JavaSE编码试题强化练习3
1.给20块钱买可乐,每瓶可乐3块钱,喝完之后退瓶子可以换回1块钱,问最多可以喝到多少瓶可乐。
public class TestCirculation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int money = 20;
int price = 3;
/**
* temp为每一次可以买的可乐的瓶数
*/
int temp = 0;
/**
* change表示每次购买完可乐剩下的钱
*/
int change = 0;
/**
* sum表示总的可乐瓶数
*/
int sum = 0;
/**
* 判断条件:如果钱数大于可乐价格
*/
while (money >= price){
/**
* 购买可乐
*/
temp = money / price;
/**
* 可乐总瓶数增加
*/
sum += temp;
/**
* 计算剩下的钱
*/
change = money % price;
/**
* 兑换可乐瓶子,计算剩余的总钱数
*/
money = change + temp;
}
/**
* 输出结果
*/
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
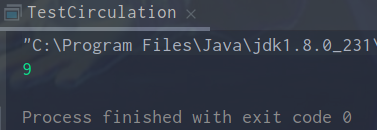
运行结果:
2.写一个方法对任意数据类型数组进行排序。
public class TestSortArr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String [] str = {"D","C","B","A"};
sortArr(str);
}
public static void sortArr(Object [] arr){
/**
* 输出排序前的数组
*/
System.out.print("排序前:");
for (int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
/**
* 大循环,一共n个元素,达到最终有序,至多n - 1趟循环
*/
Object temp;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1;i++) {
/**
* 定义一个符号量,没发生交换,有序
*/
boolean flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
/**
* 小循环
*/
Comparable c1 = (Comparable)arr[j];
Comparable c2 = (Comparable)arr[j + 1];
if (c1.compareTo(c2) > 0){
/**
* 交换
*/
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
/**
* 修改符号量,交换过,无序
*/
flag = false;
}
}
/**
* 判断一趟小循环下来数组是否有序
*/
if (flag){
/**
* 中断循环
*/
break;
}
}
/**
* 输出排序后的数组
*/
System.out.print("排序后:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
}
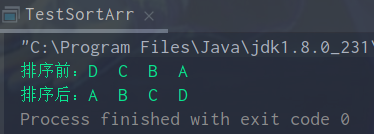
运行结果:
3. 实现List和Map数据的转换。
思路:
功能1:定义方法public static void listToMap( ){ }将List中Student元素封装到Map中
1) 使用构造方法Student(int stuId, String name, int age, double score)创建多个学生信息并加入List
2) 遍历List,输出每个Student信息
3) 将List中数据放入Map,使用Student的stuId属性作为key,使用Student对象信息作为value
4) 遍历Map,输出每个Entry的key和value
功能2:定义方法public static void mapToList( ){ }将Map中Student映射信息封装到List
1) 创建实体类StudentEntry,可以存储Map中每个Entry的信息
2) 使用构造方法Student(int stuId, String name, int age, double score)创建多个学生信息,并使用Student的stuId属性作为key,存入Map
3) 创建List对象,每个元素类型是StudentEntry
4) 将Map中每个Entry信息放入List对象,遍历List输出key和value
/**
* 创建学生类,实现Comparable接口
*/
public class Student {
/**
* 私有属性:学号,姓名,年龄,分数
*/
private int stuId;
private String name;
private int age;
private double score;
/**
*构造方法
*/
public Student() {
} public Student(int stuId, String name, int age, double score) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
/**
* getter和setter方法
*/
public int getStuId() {
return stuId;
} public void setStuId(int stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} public double getScore() {
return score;
} public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stuId=" + stuId +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
public class TestListToMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
listToMap();
}
public static void listToMap(){
/**
* 1.创建多个学生信息
*/
Student stu1 = new Student(1101,"张三",22,98.0);
Student stu2 = new Student(1102,"李思",23,78.0);
Student stu3 = new Student(1103,"王武",22,92.0);
Student stu4 = new Student(1104,"孙琦",21,98.0);
/**
* 2.加入List
*/
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
