HDU4453--Looploop (Splay伸展树)
Looploop
XXX gets a new toy named Looploop. The toy has N elements arranged in a loop, an arrow pointing to one of the elements, and two preset parameters k1 and k2. Every element has a number on it.
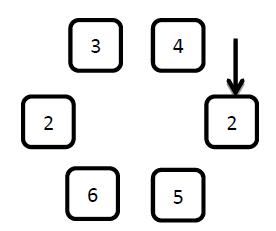
The figure above shows a Looploop of 6 elments. Let's assuming the preset parameter k1 is 3, and k2 is 4.
XXX can do six operations with the toy.
1: add x
Starting from the arrow pointed element, add x to the number on the clockwise first k2 elements.
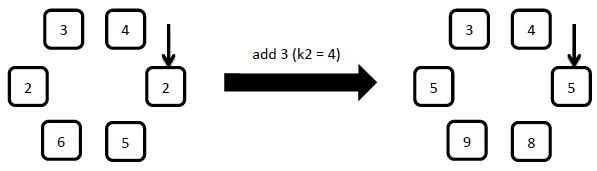
2: reverse
Starting from the arrow pointed element, reverse the first k1 clockwise elements.
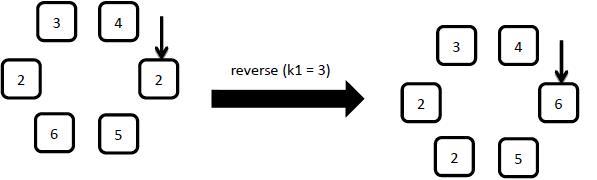
3: insert x
Insert a new element with number x to the right (along clockwise) of the arrow pointed element.
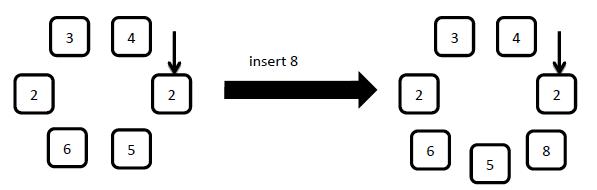
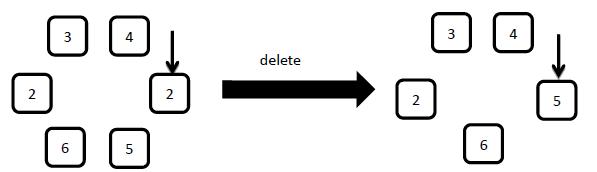
4: delete
Delete the element the arrow pointed and then move the arrow to the right element.
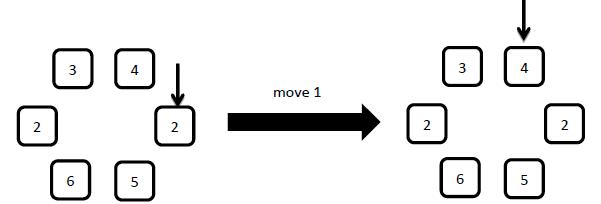
5: move x
x can only be 1 or 2. If x = 1 , move the arrow to the left(along the counterclockwise) element, if x = 2 move the arrow to the right element.
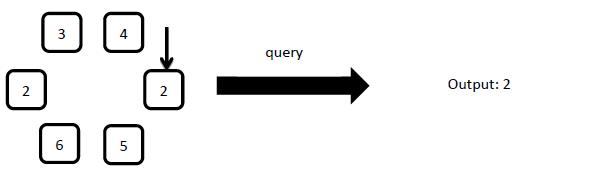
6: query
Output the number on the arrow pointed element in one line.
XXX wants to give answers to every query in a serial of operations.
For each test case the first line contains N,M,k1,k2(2≤k1<k2≤N≤105, M≤105) indicating the initial number of elements, the total number of operations XXX will do and the two preset parameters of the toy.
Second line contains N integers ai(-104≤ai≤104) representing the N numbers on the elements in Looploop along clockwise direction. The arrow points to first element in input at the beginning.
Then m lines follow, each line contains one of the six operations described above.
It is guaranteed that the "x" in the "add","insert" and "move" operations is always integer and its absolute value ≤104. The number of elements will never be less than N during the operations.
The input ends with a line of 0 0 0 0.
