Focal Loss笔记
论文:《Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection》
Focal Loss 是何恺明设计的为了解决one-stage目标检测在训练阶段前景类和背景类极度不均衡(如1:1000)的场景的损失函数。它是由二分类交叉熵改造而来的。
标准交叉熵
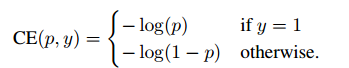
其中,p是模型预测属于类别y=1的概率。为了方便标记,定义:
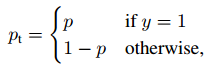
交叉熵CE重写为:

α-平衡交叉熵:
有一种解决类别不平衡的方法是引入一个值介于[0; 1]之间的权重因子α:当y=1时,取α; 当y=0时,取1-α。
这种方法,当y=0(即背景类)时,随着α的增大,会对损失进行很大惩罚(降低权重),从而减轻背景类
太多对训练的影响。
类似Pt,可将α-CE重写为:
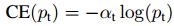
Focal Loss定义
虽然α-CE起到了平衡正负样本的在损失函数值中的贡献,但是它没办法区分难易样本的样本对损失的贡献。因此就有了Focal Loss,定义如下:

其中,alpha和gamma均为可以调节的超参数。y'为模型预测,其值介于(0-1)之间。
当y=1时,y'->1,表示easy positive,它对权重的贡献->0;
当y=0是,y'->0,表示easy negative,它对权重的贡献->0.
因此,Focal Loss不仅降低了背景类的权重,还降低了easy positive/negative的权重。
gamma是对损失函数的调节,当gamma=0是,Focal Loss与α-CE等价。以下是gamma
对Focal Loss的调节。

