut down this ShuffleManager. */
def stop(): Unit
}
/**
* :: DeveloperApi ::
* Represents a dependency on the output of a shuffle stage. Note that in the case of shuffle,
* the RDD is transient since we don't need it on the executor side.
*
* @param _rdd the parent RDD
* @param partitioner partitioner used to partition the shuffle output
* @param serializer [[org.apache.spark.serializer.Serializer Serializer]] to use. If set to None,
* the default serializer, as specified by `spark.serializer` config option, will
* be used.
*/
@DeveloperApi
class ShuffleDependency[K, V, C](
@transient _rdd: RDD[_ <: Product2[K, V]],
val partitioner: Partitioner,
val serializer: Option[Serializer] = None,
val keyOrdering: Option[Ordering[K]] = None,
val aggregator: Option[Aggregator[K, V, C]] = None,
val mapSideCombine: Boolean = false)
extends Dependency[Product2[K, V]] {
override def rdd = _rdd.asInstanceOf[RDD[Product2[K, V]]]
val shuffleId: Int = _rdd.context.newShuffleId()
val shuffleHandle: ShuffleHandle = _rdd.context.env.shuffleManager.registerShuffle(
shuffleId, _rdd.partitions.size, this)
_rdd.sparkContext.cleaner.foreach(_.registerShuffleForCleanup(this))
}
/**
* A basic ShuffleHandle implementation that just captures registerShuffle's parameters.
*/
private[spark] class BaseShuffleHandle[K, V, C](
shuffleId: Int,
val numMaps: Int,
val dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C])
extends ShuffleHandle(shuffleId)
/**
* Class that keeps track of the location of the map output of
* a stage. This is abstract because different versions of MapOutputTracker
* (driver and worker) use different HashMap to store its metadata.
*/
private[spark] abstract class MapOutputTracker(conf: SparkConf) extends Logging {
/**
* Result returned by a ShuffleMapTask to a scheduler. Includes the block manager address that the
* task ran on as well as the sizes of outputs for each reducer, for passing on to the reduce tasks.
* The map output sizes are compressed using MapOutputTracker.compressSize.
*/
private[spark] class MapStatus(var location: BlockManagerId, var compressedSizes: Array[Byte])
extends Externalizable {
private[spark] class BlockMessage() {
// Un-initialized: typ = 0
// GetBlock: typ = 1
// GotBlock: typ = 2
// PutBlock: typ = 3
private var typ: Int = BlockMessage.TYPE_NON_INITIALIZED
private var id: BlockId = null
private var data: ByteBuffer = null
private var level: StorageLevel = null
private[spark] class HashShuffleReader[K, C](
handle: BaseShuffleHandle[K, _, C],
startPartition: Int,
endPartition: Int,
context: TaskContext)
extends ShuffleReader[K, C]
{
require(endPartition == startPartition + 1,
"Hash shuffle currently only supports fetching one partition")
private val dep = handle.dependency
/** Read the combined key-values for this reduce task */
override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = {
val readMetrics = context.taskMetrics.createShuffleReadMetricsForDependency()
val ser = Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer)
val iter = BlockStoreShuffleFetcher.fetch(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, context, ser,
readMetrics)
--下面这段是获取聚合器,它可以配置指定是map阶段聚合还是reduce阶段聚合。
val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
new InterruptibleIterator(context, dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(iter, context))
} else {
new InterruptibleIterator(context, dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(iter, context))
}
} else if (dep.aggregator.isEmpty && dep.mapSideCombine) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Aggregator is empty for map-side combine")
} else {
// Convert the Product2s to pairs since this is what downstream RDDs currently expect
iter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]].map(pair => (pair._1, pair._2))
}
// Sort the output if there is a sort ordering defined.
dep.keyOrdering match {
case Some(keyOrd: Ordering[K]) => --是否有自定义的排序算法
// Create an ExternalSorter to sort the data. Note that if spark.shuffle.spill is disabled,
// the ExternalSorter won't spill to disk.
val sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, C, C](ordering = Some(keyOrd), serializer = Some(ser))
sorter.insertAll(aggregatedIter)
context.taskMetrics.memoryBytesSpilled += sorter.memoryBytesSpilled
context.taskMetrics.diskBytesSpilled += sorter.diskBytesSpilled
sorter.iterator
case None =>
aggregatedIter
}
}
/** Close this reader */
override def stop(): Unit = ???
