android--------自定义控件 之 ViewGroup
前面几篇讲了自定义控件的组合控件,地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangqie/p/8985612.html
今天这篇博文主要来说说 自定义控件的 ViewGroup。
什么是ViewGroup?
ViewGroup是一种容器。它包含零个或以上的View及子View
ViewGroup有什么作用?
ViewGroup内部可以用来存放多个View控件,并且根据自身的测量模式,来测量View子控件,并且决定View子控件的位置。这在下面会逐步讲解它是怎么测量及决定子控件大小和位置的。
自定义控件
public class FlowLayoutb extends ViewGroup {
private int horizontolSpacing;
private int verticalSpacing;
public FlowLayoutb(Context context) {
super(context);
init(context);
}
public FlowLayoutb(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init(context);
}
private Line currentline;// 当前的行
private int useWidth = 0;// 当前行使用的宽度
private List<Line> mLines = new ArrayList<Line>();
private int width;
public FlowLayoutb(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context);
}
private void init(Context context) {
horizontolSpacing = Util.dip2px(13, context);
verticalSpacing = Util.dip2px(13, context);
}
// 测量 当前控件Flowlayout
// 父类是有义务测量每个子View的
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mLines.clear();
currentline = null;
useWidth = 0;
/**
* 获得此ViewGroup上级容器为其推荐的宽和高,以及计算模式
*/
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 计算出所有的childView的宽和高
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - getPaddingBottom() - getPaddingTop(); // 获取到宽和高
int childeWidthMode;
int childeHeightMode;
// 为了测量每个子View 需要指定每个子View测量规则
childeWidthMode = widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : widthMode;
childeHeightMode = heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? MeasureSpec.AT_MOST : heightMode;
int childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childeWidthMode, width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childeHeightMode, height);
currentline = new Line();// 创建了第一行
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量每个子View
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
useWidth += measuredWidth;// 让当前行加上使用的长度
if (useWidth <= width) {
currentline.addChild(child);//这时候证明当前的子View是可以放进当前的行里,放进去
useWidth += horizontolSpacing;
} else {
//换行
newLine(child);
}
}
if (!mLines.contains(currentline)) {
mLines.add(currentline);// 添加最后一行
}
int totalheight = 0;
for (Line line : mLines) {
totalheight += line.getHeight();
}
totalheight += verticalSpacing * (mLines.size() - 1) + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
System.out.println(totalheight);
setMeasuredDimension(width + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(), resolveSize(totalheight, heightMeasureSpec));
}
private void newLine(View child) {
mLines.add(currentline);// 记录之前的行
currentline = new Line();// 创建新的一行
currentline.addChild(child);
useWidth = currentline.lineWidth;
}
private class Line {
int height = 0; //当前行的高度
int lineWidth = 0;
private List<View> children = new ArrayList<View>();
/**
* 添加一个子View
*
* @param child
*/
public void addChild(View child) {
children.add(child);
if (child.getMeasuredHeight() > height) {
height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
lineWidth += child.getMeasuredWidth();
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
/**
* 返回子View的数量
*
* @return
*/
public int getChildCount() {
return children.size();
}
public void layout(int l, int t) {
lineWidth += horizontolSpacing * (children.size() - 1);
int surplusChild = 0;
int surplus = width - lineWidth;
if (surplus > 0 && children.size() > 0) {
surplusChild = surplus / children.size();
}
for (int i = 0; i < children.size(); i++) {
View child = children.get(i);
child.layout(l, t, l + child.getMeasuredWidth() + surplusChild, t + child.getMeasuredHeight());
l += child.getMeasuredWidth() + surplusChild;
l += horizontolSpacing;
}
}
}
// 分配每个子View的位置
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
l += getPaddingLeft();
t += getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < mLines.size(); i++) {
Line line = mLines.get(i);
line.layout(l, t); //交给每一行去分配
t += line.getHeight() + verticalSpacing;
}
}
}
自定义ViewGroup的步骤:
- 继承ViewGroup,覆盖构造方法
- 重写onMeasure方法测量子控件和自身宽高
- 实现onLayout方法摆放子控件
效果图:
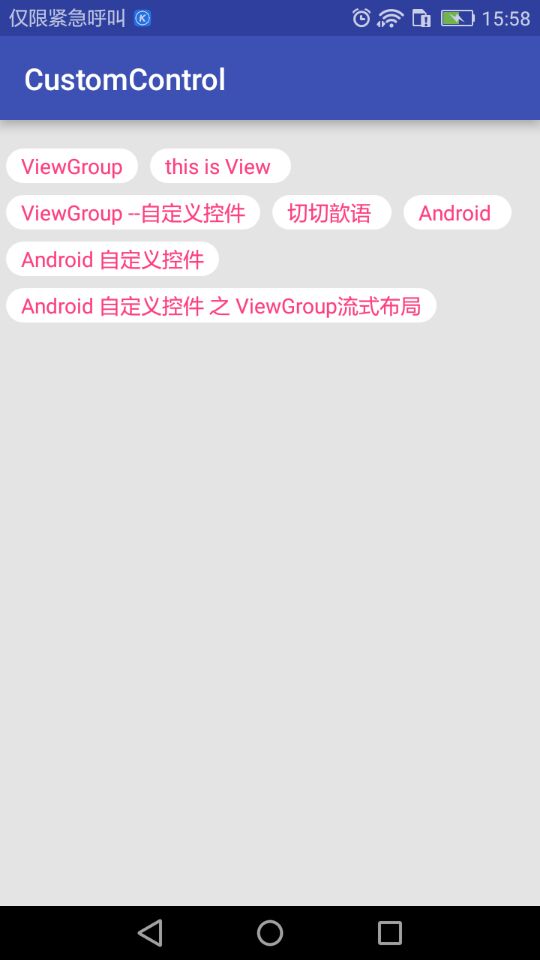

源码地址:https://github.com/DickyQie/android-custom-control
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/shineflowers/article/details/48055879
https://blog.csdn.net/zxt0601/article/details/50533658
https://blog.csdn.net/shakespeare001/article/details/51089453
android--------自定义控件 之 ViewGroup的更多相关文章
- android 自定义控件之ViewGroup生命周期执行步骤
前言 了解ViewGroup的生命周期的执行步骤对于自己自定义ViewGroup的时候十分重要,清楚了整个流程才能对ViewGroup有更深的理解.本文从个人的总结,来阐述一下执行的顺序.执行说明 首 ...
