讲讲Handler+Looper+MessageQueue 关系
Handler+Looper+MessageQueue这三者的关系其实就是Android的消息机制。这块内容相比开发人员都不陌生,在面试中,或者日常开发中都会碰到,今天就来讲这三者的关系。
概述:
Handler 、 Looper 、Message 这三者都与Android异步消息处理线程相关的概念。那么什么叫异步消息处理线程呢?
关系图:
先给出这三者之间的关系图
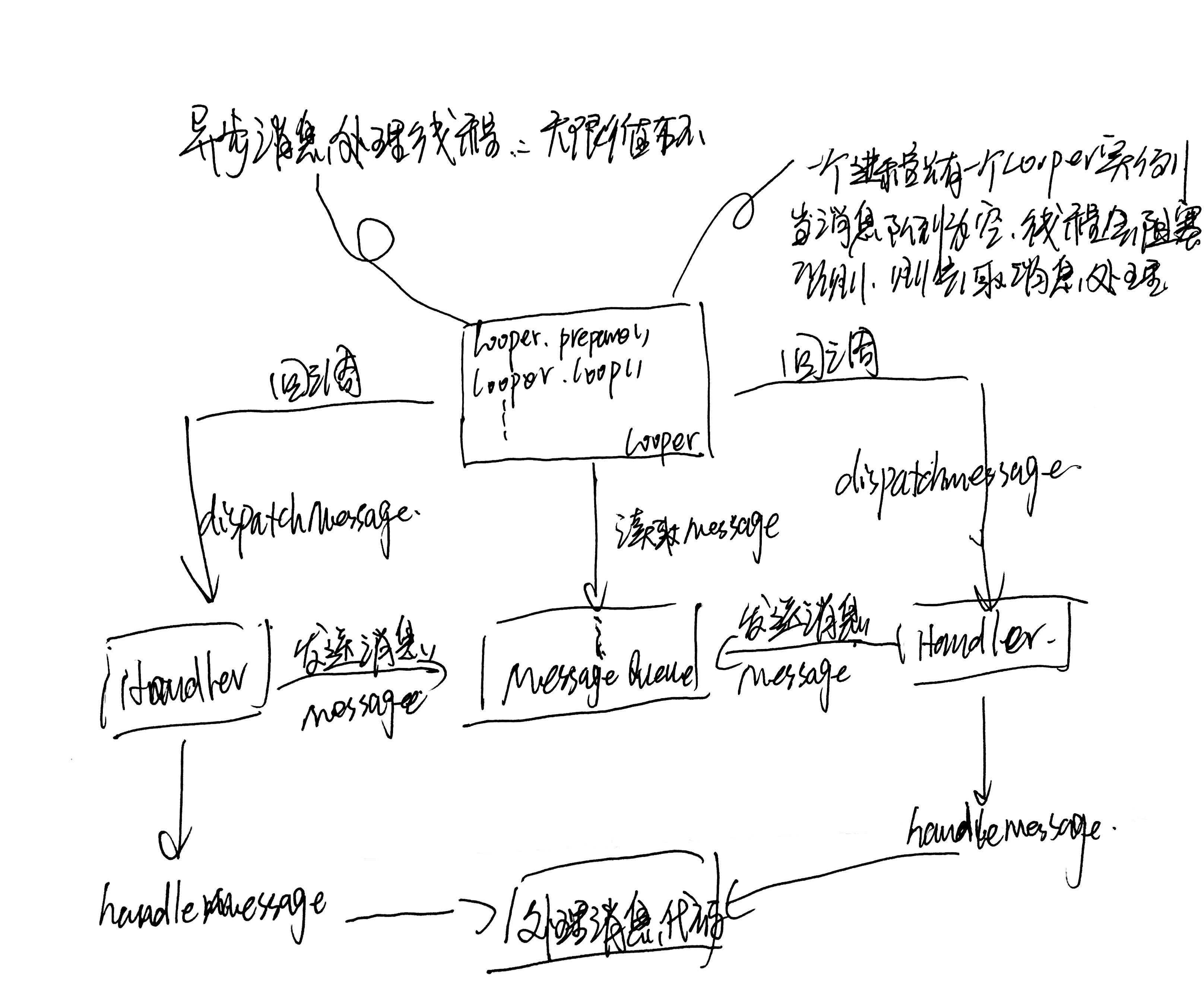
原因:
Looper类
Looper扮演的角色就是消息循环,不断从MessageQueue中查看是否有新消息,如果有新消息到来就会立刻处理,否则就一直祖塞在那里,在它的构造方法,默认会创建一个MessageQueue的消息队列,然后将当前线程的对象保存起来。
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mRun = true;
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
对于Looper主要是prepare()和loop()两个方法,首先看prepare()方法。
public static final void prepare() {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(true));
}
sThreadLocal是一个ThreadLocal对象,可以在一个线程中存储变量。可以看到,在第5行,将一个Looper的实例放入了ThreadLocal,并且2-4行判断了sThreadLocal是否为null,否则抛出异常。这也就说明了Looper.prepare()方法不能被调用两次,同时也保证了一个线程中只有一个Looper实例
然后我们看loop()方法:
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
msg.recycle();
}
}
方法直接返回了sThreadLocal存储的Looper实例,如果me为null则抛出异常,也就是说looper方法必须在prepare方法之后运行。
拿到该looper实例中的mQueue(消息队列)
就进入了我们所说的无限循环。
取出一条消息,如果没有消息则阻塞。
使用调用 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);把消息交给msg的target的dispatchMessage方法去处理。Msg的target是什么呢?其实就是handler对象,下面会进行分析。
释放消息占据的资源。
Looper主要作用:
1、 与当前线程绑定,保证一个线程只会有一个Looper实例,同时一个Looper实例也只有一个MessageQueue。
2、 loop()方法,不断从MessageQueue中去取消息,交给消息的target属性的dispatchMessage去处理。
好了,我们的异步消息处理线程已经有了消息队列(MessageQueue),也有了在无限循环体中取出消息的哥们,现在缺的就是发送消息的对象了,于是乎:Handler登场了。
Handler类
public Handler() {
this(null, false);
}
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
klass.getCanonicalName());
}
}
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
通过Looper.myLooper()获取了当前线程保存的Looper实例,然后在19行又获取了这个Looper实例中保存的MessageQueue(消息队列),这样就保证了handler的实例与我们Looper实例中MessageQueue关联上了。
然后看我们最常用的sendMessage方法
public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
} public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) {
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis);
} public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis)
{
if (delayMillis < 0) {
delayMillis = 0;
}
return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
