ZGC gc策略及回收过程-源码分析
源码文件:/src/hotspot/share/gc/z/zDirector.cpp
一、回收策略
main入口函数:
void ZDirector::run_service() {
// Main loop
while (_metronome.wait_for_tick()) {
sample_allocation_rate();
const GCCause::Cause cause = make_gc_decision();
if (cause != GCCause::_no_gc) {
ZCollectedHeap::heap()->collect(cause);
}
}
}
GCCause::Cause ZDirector::make_gc_decision() const {
// Rule 0: Timer
if (rule_timer()) {
return GCCause::_z_timer;
}
// Rule 1: Warmup
if (rule_warmup()) {
return GCCause::_z_warmup;
}
// Rule 2: Allocation rate
if (rule_allocation_rate()) {
return GCCause::_z_allocation_rate;
}
// Rule 3: Proactive
if (rule_proactive()) {
return GCCause::_z_proactive;
}
// No GC
return GCCause::_no_gc;
}
bool ZDirector::rule_timer() const {
if (ZCollectionInterval == ) {
// Rule disabled
return false;
}
// Perform GC if timer has expired.
const double time_since_last_gc = ZStatCycle::time_since_last();
const double time_until_gc = ZCollectionInterval - time_since_last_gc;
log_debug(gc, director)("Rule: Timer, Interval: %us, TimeUntilGC: %.3lfs",
ZCollectionInterval, time_until_gc);
return time_until_gc <= ;
}
rule 2:预热规则
is_warm函数判断gc次数是否已超过3次,是则不使用该策略。
注释说的很清楚,当gc次数少于3时,判断堆使用率达到10%/20%/30%时,使用该策略
bool ZDirector::rule_warmup() const {
if (is_warm()) {
// Rule disabled
return false;
}
// Perform GC if heap usage passes 10/20/30% and no other GC has been
// performed yet. This allows us to get some early samples of the GC
// duration, which is needed by the other rules.
const size_t max_capacity = ZHeap::heap()->current_max_capacity();
const size_t used = ZHeap::heap()->used();
const double used_threshold_percent = (ZStatCycle::ncycles() + ) * 0.1;
const size_t used_threshold = max_capacity * used_threshold_percent;
log_debug(gc, director)("Rule: Warmup %.0f%%, Used: " SIZE_FORMAT "MB, UsedThreshold: " SIZE_FORMAT "MB",
used_threshold_percent * , used / M, used_threshold / M);
return used >= used_threshold;
}
bool ZDirector::is_warm() const {
return ZStatCycle::ncycles() >= ;
}
// 位置:ZStat.cpp
uint64_t ZStatCycle::ncycles() {
return _ncycles; // gc次数
}
rule 3:分配速率预估
is_first函数判断如果是首次gc,则直接返回false。
ZAllocationSpikeTolerance默认值为2,分配速率策略采用正态分布模型预测内存分配速率,加上ZAllocationSpikeTolerance修正因子,可以覆盖超过99.9%的内存分配速率的可能性
bool ZDirector::rule_allocation_rate() const {
if (is_first()) {
// Rule disabled
return false;
}
// Perform GC if the estimated max allocation rate indicates that we
// will run out of memory. The estimated max allocation rate is based
// on the moving average of the sampled allocation rate plus a safety
// margin based on variations in the allocation rate and unforeseen
// allocation spikes.
// Calculate amount of free memory available to Java threads. Note that
// the heap reserve is not available to Java threads and is therefore not
// considered part of the free memory.
const size_t max_capacity = ZHeap::heap()->current_max_capacity();
const size_t max_reserve = ZHeap::heap()->max_reserve();
const size_t used = ZHeap::heap()->used();
const size_t free_with_reserve = max_capacity - used;
const size_t free = free_with_reserve - MIN2(free_with_reserve, max_reserve);
// Calculate time until OOM given the max allocation rate and the amount
// of free memory. The allocation rate is a moving average and we multiply
// that with an allocation spike tolerance factor to guard against unforeseen
// phase changes in the allocate rate. We then add ~3.3 sigma to account for
// the allocation rate variance, which means the probability is 1 in 1000
// that a sample is outside of the confidence interval.
const double max_alloc_rate = (ZStatAllocRate::avg() * ZAllocationSpikeTolerance) + (ZStatAllocRate::avg_sd() * one_in_1000);
const double time_until_oom = free / (max_alloc_rate + 1.0); // Plus 1.0B/s to avoid division by zero
// Calculate max duration of a GC cycle. The duration of GC is a moving
// average, we add ~3.3 sigma to account for the GC duration variance.
const AbsSeq& duration_of_gc = ZStatCycle::normalized_duration();
const double max_duration_of_gc = duration_of_gc.davg() + (duration_of_gc.dsd() * one_in_1000);
// Calculate time until GC given the time until OOM and max duration of GC.
