编译原理 算法3.8 LR分析 c++11实现
LR分析简介
LR分析是应用最广泛的一类分析方法,它是实用的编译器功能中最强的分析器,其特点是:
1,采用最一般的无回溯移进-规约方法。
2,可分析的文法是LL文法的真超集。
3,能够及时发现错误,及时从左扫描输入序列的最大可能。
4,分析表较为复杂,难以手工构造。
实验内容
根据LR分析表action和goto实现LR分析。
实验步骤
输入 序列$\omega$和文法$G$的LR分析表action与goto。
输出 若$\omega \in L(G)$,得到$\omega$的规范规约,否则指出一个错误。
具体实现
见代码。
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std; using Production = pair<string, vector<string>>; const int max_state = ;
const int delay_num = 5e8; struct ParserLR
{ map<string, int> mp_n; //非终结符映射
map<string, int> mp_t; //终结符映射
vector<Production> P; //产生式
vector<string> N, T; //非终结符,终结符
int state_num, operator_num, nonterminal_num, terminal_num, production_num;
vector<string> action[max_state];
vector<int> _goto[max_state];
int init(string filename)
{
N.clear();
T.clear();
P.clear();
mp_n.clear();
mp_t.clear();
for (int i = ; i < max_state; i++)
{
action[i].clear();
_goto[i].clear();
}
state_num = operator_num = nonterminal_num = terminal_num = production_num = ;
ifstream in(filename, ios::in);
if (!in.is_open())
return ;
in >> terminal_num;
for (int i = ; i < terminal_num; i++)
{
string tmp;
in >> tmp;
T.emplace_back(tmp);
mp_t[tmp] = i;
}
in >> nonterminal_num;
for (int i = ; i < nonterminal_num; i++)
{
string tmp;
in >> tmp;
N.emplace_back(tmp);
mp_n[tmp] = i;
}
in >> production_num;
for (int i = ; i < production_num; i++)
{
Production cur;
in >> cur.first;
int sz;
in >> sz;
for (int j = ; j < sz; j++)
{
string t;
in >> t;
cur.second.emplace_back(t);
}
P.emplace_back(cur);
}
in >> state_num;
for (int i = ; i <= state_num; i++)
for (int j = ; j < terminal_num; j++)
{
string tmp;
in >> tmp;
action[i].emplace_back(tmp);
}
for (int i = ; i <= state_num; i++)
for (int j = ; j < nonterminal_num; j++)
{
int tmp;
in >> tmp;
_goto[i].emplace_back(tmp);
}
return ;
}
Production getProduction(int idx)
{
return P[idx - ];
}
pair<int, vector<Production>> analyze(vector<string> input) //first->出错位置,-1代表无错
{
vector<Production> error;
vector<Production> success;
stack<string> ch; //符号栈
stack<int> st; //状态栈
ch.emplace("#");
st.emplace();
input.emplace_back("#");
int sz = input.size();
for (int i = ; i < sz;)
{
string now = input[i];
if (!mp_t.count(now))
return make_pair(i, success);
int ip = mp_t[now];
int top = st.top(); //栈顶状态
string at = action[top][ip];
if (at[] == 'r') //规约
{