list.add(stu1);
list.add(stu2);
list.add(stu3);
list.add(stu4);
/**
* 3.遍历List,输出每个学生的信息
*/
Iterator it1 = list.iterator();
while (it1.hasNext()){
Student stu = (Student) it1.next();
System.out.println(stu);
}
System.out.println(
"=============================================================");
/**
* 4.将List中数据存入Map,用Student的stuId属性作为key
*/
Map<Integer,Student> map = new HashMap<Integer,Student>();
/*map.put(stu1.getStuId(),stu1);
map.put(stu2.getStuId(),stu2);
map.put(stu3.getStuId(),stu3);
map.put(stu4.getStuId(),stu4);*/
Iterator it2 = list.iterator();
while (it2.hasNext()){
Student stu = (Student) it2.next();
map.put(stu.getStuId(),stu);
}
/**
* 5.遍历Map,输出每个Entry的key和value
*/
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,Student>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Student> entry : entrySet){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"---->"+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
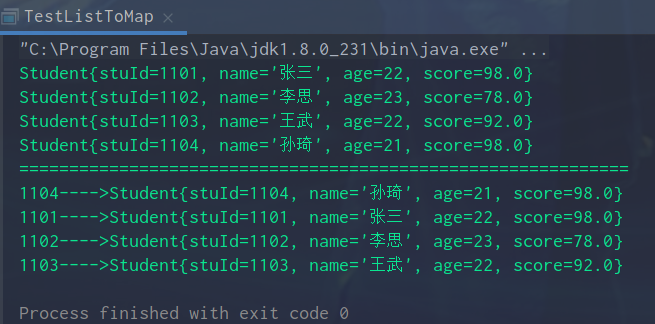
运行结果:
/**
* 创建StudentEntry存放key和value的映射关系
*/
public class StudentEntry {
/**
* key-->stuId
* value-->stu
*/
private int key;
private Student stu;
/**
* getter setter方法
*/
public void setKey(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public void setStu(Student stu) {
this.stu = stu;
} public int getKey() {
return key;
} public Student getStu() {
return stu;
}
}
public class TestMapToList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
mapToList();
}
public static void mapToList(){
/**
* 创建多个学生信息
*/
Student stu1 = new Student(1101,"张三",22,98.0);
Student stu2 = new Student(1102,"李思",23,78.0);
Student stu3 = new Student(1103,"王武",22,92.0);
Student stu4 = new Student(1104,"孙琦",21,98.0);
/**
* 使用Student的id属性作为key,存入Map
*/
Map<Integer,Student> map = new HashMap<Integer,Student>();
map.put(stu1.getStuId(),stu1);
map.put(stu2.getStuId(),stu2);
map.put(stu3.getStuId(),stu3);
map.put(stu4.getStuId(),stu4);
/**
* 遍历Map
*/
Set<Entry<Integer,Student>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<Integer,Student> entry : entrySet){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"---->"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println(
"============================================================");
/**
* 创建List对象,每个元素的类型都是StudentEntry
* 需创建StudentEntry实体类包含key--stuId和value--stu
*/
List<StudentEntry> list = new ArrayList<StudentEntry>();
/**
* 将Map对象转化为List集合
*/
for (Entry<Integer,Student> entry : map.entrySet()){
StudentEntry studentEntry = new StudentEntry();
/**
* 将Map中的一个映射关系,封装为一个StudentEntry对象
*/
studentEntry.setKey(entry.getKey());
studentEntry.setStu(entry.getValue());
/**
* 将Student对象List集合
*/
list.add(studentEntry);
}
/**
* 遍历List
*/
Iterator<StudentEntry> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
StudentEntry se = it.next();
System.out.println(se.getStu());
}
}
}
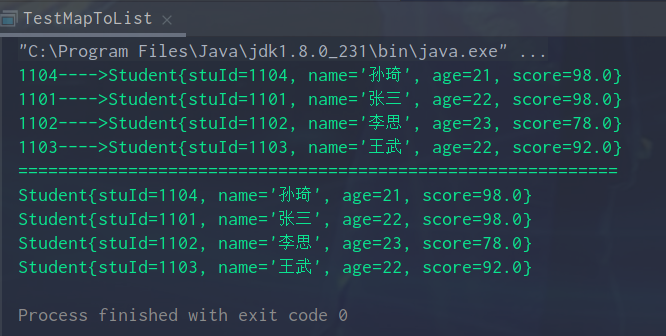
运行结果:
JavaSE编码试题强化练习3的更多相关文章
- JavaSE编码试题强化练习1
1. 编写应用程序,创建类的对象,分别设置圆的半径.圆柱体的高,计算并分别显示圆半径.圆面积.圆周长,圆柱体的体积. /** * 定义父类--圆类 */ public class Circle { / ...
- JavaSE编码试题强化练习7
1.编写应用程序,创建类的对象,分别设置圆的半径.圆柱体的高,计算并分别显示圆半径.圆面积.圆周长,圆柱体的体积. /** * 圆类 */ public class Circle { /** * 类属 ...
