.23-浅析webpack源码之事件流compilation(1)
正式开始跑编译,依次解析,首先是:
compiler.apply(
new JsonpTemplatePlugin(options.output),
// start
new FunctionModulePlugin(options.output),
new NodeSourcePlugin(options.node),
new LoaderTargetPlugin(options.target)
);
流程图如下:
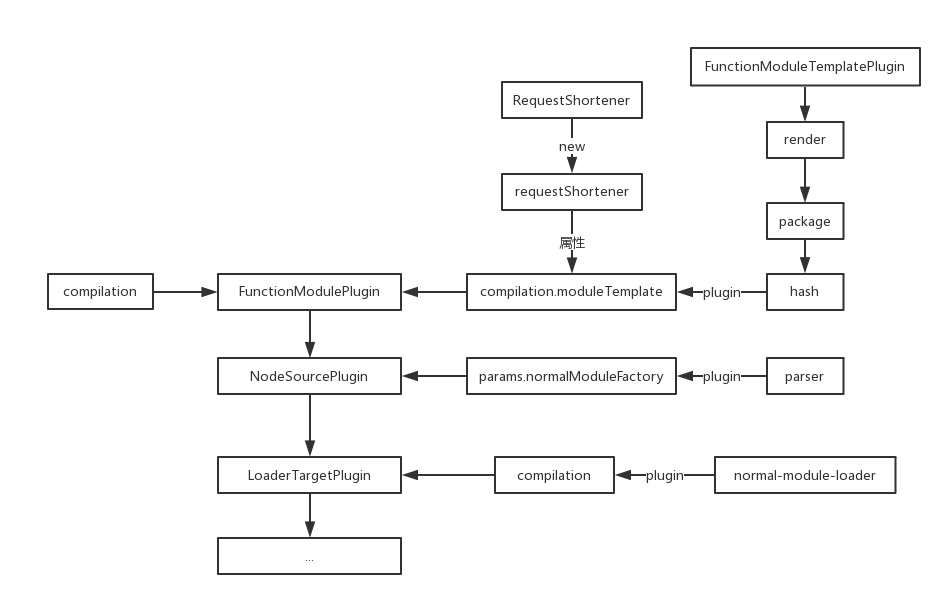
这里是第一个compilation事件注入的地方,注入代码如下:
compiler.plugin("compilation", (compilation) => {
compilation.moduleTemplate.requestShortener = this.requestShortener || new RequestShortener(compiler.context);
compilation.moduleTemplate.apply(new FunctionModuleTemplatePlugin());
});
这里的requestShortener为FunctionModulePlugin的第二个参数,没有传所以是undefined。
options.output为传入的output参数,但是这里并没有用到,而是传入了compiler.context,如果没有传默认为命令执行路径。
RequestShortener
首先看第一个,源码简化如下:
"use strict";
const path = require("path");
// 匹配反斜杠 => \
const NORMALIZE_SLASH_DIRECTION_REGEXP = /\\/g;
// 匹配特殊字符
const PATH_CHARS_REGEXP = /[-[\]{}()*+?.,\\^$|#\s]/g;
// 匹配正反斜杠 => /\
const SEPARATOR_REGEXP = /[/\\]$/;
// 匹配以'!'开头或结尾
const FRONT_OR_BACK_BANG_REGEXP = /^!|!$/g;
// 匹配 /index.js
const INDEX_JS_REGEXP = /\/index.js(!|\?|\(query\))/g;
// 将反斜杠替换为正斜杠
const normalizeBackSlashDirection = (request) => {
return request.replace(NORMALIZE_SLASH_DIRECTION_REGEXP, "/");
};
// 将路径中特殊字符转义 例如 - => \-
// 返回一个正则
const createRegExpForPath = (path) => {
const regexpTypePartial = path.replace(PATH_CHARS_REGEXP, "\\$&");
return new RegExp(`(^|!)${regexpTypePartial}`, "g");
};
class RequestShortener {
constructor(directory) { /**/ }
shorten(request) { /**/ }
}
module.exports = RequestShortener;
可以看到都是对路径做处理,正则都比较简单,接下来看一下构造函数,其中传进来的directory为命令执行上下文。
class RequestShortener {
constructor(directory) {
// 斜杠转换
directory = normalizeBackSlashDirection(directory);
// 没看懂啥用
if (SEPARATOR_REGEXP.test(directory)) directory = directory.substr(0, directory.length - 1);
// 上下文路径正则
// /(^|!)转义后的路径/g
if (directory) {
this.currentDirectoryRegExp = createRegExpForPath(directory);
}
// 返回目录名
const dirname = path.dirname(directory);
// 这里也不懂干啥用的
const endsWithSeperator = SEPARATOR_REGEXP.test(dirname);
const parentDirectory = endsWithSeperator ? dirname.substr(0, dirname.length - 1) : dirname;
// 目录正则
if (parentDirectory && parentDirectory !== directory) {
this.parentDirectoryRegExp = createRegExpForPath(parentDirectory);
}
// .....\node_modules\webpack\lib
if (__dirname.length >= 2) {
// webpack的目录
const buildins = normalizeBackSlashDirection(path.join(__dirname, ".."));
// 目录检测
const buildinsAsModule = this.currentDirectoryRegExp && this.currentDirectoryRegExp.test(buildins);
// false
this.buildinsAsModule = buildinsAsModule;
// 生成webpack目录路径正则
this.buildinsRegExp = createRegExpForPath(buildins);
}
}