} public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
最后调用了sendMessageAtTime,在此方法内部有直接获取MessageQueue然后调用了enqueueMessage方法,我们再来看看此方法:
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
enqueueMessage中首先为meg.target赋值为this,如果大家还记得Looper的loop方法会取出每个msg然后交给msg,target.dispatchMessage(msg)去处理消息,也就是把当前的handler作为msg的target属性。最终会调用queue的enqueueMessage的方法,也就是说handler发出的消息,最终会保存到消息队列中去。
现在已经很清楚了Looper会调用prepare()和loop()方法,在当前执行的线程中保存一个Looper实例,这个实例会保存一个MessageQueue对象,然后当前线程进入一个无限循环中去,不断从MessageQueue中读取Handler发来的消息。然后再回调创建这个消息的handler中的dispathMessage方法,下面我们赶快去看一看这个方法:
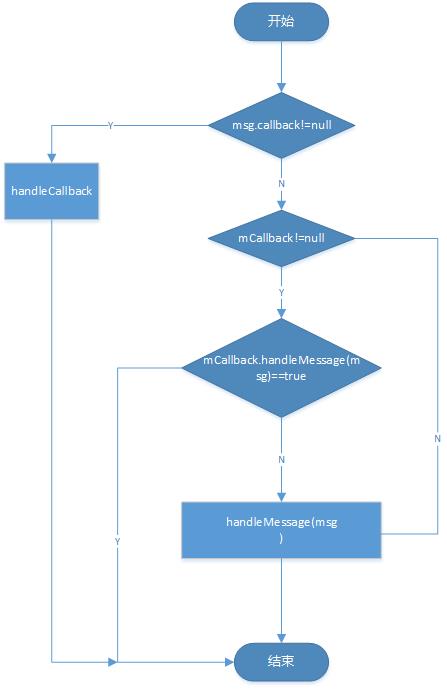
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
/**
* Subclasses must implement this to receive messages.
*/
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
}
可以看到这是一个空方法,为什么呢,因为消息的最终回调是由我们控制的,我们在创建handler的时候都是复写handleMessage方法,然后根据msg.what进行消息处理。
1、首先Looper.prepare()在本线程中保存一个Looper实例,然后该实例中保存一个MessageQueue对象;因为Looper.prepare()在一个线程中只能调用一次,所以MessageQueue在一个线程中只会存在一个。
2、Looper.loop()会让当前线程进入一个无限循环,不端从MessageQueue的实例中读取消息,然后回调msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)方法。
3、Handler的构造方法,会首先得到当前线程中保存的Looper实例,进而与Looper实例中的MessageQueue想关联。
4、Handler的sendMessage方法,会给msg的target赋值为handler自身,然后加入MessageQueue中。
5、在构造Handler实例时,我们会重写handleMessage方法,也就是msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)最终调用的方法。
Handler Post
看代码
public final boolean post(Runnable r)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);
}
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) {
Message m = Message.obtain();
m.callback = r;
return m;
}
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis)
{
if (delayMillis < 0) {
delayMillis = 0;
}
return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
}
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
可以看到,在getPostMessage中,得到了一个Message对象,然后将我们创建的Runable对象作为callback属性,赋值给了此message.
注:产生一个Message对象,可以new ,也可以使用Message.obtain()方法;两者都可以,但是更建议使用obtain方法,因为Message内部维护了一个Message池用于Message的复用,避免使用new 重新分配内存。最终和handler.sendMessage一样,调用了sendMessageAtTime,然后调用了enqueueMessage方法,给msg.target赋值为handler,最终加入MessagQueue.