- JavaSE编码试题强化练习6
1.写出选择排序的代码实现,对一个int数组进行排序 public class TestSelectSort { public static void main(String[] args) { in ...
- JavaSE编码试题强化练习5
1.不使用函数实现字符串的翻转 /** * 1.不使用函数实现字符串的翻转 */ public class TestStringReverse { public static void main(St ...
- JavaSE编码试题强化练习4
1.编写一个Worker类,为Worker类添加相应的代码,使得Worker对象能正确放入TreeSet中.并编写相应的测试代码. /** * Worker类 */ public class Work ...
- JavaSE编码试题强化练习2
1.编写递归算法程序:一列数的规则如下: 0.1.1.2.3.5.8.13.21.34...... 求数列的第40位数是多少. public class TestRecursion { public ...
- JavaSE面试题
JavaSE面试题 欢迎到我的Git仓库去提交您觉得优秀的内容! 1.是否可以从一个static方法内部发出对非static方法的调用? 不可以.当一个static方法被调用时,可能还没有创建任何实例 ...
- [002] - JavaSE面试题(二):基本数据类型与访问修饰符
第一期:Java面试 - 100题,梳理各大网站优秀面试题.大家可以跟着我一起来刷刷Java理论知识 [002] - JavaSE面试题(二):基本数据类型与访问修饰符 第1问:Java的数据类型有哪 ...
- JavaSE 面试题: 类初始化和实例初始化等
JavaSE 面试题 类初始化和实例初始化等 class Father { private int i = test(); private static int j = method(); stati ...
随机推荐
- 【长期计划】Atcoder题目泛做
之前学长跟我说的是700-的应该都能自己做? 然后1000-的应该都能有一定的思路? 记不清了 但总之是要智力康复一下 又加上文化课比较紧 所以这个大概就会是长期计划了 ————————————分鸽线 ...
- Debian10+OpenMediaVault(OMV)安装
前言:测试打造NAS平台,以下是步骤. 安装Debian10 注:请下载amd64,不要下载i836平台,因为OMV外挂插件不支持I836所以不建议用i836,如只使用官方插件可以无视 安装前-安装, ...
- GDKOI2016总结——被虐之旅
前言 一个被虐的旅程... 这次GDKOI的比赛虽然基本全上暴力,但是居然只有两道题得了分:30+30=60!我感觉整个人都不好了... day0 在去广州的路上,本来心情很好,但是坐在我斜后面的那位 ...
- Pytest安装介绍--使用(html报告)
Pytes是 一个单元测试框架,可以生成html报告. #卸载# pip uninstall pytest#安装# pip install -U pytest# 查看# pytest --versio ...
- Bugku 杂项 隐写
隐写 下载后打开压缩包发现是一张图片 用winhex打开 图中红色框内是PNG的PE头 在IHDR后面的八个字节(黄色框部分)为该图片的长度.宽度信息 将黄色框内最后一个字节由A4改为F4后另存为图片 ...
- POJ 3261 Milk Patterns ( 后缀数组 && 出现k次最长可重叠子串长度 )
题意 : 给出一个长度为 N 的序列,再给出一个 K 要求求出出现了至少 K 次的最长可重叠子串的长度 分析 : 后缀数组套路题,思路是二分长度再对于每一个长度进行判断,判断过程就是对于 Height ...
- 软件工程 in MSRA Code Search-第二次结对编程
重现基线模型 我们选择了 code2vec 模型进行复现.该模型由 Uri Alon 等作者于 2018 年提出. 模型思路: 从代码与普通语言相比的特殊性入手,首先,对于输入的代码段,作者考虑到尽管 ...
- Spring Cloud架构教程 (六)消息驱动的微服务【Dalston版】
Spring Cloud Stream是一个用来为微服务应用构建消息驱动能力的框架.它可以基于Spring Boot来创建独立的.可用于生产的Spring应用程序.它通过使用Spring Integr ...
- 个推一键认证SDK重磅推出,打造秒级登录体验,让用户一“键”倾心
移动互联网时代,用户注意力的持续时间越来越短,他们追求便捷与高效.从账号密码登录.短信验证,到第三方登录甚至人脸识别登录,APP的注册/登录方式在逐步变化,开发者希望在这重要的交互端口提升用户的体验, ...
- RESTful风格编程
参考文档:http://blog.didispace.com/springbootrestfulapi/ https://www.jianshu.com/p/91600da4df95 *)RESTfu ...