3 4 5 6 7
query
5 13 2 4
1 2 3 4 5
move 2
query
insert 8
reverse
query
add 2
query
move 1
query
move 1
query
delete
query
0 0 0 0
题意很简单,就像题目中 图片中描述的一样。Splay大法好啊。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = ;
int pre[maxn],ch[maxn][],key[maxn],addv[maxn],rev[maxn],siz[maxn];
int tot1,tot2,root,s[maxn]; //s为内存池
int a[maxn],n,m,k1,k2;
void update_add(int r,int val)
{
if (!r)
return;
key[r] += val;
addv[r] += val;
}
void update_rev(int r)
{
if (!r)
return;
swap(ch[r][],ch[r][]);
rev[r] ^= ;
}
void push_down(int r)
{
if (rev[r])
{
update_rev(ch[r][]);
update_rev(ch[r][]);
rev[r] = ;
}
if (addv[r])
{
update_add(ch[r][],addv[r]);
update_add(ch[r][],addv[r]);
addv[r] = ;
}
}
void push_up(int r)
{
siz[r] = siz[ch[r][]] + siz[ch[r][]] + ;
}
void NewNode (int &r,int father,int k)
{
if (tot2)
r = s[tot2--];
else
r = ++tot1;
pre[r] = father;
siz[r] = ;
rev[r] = ;
addv[r] = ;
ch[r][] = ch[r][] = ;
key[r] = k;
}
void build(int &x,int l,int r,int father)
{
if (l > r)
return ;
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
NewNode(x,father,a[mid]);
build(ch[x][],l,mid-,x);
build(ch[x][],mid+,r,x);
push_up(x);
}
void init()
{
tot1 = tot2 = root = ;
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++)
scanf ("%d",a+i);
NewNode(root,,inf);
NewNode(ch[root][],root,inf);
build(ch[ch[root][]][],,n,ch[root][]);
push_up(root);
push_up(ch[root][]);
}
void Rotate(int r,int kind)
{
int y = pre[r];
push_down(y);
push_down(r);
ch[y][!kind] = ch[r][kind];
pre[ch[r][kind]] = y;
if (pre[y])
ch[pre[y]][ch[pre[y]][] == y] = r;
ch[r][kind] = y;
pre[r] = pre[y];
pre[y] = r;
push_up(y);
} void Splay(int r,int goal)
{
push_down(r);
while (pre[r] != goal)
{
if (pre[pre[r]] == goal)
{
push_down(pre[r]);
push_down(r);
Rotate(r,ch[pre[r]][] == r);
}
else
{
int y = pre[r];
int kind = (ch[pre[y]][] == y);
push_down(pre[y]);
push_down(y);
push_down(r);
if (ch[y][kind] == r)
{
Rotate(y,!kind);
Rotate(r,!kind);
}
else
{
Rotate(r,kind);
Rotate(r,!kind);
}
}
}
push_up(r);
if (goal == )
root = r;
}
int Get_kth(int r,int k)
{
push_down(r);
int t = siz[ch[r][]] + ;
if (t == k)
return r;
if (t > k)
return Get_kth(ch[r][],k);
else
return Get_kth(ch[r][],k-t);
}
void ADD(int x)
{
Splay (Get_kth(root,),);
Splay(Get_kth(root,k2+),root);
update_add(ch[ch[root][]][],x);
push_up(ch[root][]);
push_up(root);
}
void Reverse(int u,int v)
{
Splay(Get_kth(root,u),);
Splay(Get_kth(root,v+),root);
update_rev(ch[ch[root][]][]);
push_up(ch[root][]);
push_up(root);
}
void Insert(int x)
{
Splay(Get_kth(root,),);
Splay(Get_kth(root,),root);
NewNode(ch[ch[root][]][],ch[root][],x);
push_up(ch[root][]);
push_up(root);
}
void eraser(int r)
{
if (!r)
return;
s[++tot2] = r;
eraser(ch[r][]);
eraser(ch[r][]);
}
void Delete()
{
Splay(Get_kth(root,),);
Splay(Get_kth(root,),root);
eraser(ch[ch[root][]][]);
pre[ch[ch[root][]][]] = ;
ch[ch[root][]][] = ;
push_up(ch[root][]);
push_up(root);
}
void Move(int x) //Move操作就是两个 区间reverse操作。
{
if (x == )
{
Reverse(,n);
Reverse(,n);
}
if (x == )
{
Reverse(,n);
Reverse(,n-);
}
}
int query()
{
Splay(Get_kth(root,),);
Splay(Get_kth(root,),root);
return key[ch[ch[root][]][]];
}
int main(void)
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
int cas = ;
while (~scanf ("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k1,&k2))
{
if (n == && m == && k1 == && k2 == )
break;
printf("Case #%d:\n",cas++);
init();
for (int i = ; i < m; i++)
{
char op[];
int x;
scanf ("%s",op);
if (op[] == 'a')
{
scanf ("%d",&x);
ADD(x);
}
if (op[] == 'r')
Reverse(,k1);
if (op[] == 'i')
{
scanf ("%d",&x);
Insert(x);
n++; // insert一个数 n自然加1
}
if (op[] == 'd')
{
Delete();
n--; //delete一个数 n减1
}
if (op[] == 'm')
{
scanf ("%d",&x);
Move(x);
}
if (op[] == 'q')
printf("%d\n",query());
}
}
return ;
}
HDU4453--Looploop (Splay伸展树)的更多相关文章
- Splay伸展树学习笔记
Splay伸展树 有篇Splay入门必看文章 —— CSDN链接 经典引文 空间效率:O(n) 时间效率:O(log n)插入.查找.删除 创造者:Daniel Sleator 和 Robert Ta ...