shorten(request) { /**/ }
}
主要是生成了3个目录匹配正则,上下文、上下文目录、webpack主目录三个。
这里上下文一般不会是webpack的目录,所以这个buildingsAsModule理论上都是flase。
再简单看一下原型方法shorten:
class RequestShortener {
constructor(directory) { /**/ }
shorten(request) {
if (!request) return request;
// 转化路径斜杠
request = normalizeBackSlashDirection(request);
// false
if (this.buildinsAsModule && this.buildinsRegExp)
request = request.replace(this.buildinsRegExp, "!(webpack)");
// 将上下文转换为!.
if (this.currentDirectoryRegExp)
request = request.replace(this.currentDirectoryRegExp, "!.");
// 将上下文目录转换为!..
if (this.parentDirectoryRegExp)
request = request.replace(this.parentDirectoryRegExp, "!..");
// false
if (!this.buildinsAsModule && this.buildinsRegExp)
request = request.replace(this.buildinsRegExp, "!(webpack)");
// 把路径中的index.js去了 留下参数
// /index.js?a=1 => ?a=1
request = request.replace(INDEX_JS_REGEXP, "$1");
// 把头尾的!去了
return request.replace(FRONT_OR_BACK_BANG_REGEXP, "");
}
}
可以看出,这个方法将传入的路径根据上下文的目录进行简化,变成了相对路径,然后去掉了index.js。
FunctionModuleTemplatePlugin
这个模块没有实质性内容,主要是对compilation.moduleTemplate注入事件流,源码如下:
"use strict";
const ConcatSource = require("webpack-sources").ConcatSource;
class FunctionModuleTemplatePlugin {
apply(moduleTemplate) {
moduleTemplate.plugin("render", function(moduleSource, module) { /**/ });
moduleTemplate.plugin("package", function(moduleSource, module) { /**/ });
moduleTemplate.plugin("hash", function(hash) { /**/ });
}
}
module.exports = FunctionModuleTemplatePlugin;
等触发的时候再回头看。
ConcatSource后面单独讲。
下面是第二个插件,源码整理如下:
class NodeSourcePlugin {
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
}
apply(compiler) {
const options = this.options;
if (options === false) // allow single kill switch to turn off this plugin
return;
function getPathToModule(module, type) { /**/ }
function addExpression(parser, name, module, type, suffix) { /**/ }
compiler.plugin("compilation", function(compilation, params) {
params.normalModuleFactory.plugin("parser", function(parser, parserOptions) { /**/ });
});
compiler.plugin("after-resolvers", (compiler) => { /**/ });
}
};
可以看到,这里只是简单判断了是否关闭了node插件,然后在之前的params参数中的normalModuleFactory属性上注入了一个parser事件。
第三个插件就更简单了,如下:
class LoaderTargetPlugin {
constructor(target) {
this.target = target;
}
apply(compiler) {
compiler.plugin("compilation", (compilation) => {
// 这个完全不懂干啥的
compilation.plugin("normal-module-loader", (loaderContext) => loaderContext.target = this.target);
});
}
}
这个plugin目前根本看不出来有什么用。
总之,前三个compilation比较水,没有什么内容。
.23-浅析webpack源码之事件流compilation(1)的更多相关文章
- .24-浅析webpack源码之事件流compilation(2)
下一个compilation来源于以下代码: compiler.apply(new EntryOptionPlugin()); compiler.applyPluginsBailResult(&quo ...