Focal Loss的Pytorch实现(蓝色字体)
以下Focal Loss=Focal Loss + Regress Loss;
代码来自:https://github.com/yhenon/pytorch-retinanet
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn def calc_iou(a, b):
area = (b[:, 2] - b[:, 0]) * (b[:, 3] - b[:, 1]) iw = torch.min(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 2], dim=1), b[:, 2]) - torch.max(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 0], 1), b[:, 0])
ih = torch.min(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 3], dim=1), b[:, 3]) - torch.max(torch.unsqueeze(a[:, 1], 1), b[:, 1]) iw = torch.clamp(iw, min=0)
ih = torch.clamp(ih, min=0) ua = torch.unsqueeze((a[:, 2] - a[:, 0]) * (a[:, 3] - a[:, 1]), dim=1) + area - iw * ih ua = torch.clamp(ua, min=1e-8) intersection = iw * ih IoU = intersection / ua return IoU class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
#def __init__(self): def forward(self, classifications, regressions, anchors, annotations):
alpha = 0.25
gamma = 2.0
batch_size = classifications.shape[0]
classification_losses = []
regression_losses = [] anchor = anchors[0, :, :] anchor_widths = anchor[:, 2] - anchor[:, 0]
anchor_heights = anchor[:, 3] - anchor[:, 1]
anchor_ctr_x = anchor[:, 0] + 0.5 * anchor_widths
anchor_ctr_y = anchor[:, 1] + 0.5 * anchor_heights for j in range(batch_size): classification = classifications[j, :, :]
regression = regressions[j, :, :] bbox_annotation = annotations[j, :, :]
bbox_annotation = bbox_annotation[bbox_annotation[:, 4] != -1] if bbox_annotation.shape[0] == 0:
regression_losses.append(torch.tensor(0).float().cuda())
classification_losses.append(torch.tensor(0).float().cuda()) continue classification = torch.clamp(classification, 1e-4, 1.0 - 1e-4) IoU = calc_iou(anchors[0, :, :], bbox_annotation[:, :4]) # num_anchors x num_annotations IoU_max, IoU_argmax = torch.max(IoU, dim=1) # num_anchors x 1 #import pdb
#pdb.set_trace() # compute the loss for classification
targets = torch.ones(classification.shape) * -1
targets = targets.cuda() targets[torch.lt(IoU_max, 0.4), :] = 0 positive_indices = torch.ge(IoU_max, 0.5) num_positive_anchors = positive_indices.sum() assigned_annotations = bbox_annotation[IoU_argmax, :] targets[positive_indices, :] = 0
targets[positive_indices, assigned_annotations[positive_indices, 4].long()] = 1 alpha_factor = torch.ones(targets.shape).cuda() * alpha alpha_factor = torch.where(torch.eq(targets, 1.), alpha_factor, 1. - alpha_factor)
82 focal_weight = torch.where(torch.eq(targets, 1.), 1. - classification, classification)
83 focal_weight = alpha_factor * torch.pow(focal_weight, gamma)
84
85 bce = -(targets * torch.log(classification) + (1.0 - targets) * torch.log(1.0 - classification))
86
87 # cls_loss = focal_weight * torch.pow(bce, gamma)
88 cls_loss = focal_weight * bce
89
90 cls_loss = torch.where(torch.ne(targets, -1.0), cls_loss, torch.zeros(cls_loss.shape).cuda())
classification_losses.append(cls_loss.sum()/torch.clamp(num_positive_anchors.float(), min=1.0)) # compute the loss for regression if positive_indices.sum() > 0:
assigned_annotations = assigned_annotations[positive_indices, :] anchor_widths_pi = anchor_widths[positive_indices]
anchor_heights_pi = anchor_heights[positive_indices]
anchor_ctr_x_pi = anchor_ctr_x[positive_indices]
anchor_ctr_y_pi = anchor_ctr_y[positive_indices] gt_widths = assigned_annotations[:, 2] - assigned_annotations[:, 0]
gt_heights = assigned_annotations[:, 3] - assigned_annotations[:, 1]
gt_ctr_x = assigned_annotations[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_widths
gt_ctr_y = assigned_annotations[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_heights # clip widths to 1
gt_widths = torch.clamp(gt_widths, min=1)
gt_heights = torch.clamp(gt_heights, min=1) targets_dx = (gt_ctr_x - anchor_ctr_x_pi) / anchor_widths_pi
targets_dy = (gt_ctr_y - anchor_ctr_y_pi) / anchor_heights_pi
targets_dw = torch.log(gt_widths / anchor_widths_pi)
targets_dh = torch.log(gt_heights / anchor_heights_pi) targets = torch.stack((targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh))
targets = targets.t() targets = targets/torch.Tensor([[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]]).cuda() negative_indices = 1 - positive_indices regression_diff = torch.abs(targets - regression[positive_indices, :]) regression_loss = torch.where(
torch.le(regression_diff, 1.0 / 9.0),
0.5 * 9.0 * torch.pow(regression_diff, 2),
regression_diff - 0.5 / 9.0
)
regression_losses.append(regression_loss.mean())
else:
regression_losses.append(torch.tensor(0).float().cuda()) return torch.stack(classification_losses).mean(dim=0, keepdim=True), torch.stack(regression_losses).mean(dim=0, keepdim=True)
Focal Loss笔记的更多相关文章
- 论文阅读笔记四十四:RetinaNet:Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection(ICCV2017)
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002 github代码:https://github.com/fizyr/keras-retinanet 摘要 目前,具有较高准确 ...
- 深度学习笔记(八)Focal Loss
论文:Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002 一. 提出背景 object detect ...
- 目标检测 | RetinaNet:Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection
论文分析了one-stage网络训练存在的类别不平衡问题,提出能根据loss大小自动调节权重的focal loss,使得模型的训练更专注于困难样本.同时,基于FPN设计了RetinaNet,在精度和速 ...
- Focal Loss理解
1. 总述 Focal loss主要是为了解决one-stage目标检测中正负样本比例严重失衡的问题.该损失函数降低了大量简单负样本在训练中所占的权重,也可理解为一种困难样本挖掘. 2. 损失函数形式 ...
- Focal Loss
为了有效地同时解决样本类别不均衡和苦难样本的问题,何凯明和RGB以二分类交叉熵为例提出了一种新的Loss----Focal loss 原始的二分类交叉熵形式如下: Focal Loss形式如下: 上式 ...
- Focal Loss(RetinaNet) 与 OHEM
Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection-RetinaNet YOLO和SSD可以算one-stage算法里的佼佼者,加上R-CNN系列算法,这几种算法可以说是目标检 ...
- Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection 论文阅读
何凯明大佬 ICCV 2017 best student paper 作者提出focal loss的出发点也是希望one-stage detector可以达到two-stage detector的准确 ...
- Focal Loss 的前向与后向公式推导
把Focal Loss的前向和后向进行数学化描述.本文的公式可能数学公式比较多.本文尽量采用分解的方式一步一步的推倒.达到能易懂的目的. Focal Loss 前向计算 其中 是输入的数据 是输入的标 ...
- focal loss和ohem
公式推导:https://github.com/zimenglan-sysu-512/paper-note/blob/master/focal_loss.pdf 使用的代码:https://githu ...
随机推荐
- 【刷题】HDU 1853 Cyclic Tour
Problem Description There are N cities in our country, and M one-way roads connecting them. Now Litt ...
- [洛谷P4705]玩游戏
题目大意:对于每个$k\in[1,t]$,求:$$\dfrac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^n\sum\limits_{j=1}^m(a_i+b_j)^k}{nm}$$$n,m,t\leqsl ...
- Java开发23种设计模式
设计模式(Design Patterns) -- -- -- 可复用面向对象软件的基础 设计模式(Design Patterns)是一套被反复使用.多数人知晓的.经过分类编目的.代码设计经验的总结. ...
- WEB入门.八 背景特效
学习内容 background属性 CSS Sprite 技术 滑动门技术 能力目标 使用background设置网页背景 使用Sprites制作平滑投票特效 使用滑动门技术实现Tab菜单 本章简介 ...
- 前端学习 -- Css -- 兄弟元素选择器
为一个元素后边的元素设置css样式: 语法:前一个 + 后一个. 作用:可以选中一个元素后紧挨着的指定的兄弟元素. 为一个元素后边的所有相同元素设置css样式: 语法:前一个 ~ 后边所有. < ...
- 解题:USACO14MAR Counting Friends
题面 枚举每个数字是否能被删去,然后就是如何判定图是否存在.应该从按“度数”从大到小排序,从最大的顺次向其他点连边(先连“度数”小的可能会把一些可以和大“度数”点连接的点用掉).但是这个排序每连一次都 ...
- PACS&DICOM
What is DICOM, PACS, and Workstation? What is DICOM? We will take them one at a time – So first of a ...
- Java虚拟机性能监控与调优
1 基于JDK命令行工具的监控 1.1 JVM的参数类型 1.1.1 标准参数 在JVM的各个版本基本上保持不变,很稳定的. -help -server -client -version -showv ...
- iterm2切换显示屏vim乱行解决
http://note.youdao.com/noteshare?id=5aec9d82cc3a95b6909e9966b4aa3227
- python map对象
工作中遇到需要将List对象中的元素(list类型)转化为集合(set)类型,转化完成之后需要需要访问其中的元素. 第一步,使用map方法进行转换 data = [[1, 3, 4], [2, 3, ...