}
private[spark] class HashShuffleWriter[K, V](
handle: BaseShuffleHandle[K, V, _],
mapId: Int,
context: TaskContext)
extends ShuffleWriter[K, V] with Logging {
private val blockManager = SparkEnv.get.blockManager
private val shuffleBlockManager = blockManager.shuffleBlockManager
private val ser = Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer.getOrElse(null))
private val shuffle = shuffleBlockManager.forMapTask(dep.shuffleId, mapId, numOutputSplits, ser,
writeMetrics)
/** Write a bunch of records to this task's output */
override def write(records: Iterator[_ <: Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
val iter = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(records, context)
} else {
records
}
} else if (dep.aggregator.isEmpty && dep.mapSideCombine) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Aggregator is empty for map-side combine")
} else {
records
}
for (elem <- iter) {
val bucketId = dep.partitioner.getPartition(elem._1)
shuffle.writers(bucketId).write(elem)
}
}
private[spark] class SortShuffleWriter[K, V, C](
handle: BaseShuffleHandle[K, V, C],
mapId: Int,
context: TaskContext)
extends ShuffleWriter[K, V] with Logging {
private val dep = handle.dependency
private val numPartitions = dep.partitioner.numPartitions
private val blockManager = SparkEnv.get.blockManager
private val ser = Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer.orNull)
private val conf = SparkEnv.get.conf
private val fileBufferSize = conf.getInt("spark.shuffle.file.buffer.kb", 32) * 1024
private var sorter: ExternalSorter[K, V, _] = null
private var outputFile: File = null
private var indexFile: File = null
// Are we in the process of stopping? Because map tasks can call stop() with success = true
// and then call stop() with success = false if they get an exception, we want to make sure
// we don't try deleting files, etc twice.
private var stopping = false
private var mapStatus: MapStatus = null
private val writeMetrics = new ShuffleWriteMetrics()
context.taskMetrics.shuffleWriteMetrics = Some(writeMetrics)
/** Write a bunch of records to this task's output */
override def write(records: Iterator[_ <: Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
if (!dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Aggregator is empty for map-side combine")
}
sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
sorter.insertAll(records)
} else {
// In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't
// care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side
// if the operation being run is sortByKey.
sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
None, Some(dep.partitioner), None, dep.serializer)
sorter.insertAll(records)
}
// Create a single shuffle file with reduce ID 0 that we'll write all results to. We'll later
// serve different ranges of this file using an index file that we create at the end.
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(dep.shuffleId, mapId, 0)
outputFile = blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile(blockId)
indexFile = blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile(blockId.name + ".index")
val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, context)
// Register our map output with the ShuffleBlockManager, which handles cleaning it over time
blockManager.shuffleBlockManager.addCompletedMap(dep.shuffleId, mapId, numPartitions)
mapStatus = new MapStatus(blockManager.blockManagerId,
partitionLengths.map(MapOutputTracker.compressSize))
}
spark 笔记 15: ShuffleManager,shuffle map两端的stage/task的桥梁的更多相关文章
- Spark技术内幕:Shuffle Map Task运算结果的处理
Shuffle Map Task运算结果的处理 这个结果的处理,分为两部分,一个是在Executor端是如何直接处理Task的结果的:还有就是Driver端,如果在接到Task运行结束的消息时,如何对 ...
- 【hadoop代码笔记】Mapreduce shuffle过程之Map输出过程
一.概要描述 shuffle是MapReduce的一个核心过程,因此没有在前面的MapReduce作业提交的过程中描述,而是单独拿出来比较详细的描述. 根据官方的流程图示如下: 本篇文章中只是想尝试从 ...