- Android自定义控件之自定义ViewGroup实现标签云
前言: 前面几篇讲了自定义控件绘制原理Android自定义控件之基本原理(一),自定义属性Android自定义控件之自定义属性(二),自定义组合控件Android自定义控件之自定义组合控件(三),常言 ...
- Android自定义控件之自定义组合控件
前言: 前两篇介绍了自定义控件的基础原理Android自定义控件之基本原理(一).自定义属性Android自定义控件之自定义属性(二).今天重点介绍一下如何通过自定义组合控件来提高布局的复用,降低开发 ...
- Android自定义控件之自定义属性
前言: 上篇介绍了自定义控件的基本要求以及绘制的基本原理,本篇文章主要介绍如何给自定义控件自定义一些属性.本篇文章将继续以上篇文章自定义圆形百分比为例进行讲解.有关原理知识请参考Android自定义控 ...
- Android自定义控件之基本原理
前言: 在日常的Android开发中会经常和控件打交道,有时Android提供的控件未必能满足业务的需求,这个时候就需要我们实现自定义一些控件,今天先大致了解一下自定义控件的要求和实现的基本原理. 自 ...
- Android自定义控件 开源组件SlidingMenu的项目集成
在实际项目开发中,定制一个菜单,能让用户得到更好的用户体验,诚然菜单的样式各种各样,但是有一种菜单——滑动菜单,是被众多应用广泛使用的.关于这种滑动菜单的实现,我在前面的博文中也介绍了如何自定义去实现 ...
- Android自定义控件之基本原理(一)
前言: 在日常的Android开发中会经常和控件打交道,有时Android提供的控件未必能满足业务的需求,这个时候就需要我们实现自定义一些控件,今天先大致了解一下自定义控件的要求和实现的基本原理. 自 ...
- Android自定义控件之自定义组合控件(三)
前言: 前两篇介绍了自定义控件的基础原理Android自定义控件之基本原理(一).自定义属性Android自定义控件之自定义属性(二).今天重点介绍一下如何通过自定义组合控件来提高布局的复用,降低开发 ...
- Android自定义控件View(三)组合控件
不少人应该见过小米手机系统音量控制UI,一个圆形带动画效果的音量加减UI,效果很好看.它是怎么实现的呢?这篇博客来揭开它的神秘面纱.先上效果图 相信很多人都知道Android自定义控件的三种方式,An ...
- android之自定义viewGroup仿scrollView的两种实现(滚动跟粘性)
最近一直在研究自定义控件,一般大致分为三种情况:自绘控件,组合控件,继承控件.接下来我们来看下继承控件.在此借鉴一位博主的文章,补充粘性的实现效果,并且加注自己的一些理解.大家也可以查看原文博客.an ...
随机推荐
- topcoder srm 430 div1
problem1 link 其实就是找到一个数字$t$,使得$x$的二进制为1 的位上$t$也都为1.然后$t$删掉所有那些$x$为1的二进制位就是$k$. problem2 link 设所有合法的边 ...
- scrapy 关于特殊字符的处理
今天scrapy 发送一段url的时候,如下 http://apis.map.qq.com/lbscloud/v1/poi/search?poi_table=gas_station&key=R ...
- Python3 tkinter基础 Checkbutton anchor for生成多个控件并西对齐
Python : 3.7.0 OS : Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS IDE : PyCharm 2018.2.4 Conda ...
- Python3基础 dict pop 弹出指定键的项
Python : 3.7.0 OS : Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS IDE : PyCharm 2018.2.4 Conda ...
- Python 打包中 setpy.py settuptools pbr 的了解
背景 nova服务构建失败,报错: 'tests_require' must be a string or list of strings containing valid project/versi ...
- Ubuntu: repository/PPA 源
在Ubuntu中,每个PPA源是单独存放在/etc/apt/sources.list.d/文件夹中的,进入到该文件夹,使用ls命令查询即可列出当前系统添加的PPA源. 添加 sudo add-apt- ...
- 网络_TCP连接的建立与释放
三报文握手 1.概述 TCP是面向连接的协议.TCP建立连接的过程叫做握手,握手需要在客户和服务器之间交换三个TCP报文段,即我们说的"三次握手"(严格讲是一次握手过程中交换了三个 ...
- MongoDB集群配置笔记一
MongoDB 的部署方案有单机部署.复本集(主备)部署.分片部署.复本集与分片混合部署.混合的部署方式如图: 分片集群的构造 (1)mongos :数据路由,和客户端打交道的模块.mongos本身没 ...
- numa.h:No such file or directory 解决方法
参考: numa.h:No such file or directory numa.h:No such file or directory 解决方法 Ubuntu: $ apt-get install ...
- -第3章 jQuery方法实现下拉菜单显示和隐藏
知识点 jquery 的引入方式 本地下载引入 在线引入 children 只获取子元素,不获取孙元素 show() 显示. hide() 隐藏. 完整代码 <!-- Author: XiaoW ...