- .22-浅析webpack源码之事件流compilation总览
呃,终于到了这地方-- newCompilation(params) { // ... this.applyPlugins("this-compilation", compilat ...
- .25-浅析webpack源码之事件流compilation(3)
这一节跑下一批plugin. compiler.apply( new EnsureChunkConditionsPlugin(), new RemoveParentModulesPlugin(), n ...
- .21-浅析webpack源码之事件流this-compilation
上一节生成Compilation实例后,添加了一些属性,随后触发this-compilation事件流,如下: Compiler.prototype.newCompilation = (params) ...
- .34-浅析webpack源码之事件流make(3)
新年好呀~过个年光打游戏,function都写不顺溜了. 上一节的代码到这里了: // NormalModuleFactory的resolver事件流 this.plugin("resolv ...
- .27-浅析webpack源码之事件流make(2)
上一节跑到了NormalModuleFactory模块,调用了原型方法create后,依次触发了before-rsolve.factory.resolver事件流,这节从resolver事件流开始讲. ...
- .26-浅析webpack源码之事件流make(1)
compilation事件流中,依然只是针对细节步骤做事件流注入,代码流程如图: // apply => this-compilation // apply => compilation ...
- .37-浅析webpack源码之事件流make(4)
赶紧完结这个系列咯,webpack4都已经出正式版了. 之前的代码搜索到js文件的对应loader,并添加到了对象中返回,流程如下: this.plugin("factory", ...
- 浅析libuv源码-node事件轮询解析(3)
好像博客有观众,那每一篇都画个图吧! 本节简图如下. 上一篇其实啥也没讲,不过node本身就是这么复杂,走流程就要走全套.就像曾经看webpack源码,读了300行代码最后就为了取package.js ...
随机推荐
- pstree 命令详解
作用: 以命令树状图的方式展现进程之间的派生关系, 显示效果比较直观. 选项: -a 显示每个程序的完整指令, 包含路径, 参数或者是常驻服务的标志 -c 不使用精简标示法 -h 列出树状图,特别标明 ...
- 【简单理解】gulp和webpack的区别
Gulp和Webpack的基本区别: gulp可以进行js,html,css,img的压缩打包,是自动化构建工具,可以将多个js文件或是css压缩成一个文件,并且可以压缩为一行,以此来减少文件体积,加 ...
- 【转】nginx提示:500 Internal Server Error错误的解决方法
本文转自:http://www.jb51.net/article/35675.htm 现在越来越多的站点开始用 Nginx ,("engine x") 是一个高性能的 HTTP 和 ...
- ITS简要分析流程(using Qiime)
Qiime安装 参考资料:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_83f77c940101h2rp.html Qiime script官方说明http://qiime.org/s ...
- 面试经验And总结
作为一个实习生,我大二即将读完,因为自己是大专的和本科没法比,没有他们的 知识基础,没有他们的充裕的时间,没有那个本科毕业证,没有学位证书.作为一个大专生我在找工作的时候总是充满了自卑,可自己有事那种 ...
- vue2.0 关于Vue实例的生命周期
什么是生命周期 Vue实例有一个完整的生命周期,也就是从开始创建.初始化数据.编译模板.挂载Dom.渲染→更新→渲染.卸载等一系列过程,我们称这是Vue的生命周期.通俗说就是Vue实例从创建到销毁的过 ...
- 2018年手机应用UI设计趋势预测
用户需求瞬息万变,而手机软件UI设计为适应变化的用户需求,也相应的发生着变化.但是,这并不意味着用户需求和UI设计趋势就是无迹可寻的.事实上,根据前几年的手机app界面设计变化的特点,尤其是2017年 ...
- voip技术研究
voip:是一种通过ip现实电话通信的技术统称 sip:voip现在一般都采用sip协议 参考资料: android sip学习 问题: SipManager.newInstance(this)为nu ...
- ionic2 App搭建(三)
cmd命令提示框中进入项目文件夹 运行命令 ionic serve --lab 结构如下图 这里数据是没有接受到的,是因为跨域的问题,解决方案是谷歌浏览器配置跨域指令如下: 配置chrome浏览器允 ...
- 使用Git命令把本地项目上传到github上托管
(1)在github上,新建一个仓库 (2)打开git-bash,进入项目目录下 (3)git init (4)git add . (5)git status (6)git commit -m &qu ...