可以看到,这里msg的callback和target都有值,那么会执行哪个呢?
dispatchMessage方法
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
Handler使用流程图:
阅读扩展

讲讲Handler+Looper+MessageQueue 关系的更多相关文章
- Handler Looper MessageQueue 之间的关系
Handler Looper MessageQueue 之间的关系 handler在安卓开发中常用于更新界面ui,以及其他在主线程中的操作.内部结构大概图为: 1.handler持有一个Looper对 ...
- Handler+Looper+MessageQueue深入详解
概述:Android中的异步处理机制由四部分组成:Handler+Looper+MessageQueue+message,用于实现线程间的通信. 用到的概念: Handler: 主要作用是发送消息和处 ...
- Handler,Looper,MessageQueue流程梳理
目的:handle的出现主要是为了解决线程间通讯. 举个例子,android是不允许在主线程中访问网络,因为这样会阻塞主线程,影响性能,所以访问网络都是放在子线程中执行,对于网络返回的结果则需要显示在 ...
- android学习11——Handler,Looper,MessageQueue工作原理
Message是Handler接收和处理的消息对象. 每个线程只能拥有一个Looper.它的loop方法读取MessageQueue中的消息,读到消息之后就把消息交给发送该消息的Handler进行处理 ...
- Android异步处理三:Handler+Looper+MessageQueue深入详解
在<Android异步处理一:使用Thread+Handler实现非UI线程更新UI界面>中,我们讲到使用Thread+Handler的方式来实现界面的更新,其实是在非UI线程发送消息到U ...
- Handler Looper 解析
文章讲述Looper/MessageQueue/Handler/HandlerThread相关的技能和使用方法. 什么是Looper?Looper有什么作用? Looper是用于给线程(Thread) ...
- Android消息机制:Looper,MessageQueue,Message与handler
Android消息机制好多人都讲过,但是自己去翻源码的时候才能明白. 今天试着讲一下,因为目标是讲清楚整体逻辑,所以不追究细节. Message是消息机制的核心,所以从Message讲起. 1.Mes ...
- Android Handler处理机制 ( 三 ) ——Handler,Message,Looper,MessageQueue
在android中提供了一种异步回调机制Handler,使用它,我们可以在完成一个很长时间的任务后做出相应的通知 handler基本使用: 在主线程中,使用handler很简单,new一个Handle ...
- 解析Android消息处理机制:Handler/Thread/Looper & MessageQueue
解析Android消息处理机制 ——Handler/Thread/Looper & MessageQueue Keywords: Android Message HandlerThread L ...
随机推荐
- Secret Codes
Secret Codes This is a list of codes that can be entered into the dialer to output the listed info ...
- 解剖SQLSERVER 第十二篇 OrcaMDF 行压缩支持(译)
解剖SQLSERVER 第十二篇 OrcaMDF 行压缩支持(译) http://improve.dk/orcamdf-row-compression-support/ 在这两个月的断断续续的开发 ...
- SVN分支管理策略个人见解
本篇目录 前言 SVN分支管理策略 VisualSVN Server TortoiseSVN客户端 Repository的创建 Check out trunk创建新项目MyProject trunk更 ...
- 我的ORM之三 -- 更新
我的ORM索引 更新语法 var 影响行数 = dbr.表.Update(实体).Where(条件).Execute(); 实体类型: 更新的实体类型和添加的实体类型一样,有三类: 1. 任何C#类. ...
- 手把手搭建WAMP+PHP+SVN开发环境
一:WAMP 这款软件在安装的过程中就已经把Apache.MySQL.PHP继承好了,而且也做好了相应的配置,除此之外,还加上了SQLitemanager和Phpmyadmin,省去了很多复杂的配置过 ...
- [我给Unity官方视频教程做中文字幕]beginner Graphics – Lessons系列之摄像机介绍Cameras
[我给Unity官方视频教程做中文字幕]beginner Graphics – Lessons系列之摄像机介绍Cameras 最近得到一些Unity官方视频教程,一看全是纯英文的讲解,没有任何字幕或者 ...
- jQuery自动加载更多程序
1.1.1 摘要 现在,我们经常使用的微博.微信或其他应用都有异步加载功能,简而言之,就是我们在刷微博或微信时,移动到界面的顶端或低端后程序通过异步的方式进行加载数据,这种方式加快了数据的加载速度,由 ...
- PDO事务处理
PDO事务处理 2014-9-3 10:44:19 By jiancaigege==================================== 概要:将多条sql操作(增删改)作为一个操作单 ...
- salesforce 零基础学习(三十七) DML及Database方法简单描述
在apex中通过soql查询可以使用两种方式,使用DML语句或者使用Database的方法. 使用DML语句和使用Database类的方法对于我们来说用的都很多,并且都很常见.对于数据库常见的操作:增 ...
- js判断函数是否存在、判断是否为函数
代码: <script type="text/javascript"> //判断是否为函数 try { if(typeof FunName === "func ...