// We also deduct the sample interval, so that we don't overshoot the target
// time and end up starting the GC too late in the next interval.
const double sample_interval = 1.0 / ZStatAllocRate::sample_hz;
const double time_until_gc = time_until_oom - max_duration_of_gc - sample_interval;
log_debug(gc, director)("Rule: Allocation Rate, MaxAllocRate: %.3lfMB/s, Free: " SIZE_FORMAT "MB, MaxDurationOfGC: %.3lfs, TimeUntilGC: %.3lfs",
max_alloc_rate / M, free / M, max_duration_of_gc, time_until_gc);
return time_until_gc <= ;
}
bool ZDirector::is_first() const {
return ZStatCycle::ncycles() == ;
}
rule 4:积极回收策略
通过ZProactive可启用积极回收策略,is_warm函数判断启用该策略必须是在预热之后(gc次数超过3次)
自上一次gc后,堆使用率达到xmx的10%或者已过了5分钟,这个参数是弥补第三个规则中没有覆盖的场景,从上述分析可以得到第三个条件更多的覆盖分配速率比较高的场景。
bool ZDirector::rule_proactive() const {
if (!ZProactive || !is_warm()) {
// Rule disabled
return false;
}
// Perform GC if the impact of doing so, in terms of application throughput
// reduction, is considered acceptable. This rule allows us to keep the heap
// size down and allow reference processing to happen even when we have a lot
// of free space on the heap.
// Only consider doing a proactive GC if the heap usage has grown by at least
// 10% of the max capacity since the previous GC, or more than 5 minutes has
// passed since the previous GC. This helps avoid superfluous GCs when running
// applications with very low allocation rate.
const size_t used_after_last_gc = ZStatHeap::used_at_relocate_end();
const size_t used_increase_threshold = ZHeap::heap()->current_max_capacity() * 0.10; // 10%
const size_t used_threshold = used_after_last_gc + used_increase_threshold;
const size_t used = ZHeap::heap()->used();
const double time_since_last_gc = ZStatCycle::time_since_last();
const double time_since_last_gc_threshold = * ; // 5 minutes