string res = at.substr(, at.size());
int num = stoi(res);
Production trans = getProduction(num);
for (int i = ; i < trans.second.size(); i++)
{
st.pop();
ch.pop();
}
top = st.top();
string cur = trans.first;
ch.emplace(cur);
st.emplace(_goto[top][mp_n[cur]]);
success.emplace_back(trans);
}
else if (at[] == 's') //移进
{
string res = at.substr(, at.size());
int to_state = stoi(res);
st.emplace(to_state);
ch.emplace(now);
i++;
}
else if (at == "acc") //接受
return make_pair(-, success);
else //error
{
if (now == "#")
return make_pair(i - , success);
return make_pair(i, success);
}
}
return make_pair(, error);
}
};
inline void delay()
{
for (int i = ; i < delay_num; i++)
;
}
inline void display(const pair<int, vector<Production>> &out)
{
if (out.first == -)
{
for (int i = ; i < out.second.size(); i++)
{
cout << out.second[i].first << "->";
for (int j = ; j < out.second[i].second.size(); j++)
cout << out.second[i].second[j];
cout << "\n";
}
}
else
cout << "在第" << out.first + << "个终结符出错.\n";
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ParserLR app;
string filename = "prj3_8_in.txt";
if (app.init(filename))
{ cout << "构建分析器中";
delay();
cout << ".";
delay();
cout << ".";
delay();
cout << ".\n";
delay();
cout << "构建成功.\n";
cout << "请输入终结符个数:";
int sz;
cin >> sz;
cout << "请输入包含" << sz << "个终结符的待分析序列, 终结符间需用空格分离:";
vector<string> al;
for (int i = ; i < sz; i++)
{
string tmp;
cin >> tmp;
al.emplace_back(tmp);
}
cout << "开始分析";
delay();
cout << ".";
delay();
cout << ".";
delay();
cout << ".\n";
delay();
cout << "分析结束.\n";
pair<int, vector<Production>> out = app.analyze(al);
cout << "分析成功,结果如下:\n";
display(out);
}
return ;
}
源代码
id - * # E T F E E - T
E T
T T * F
T F
F - F
F id s4 s5 null null
null s6 null acc
null r2 s7 r2
null r4 r4 r4
null r6 r6 r6
s4 s5 null null
s4 s5 null null
s4 s5 null null
null r5 r5 r5
null r1 s7 r1
null r3 r3 r3 - - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- -
-
- -
- - -
- - -
- - -
输入文件
效果展示
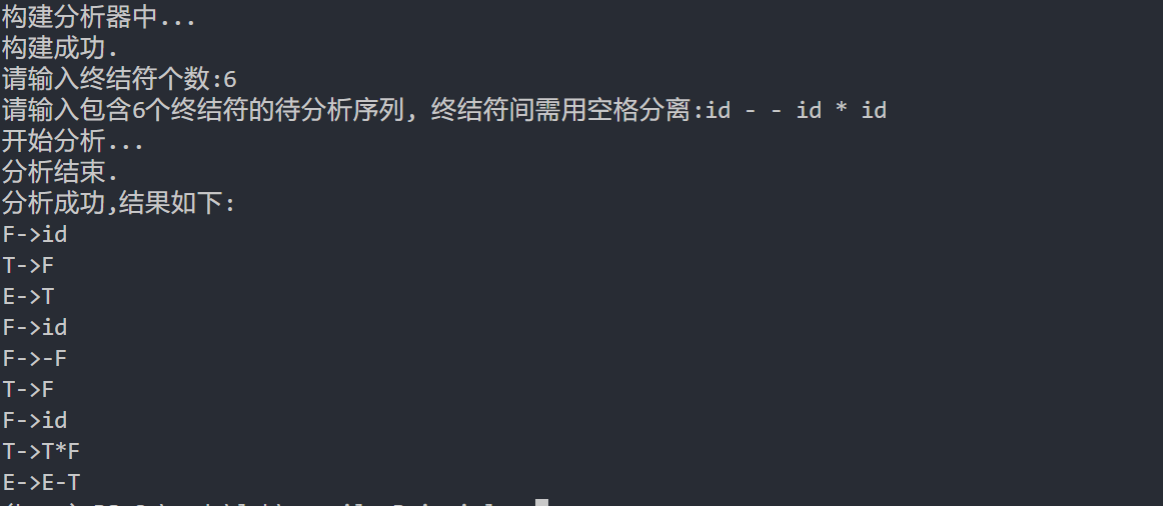
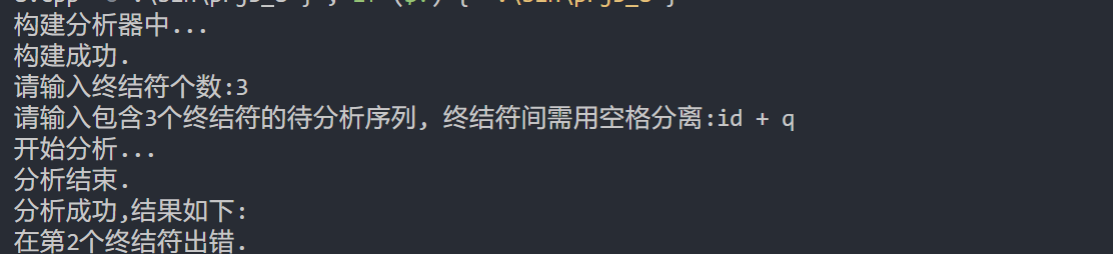
代码使用部分c++11特性,如有本地编译需要,请确认环境。
欢迎下方留言。
编译原理 算法3.8 LR分析 c++11实现的更多相关文章
- 《编译原理》构造 LL(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析
<编译原理>构造 LL(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析 易错点及扩展: 1.求每个产生式的 SELECT 集 2.注意区分是对谁 FIRST 集 FOLLOW 集 3.开始符号的 FOL ...