- Spark技术内幕:Shuffle Pluggable框架详解,你怎么开发自己的Shuffle Service?
首先介绍一下需要实现的接口.框架的类图如图所示(今天CSDN抽风,竟然上传不了图片.如果需要实现新的Shuffle机制,那么需要实现这些接口. 1.1.1 org.apache.spark.shuf ...
- 【原创】大数据基础之Spark(5)Shuffle实现原理及代码解析
一 简介 Shuffle,简而言之,就是对数据进行重新分区,其中会涉及大量的网络io和磁盘io,为什么需要shuffle,以词频统计reduceByKey过程为例, serverA:partition ...
- Spark优化一则 - 减少Shuffle
Spark优化一则 - 减少Shuffle 看了Spark Summit 2014的A Deeper Understanding of Spark Internals,视频(要***)详细讲解了Spa ...
- Spark性能优化:shuffle调优
调优概述 大多数Spark作业的性能主要就是消耗在了shuffle环节,因为该环节包含了大量的磁盘IO.序列化.网络数据传输等操作.因此,如果要让作业的性能更上一层楼,就有必要对shuffle过程进行 ...
- spark源码阅读--shuffle过程分析
ShuffleManager(一) 本篇,我们来看一下spark内核中另一个重要的模块,Shuffle管理器ShuffleManager.shuffle可以说是分布式计算中最重要的一个概念了,数据的j ...
- spark笔记 环境配置
spark笔记 spark简介 saprk 有六个核心组件: SparkCore.SparkSQL.SparkStreaming.StructedStreaming.MLlib,Graphx Spar ...
- spark 笔记 8: Stage
Stage 是一组独立的任务,他们在一个job中执行相同的功能(function),功能的划分是以shuffle为边界的.DAG调度器以拓扑顺序执行同一个Stage中的task. /** * A st ...
随机推荐
- O002、虚拟化
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/CloudMan6/p/5233484.html OpenStack 是云操作系统,要学习 OpenStack,首先需要掌握一些虚拟化和云计算的 ...
- 02 Redis防止入侵
在使用云服务器时,安装的redis3.0+版本都关闭了protected-mode,因而都遭遇了挖矿病毒的攻击,使得服务器99%的占用率!! 因此我们在使用redis时候,最好更改默认端口,并且使用r ...
- 新技能get,文件夹隐藏
attrib命令用来显示或更改文件属性. ATTRIB [+R | -R] [+A | -A ] [+S | -S] [+H | -H] [[drive:] [path] filename] [/S ...
- VMware虚拟化集群的配置(一)
一.VMware介绍 VMware vSphere 是业界领先且最可靠的虚拟化平台.vSphere将应用程序和操作系统从底层硬件分离出来,从而简化了 IT操作. VMware集群最主要的两个部分ESX ...
- Sql Server 常用日期格式
SQL Server中文版的默认的日期字段datetime格式是yyyy-mm-dd Thh:mm:ss.mmm 例如: select getdate() 2004-09-12 11:06:08.17 ...
- web规范文档说明三
网站头部: head/header(头部) top(顶部)导航: nanv 导航具体区分:topnav(顶部导航).mainnav(主导航).mininav(迷你导航).textnav(导航 ...
- lightinthebox 批量设置分类产品排列方式为List、Grid、Gallery
lightinthebox 批量设置分类产品排列方式为Grid categories_type = '1'表示List,2表示Grid,3表示Gallery方式 设置单个分类 ; ; ; 设置全部 ' ...
- google guava工具包
guava这个工具包里有好多有用的工具类 <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifact ...
- STL源码阅读-traits与迭代器
迭代器模式 提供一种方法,使之能够依序访问容器的各个元素,而又无需暴露容器的内部表述方式 STL设计的中心思想在于将数据容器和算法分离开,容器和算法分开设计,迭代器则是两者之间的胶着剂,一般迭代器的设 ...
- echarts-all.js:1 Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property 'getAttribute' of null
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/you23hai45/article/details/51595108 由于echarts图形ID是由后台传输过来的,并且是根据图形数据一起传过来,出 ...