if (used < used_threshold && time_since_last_gc < time_since_last_gc_threshold) {
// Don't even consider doing a proactive GC
log_debug(gc, director)("Rule: Proactive, UsedUntilEnabled: " SIZE_FORMAT "MB, TimeUntilEnabled: %.3lfs",
(used_threshold - used) / M,
time_since_last_gc_threshold - time_since_last_gc);
return false;
}
const double assumed_throughput_drop_during_gc = 0.50; // 50%
const double acceptable_throughput_drop = 0.01; // 1%
const AbsSeq& duration_of_gc = ZStatCycle::normalized_duration();
const double max_duration_of_gc = duration_of_gc.davg() + (duration_of_gc.dsd() * one_in_1000);
const double acceptable_gc_interval = max_duration_of_gc * ((assumed_throughput_drop_during_gc / acceptable_throughput_drop) - 1.0);
const double time_until_gc = acceptable_gc_interval - time_since_last_gc;
log_debug(gc, director)("Rule: Proactive, AcceptableGCInterval: %.3lfs, TimeSinceLastGC: %.3lfs, TimeUntilGC: %.3lfs",
acceptable_gc_interval, time_since_last_gc, time_until_gc);
return time_until_gc <= ;
}
最后,当所有策略都不满足时,返回_no_gc,表示不进行gc
二、回收过程
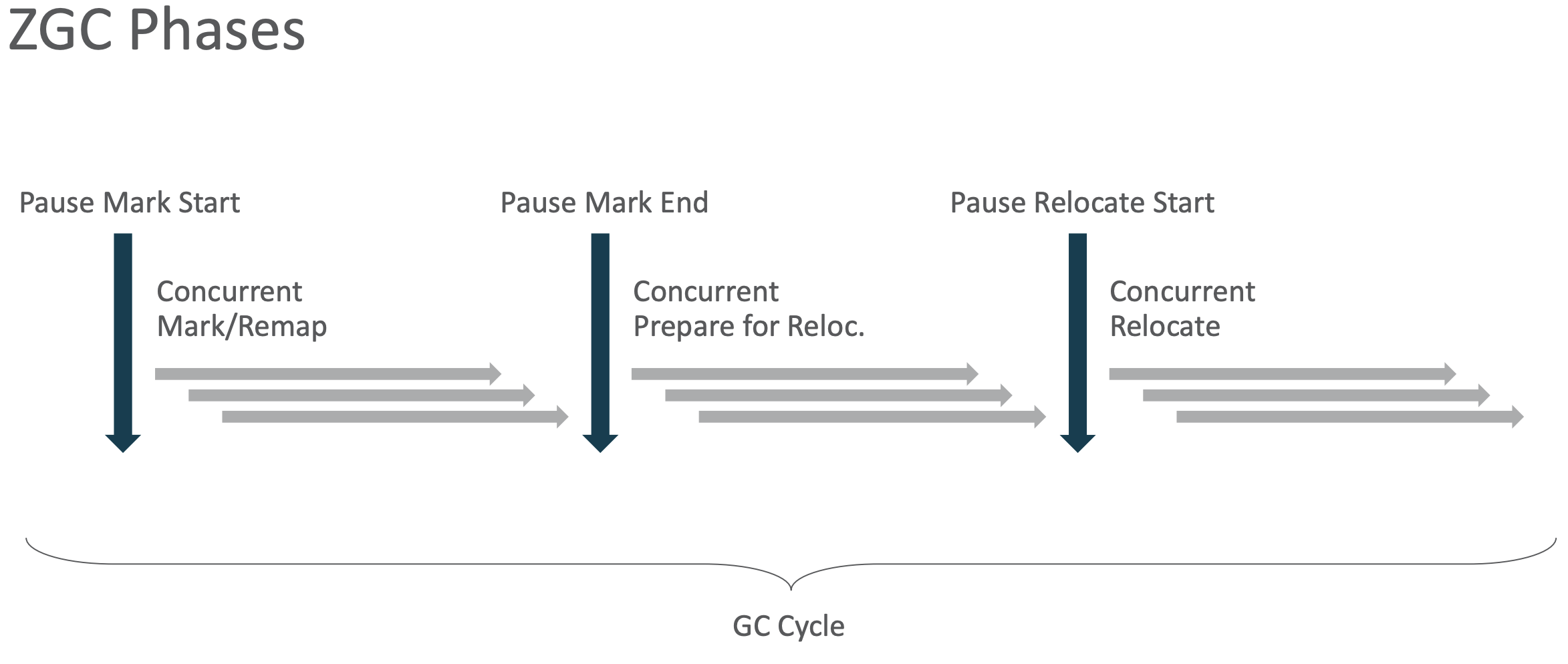
gc整个周期:
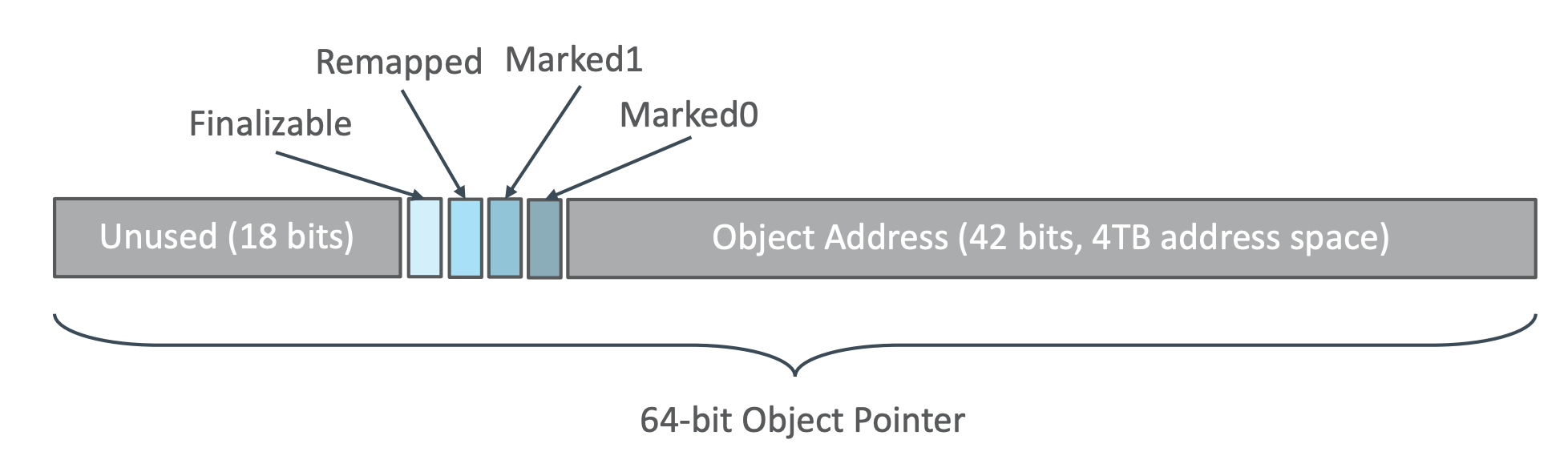
彩色指针示意图:
- (STW)Pause Mark Start,开始标记,这个阶段只会标记(Mark0)由root引用的object,组成Root Set
- Concurrent Mark,并发标记,从Root Set出发,并发遍历Root Set object的引用链并标记(Mark1)
- (STW)Pause Mark End,检查是否已经并发标记完成,如果不是,需要进行多一次Concurrent Mark
- Concurrent Process Non-Strong References,并发处理弱引用
- Concurrent Reset Relocation Set
- Concurrent Destroy Detached Pages
- Concurrent Select Relocation Set,并发选择Relocation Set;
- Concurrent Prepare Relocation Set,并发预处理Relocation Set
- (STW)Pause Relocate Start,开始转移对象,依然是遍历root引用
- Concurrent Relocate,并发转移,将需要回收的Page里的对象转移到Relocation Set,然后回收Page给系统重新利用
run_gc_cycle函数(/src/hotspot/share/gc/z/zDriver.cpp):