- 【学时总结】◆学时·VI◆ SPLAY伸展树
◆学时·VI◆ SPLAY伸展树 平衡树之多,学之不尽也…… ◇算法概述 二叉排序树的一种,自动平衡,由 Tarjan 提出并实现.得名于特有的 Splay 操作. Splay操作:将节点u通过单旋. ...
- Splay 伸展树
废话不说,有篇论文可供参考:杨思雨:<伸展树的基本操作与应用> Splay的好处可以快速分裂和合并. ===============================14.07.26更新== ...
- [Splay伸展树]splay树入门级教程
首先声明,本教程的对象是完全没有接触过splay的OIer,大牛请右上角.. 首先引入一下splay的概念,他的中文名是伸展树,意思差不多就是可以随意翻转的二叉树 PS:百度百科中伸展树读作:BoGa ...
- Splay伸展树入门(单点操作,区间维护)附例题模板
Pps:终于学会了伸展树的区间操作,做一个完整的总结,总结一下自己的伸展树的单点操作和区间维护,顺便给未来的自己总结复习用. splay是一种平衡树,[平均]操作复杂度O(nlogn).首先平衡树先是 ...
- Codeforces 675D Tree Construction Splay伸展树
链接:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/675/D 题意: 给一个二叉搜索树,一开始为空,不断插入数字,每次插入之后,询问他的父亲节点的权值 题解: ...
- UVA 11922 Permutation Transformer —— splay伸展树
题意:根据m条指令改变排列1 2 3 4 … n ,每条指令(a, b)表示取出第a~b个元素,反转后添加到排列尾部 分析:用一个可分裂合并的序列来表示整个序列,截取一段可以用两次分裂一次合并实现,粘 ...
- [算法] 数据结构 splay(伸展树)解析
前言 splay学了已经很久了,只不过一直没有总结,鸽了好久来写一篇总结. 先介绍 splay:亦称伸展树,为二叉搜索树的一种,部分操作能在 \(O( \log n)\) 内完成,如插入.查找.删除. ...
- HDU 4453 Looploop (伸展树splay tree)
Looploop Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- ZOJ3765---Lights (Splay伸展树)
Lights Time Limit: 8 Seconds Memory Limit: 131072 KB Now you have N lights in a line. Don't wor ...
随机推荐
- TypeScript 素描 - 装饰器
/* 装饰器 简单理解为C#中的Attribute 可以装饰到类.函数.讯问符.属性.参数上 语法 @xxx 装饰器其实是一个函数 @xxx 就要有一个 function xxx 多个装饰器可以用来装 ...
- CSS3: box-sizing 属性的简单认识
定义和用法: box-sizing 属性允许您以特定的方式定义匹配某个区域的特定元素. 默认值:content-box; 继承性:无: css版本:css3 语法:box-sizing: conten ...
- Android中BroadCast与Activity之间的通信
在看本文之前,假设你对于Android的广播机制不是非常了解.建议先行阅读我转载的一篇博文:图解 Android 广播机制. 因为本案例比較简单,故直接在此贴出代码,不做过多的阐述. 先上效果截图: ...
- Qt使用AES加密算法对字符串进行加密
因工作需要,需要对字符串进行加密处理,在网上找了很长时间,终于找到了一个可以使用的aes加密算法.其源代码采用c++编写而成,但其头文件引用windows.h,经过修改部分代码,将#inc ...
- Linux下查看显卡型号
查看显卡使用 lspci |grep VGAemos@emos-desktop:~$ lspci -vnn | grep -i vga00:02.0 VGA compatible controller ...
- Java基础知识强化61:经典查找之 常见查找算法小结
一.顺序查找 条件:无序或有序队列. 原理:按顺序比较每个元素,直到找到关键字为止. 时间复杂度:O(n) 二.二分查找(折半查找) 条件:有序数组 原理:查找过程从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正 ...
- JavaScript绑定事件的方法[3种]
在JavaScript中,有三种常用的绑定事件的方法: 在DOM元素中直接绑定: 在JavaScript代码中绑定: 绑定事件监听函数. 一. 在DOM元素中直接绑定 这里的DOM元素,可以理解为HT ...
- x++ and ++x
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6c762bb30101ar1w.html 看到个东西,搞不清的时候可以看看 =.=
- Xcode7国际化(根据系统语言切换App显示的语言) - 元宵节快乐!
老规矩, 上gif 下面是配置的大概流程: 这个是要显示中文的.strings文件的内容和格式 这个是要显示英文的.strings文件的内容和格式 下面是应用名部分: 然后下面是代码部分: impor ...
- NOIP201504推销员
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #in ...