- 编译原理实验之SLR1文法分析
---内容开始--- 这是一份编译原理实验报告,分析表是手动造的,可以作为借鉴. 基于 SLR(1) 分析法的语法制导翻译及中间代码生成程序设计原理与实现1 .理论传授语法制导的基本概念,目标代码结 ...
- 编译原理(六)自底向上分析之LR分析法
自底向上分析之LR分析法 说明:以老师PPT为标准,借鉴部分教材内容,AlvinZH学习笔记. 基本概念 1. LR分析:从左到右扫描(L)自底向上进行规约(R),是规范规约,也即最右推导(规范推导) ...
- 【编译原理】语法分析LL(1)分析法的FIRST和FOLLOW集
近来复习编译原理,语法分析中的自上而下LL(1)分析法,需要构造求出一个文法的FIRST和FOLLOW集,然后构造分析表,利用分析表+一个栈来做自上而下的语法分析(递归下降/预测分析),可是这个FIR ...
- 编译原理实习(应用预测分析法LL(1)实现语法分析)
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<iomanip> #include<cstdio> #inc ...
- 编译原理 #02# 简易递归下降分析程序(js实现)
// 实验存档 截图: 代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"&g ...
- 【编译原理】c++实现自下而上语法分析器
写在前面:本博客为本人原创,严禁任何形式的转载!本博客只允许放在博客园(.cnblogs.com),如果您在其他网站看到这篇博文,请通过下面这个唯一的合法链接转到原文! 本博客全网唯一合法URL:ht ...
- 编译原理根据项目集规范族构造LR(0)分析表
转载于https://blog.csdn.net/Johan_Joe_King/article/details/79058597?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.n ...
- 《编译原理》LR 分析法与构造 LR(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析
<编译原理>LR 分析法与构造 LR(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析 笔记 直接做题是有一些特定步骤,有技巧.但也必须先了解一些基本概念,本篇会通过例题形式解释概念,会容易理解和记忆,以 ...
随机推荐
- 使用Typescript重构axios(七)——实现基础功能:处理响应header
0. 系列文章 1.使用Typescript重构axios(一)--写在最前面 2.使用Typescript重构axios(二)--项目起手,跑通流程 3.使用Typescript重构axios(三) ...
- 洛谷 P 5 3 0 4 [GXOI/GZOI2019]旅行者
题目描述 J 国有 n 座城市,这些城市之间通过 m 条单向道路相连,已知每条道路的长度. 一次,居住在 J 国的 Rainbow 邀请 Vani 来作客.不过,作为一名资深的旅行者,Vani 只对 ...
- IntelliJ IDEA 中设置左菜单字体, 编辑器字体和控制台的字体
IntelliJ IDEA 中设置左菜单字体大小 File-Settings,然后选择appearance,下图右侧红色边框中的内容即设置菜单的字体和大小 IntelliJ IDEA 中设置当前编 ...
- 生活问题 | 对华为畅玩手机5X进行升级
步骤一:准备一张SD卡,建议使用Sandisk, Kingstone, 或Kingmax,大小建议在2G KIW-AL10C00B258 软件版本升级指导书 Secret 2016-11-25 Hu ...
- Linux下安装nexus
下载地址:https://help.sonatype.com/repomanager3/download tar xf nexus-linux-3.19.1-01.tar.gz cd nexus-li ...
- 学Linux到底学什么?
前言 我们常常听到很多人说要学学Linux或者被人告知说应该学学Linux,那么学Linux到底要学什么? 为什么要学Linux 在回答学什么之前,我们先看看为什么要学.首先我们需要认识到的是,很多服 ...
- PHP常用的header头部定义
<?php header('HTTP/1.1 200 OK'); // ok 正常访问 header('HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found'); //通知浏览器 页面不存在 heade ...
- windows7设置定时任务运行ThinkPHP框架程序
1. 设置Windows的任务计划 可以参考win7计划任务的设置方法 2. 新建Windows执行文件bat 新建cron.bat文件,内容如下: D: cd \wamp\www\tp32 D:\w ...
- nyoj 217-a letter and a number (char)
217-a letter and a number 内存限制:64MB 时间限制:3000ms 特判: No 通过数:4 提交数:5 难度:1 题目描述: we define f(A) = 1, f( ...
- shodan 文档学习笔记
Table of Contents 1. Introduction 1.1. All About the Data 1.2. Data Collection 1.3. SSL in Depth 1.3 ...