void ZDriver::run_gc_cycle(GCCause::Cause cause) {
ZDriverCycleScope scope(cause);
// Phase 1: Pause Mark Start
{
ZMarkStartClosure cl;
vm_operation(&cl);
}
// Phase 2: Concurrent Mark
{
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentMark);
ZHeap::heap()->mark();
}
// Phase 3: Pause Mark End
{
ZMarkEndClosure cl;
while (!vm_operation(&cl)) {
// Phase 3.5: Concurrent Mark Continue
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentMarkContinue);
ZHeap::heap()->mark();
}
}
// Phase 4: Concurrent Process Non-Strong References
{
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentProcessNonStrongReferences);
ZHeap::heap()->process_non_strong_references();
}
// Phase 5: Concurrent Reset Relocation Set
{
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentResetRelocationSet);
ZHeap::heap()->reset_relocation_set();
}
// Phase 6: Concurrent Destroy Detached Pages
{
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentDestroyDetachedPages);
ZHeap::heap()->destroy_detached_pages();
}
// Phase 7: Concurrent Select Relocation Set
{
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentSelectRelocationSet);
ZHeap::heap()->select_relocation_set();
}
// Phase 8: Concurrent Prepare Relocation Set
{
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentPrepareRelocationSet);
ZHeap::heap()->prepare_relocation_set();
}
// Phase 9: Pause Relocate Start
{
ZRelocateStartClosure cl;
vm_operation(&cl);
}
// Phase 10: Concurrent Relocate
{
ZStatTimer timer(ZPhaseConcurrentRelocated);
ZHeap::heap()->relocate();
}
}
未完待续
ZGC gc策略及回收过程-源码分析的更多相关文章
- (3.10)mysql基础深入——mysqld 服务器与客户端连接过程 源码分析【待写】
(3.10)mysql基础深入——mysqld 服务器与客户端连接过程 源码分析[待写]
- Netty源码分析 (七)----- read过程 源码分析
在上一篇文章中,我们分析了processSelectedKey这个方法中的accept过程,本文将分析一下work线程中的read过程. private static void processSele ...
- 设计模式(二十三)——策略模式(Arrays源码分析)
1 编写鸭子项目,具体要求如下: 1) 有各种鸭子(比如 野鸭.北京鸭.水鸭等, 鸭子有各种行为,比如 叫.飞行等) 2) 显示鸭子的信息 2 传统方案解决鸭子问题的分析和代码实现 1) 传统的设计方 ...
- YARN(MapReduce 2)运行MapReduce的过程-源码分析
这是我的分析,当然查阅书籍和网络.如有什么不对的,请各位批评指正.以下的类有的并不完全,只列出重要的方法. 如要转载,请注上作者以及出处. 一.源码阅读环境 需要安装jdk1.7.0版本及其以上版本, ...
- Flink中TaskManager端执行用户逻辑过程(源码分析)
TaskManager接收到来自JobManager的jobGraph转换得到的TDD对象,启动了任务,在StreamInputProcessor类的processInput()方法中 通过一个whi ...
- Netty源码分析 (八)----- write过程 源码分析
上一篇文章主要讲了netty的read过程,本文主要分析一下write和writeAndFlush. 主要内容 本文分以下几个部分阐述一个java对象最后是如何转变成字节流,写到socket缓冲区中去 ...
- HDFS dfsclient写文件过程 源码分析
HDFS写入文件的重要概念 HDFS一个文件由多个block构成.HDFS在进行block读写的时候是以packet(默认每个packet为64K)为单位进行的.每一个packet由若干个chunk( ...
- spring启动component-scan类扫描加载过程---源码分析
http://blog.csdn.net/xieyuooo/article/details/9089441#comments
- elasticsearch 5.5 query 过程 源码分析
(1)请求 transfer to 任意node 节点 标记为coordinate node server入口函数 transportSearchAction doExecute方法 coordin ...
随机推荐
- Microsoft Office 365的安装
一.安装准备 本教程中需要用到的工具包括:最新版的Office离线包,虚拟光驱软件,离线Kms激活工具, 下载地址:百度网盘 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1sQk7zE40 ...
- pandas可视化:各种图的简单使用
一.Matplotlib中几种图的名字 折线图:plot 柱形图:bar 直方图:hist 箱线图:box 密度图:kde 面积图:area 散点图:scatter 散点图矩阵:scatter_mat ...
- 史上最详 Thymeleaf 使用教程
前言 操作前建议先参考我的另一篇博客:玩转 SpringBoot 2 快速整合 | Thymeleaf 篇 查看如何在SpringBoot 中使用 Thymeleaf.还有一点需要注意的是:模版页面中 ...
- Redis继续学习
1.Redis一共16个数据库 # Set the number of databases. The , you can select # a different one on a per-conne ...
- iOS 13 正式发布,来看看有哪些 API 变动
iOS 13 已正式发布,网上对其用户体验上的新特性的描述也很多.对于开发来说,需要关注的另一方面是新系统在 API 层面做了哪些改动,从而会对我们现有的代码产生什么影响. 在这里,我们基于 iOS ...
- log4j日志不输出的问题
今天服务器上报错,想先去看一下日志进行排查,结果发现日志很久都没有输出过了.从上午排查到下午,刚刚解决,因此记录一下,但现在也只是知其然,并不知其所以然,所以如果大家有什么想法请在下方评论. 先说一下 ...
- springboot jsp,过滤器,拦截器
springboot使用jsp,过滤器,拦截器(拦截器与过滤器区别重点) jsp使用配置 一 创建springboot项目在maven中暂时只添加两个Dependencies :devtools(热部 ...
- git使用和操作
git提交日志的规范 为了更规范的开发,特别是团队协同开发,对于代码托管工具的提交上都会有要求的. 作为开发者,我们一定要注重提交日志的规范性,我们要对自己写的代码负责.提交日志规范很多,最近看到了一 ...
- Java面试-interrupt
我们都知道,Java中停止一个线程不能用stop,因为stop会瞬间强行停止一个线程,且该线程持有的锁并不能释放.大家多习惯于用interrupt,那么使用它又有什么需要注意的呢? interrupt ...
- Django&,Flask&pyrthon原生sql语句 基本操作
Django框架 ,Flask框架 ORM 以及pyrthon原生sql语句操作数据库 WHAT IS ORM? ORM( Object Relational Mapping) 对象关系映射 , 即通 ...
