E - Closest Common Ancestors
Write a program that takes as input a rooted tree and a list of pairs of vertices. For each pair (u,v) the program determines the closest common ancestor of u and v in the tree. The closest common ancestor of two nodes u and v is the node w that is an ancestor of both u and v and has the greatest depth in the tree. A node can be its own ancestor (for example in Figure 1 the ancestors of node 2 are 2 and 5)
Input
The data set, which is read from a the std input, starts with the tree description, in the form:
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For each common ancestor the program prints the ancestor and the number of pair for which it is an ancestor. The results are printed on the standard output on separate lines, in to the ascending order of the vertices, in the format: ancestor:times
For example, for the following tree:
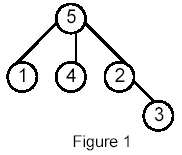
Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1
5:5
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
输出公共节点的个数(抄的板子有毒..)输入要特殊处理
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<float.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#define sf scanf
#define scf(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define pf printf
#define prf(x) printf("%d\n",x)
#define mm(x,b) memset((x),(b),sizeof(x))
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i<n;i++)
#define per(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i>=n;i--)
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=1e9+100;
const double eps=1e-8;
using namespace std;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int inf=0xfffffff;
const int MAXN = 1010;
int rmq[2*MAXN];//rmq数组,就是欧拉序列对应的深度序列
struct ST
{
int mm[2*MAXN];
int dp[2*MAXN][20];//最小值对应的下标
void init(int n)
{
mm[0] = -1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
mm[i] = ((i&(i-1)) == 0)?mm[i-1]+1:mm[i-1];
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for(int j = 1; j <= mm[n];j++)
for(int i = 1; i + (1<<j) - 1 <= n; i++)
dp[i][j] = rmq[dp[i][j-1]] < rmq[dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]]?dp[i][j-1]:dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1];
}
int query(int a,int b)//查询[a,b]之间最小值的下标
{
if(a > b)swap(a,b);
int k = mm[b-a+1];
return rmq[dp[a][k]] <= rmq[dp[b-(1<<k)+1][k]]?dp[a][k]:dp[b-(1<<k)+1][k];
}
};
//边的结构体定义
struct Edge
{
int to,next;
};
Edge edge[MAXN*2];
int tot,head[MAXN];
int F[MAXN*2];//欧拉序列,就是dfs遍历的顺序,长度为2*n-1,下标从1开始
int P[MAXN];//P[i]表示点i在F中第一次出现的位置
int cnt;
ST st;
void init()
{
tot = 0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void addedge(int u,int v)//加边,无向边需要加两次
{
edge[tot].to = v;
edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
}
void dfs(int u,int pre,int dep)
{
F[++cnt] = u;
rmq[cnt] = dep;
P[u] = cnt;
for(int i = head[u];i != -1;i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if(v == pre)continue;
dfs(v,u,dep+1);
F[++cnt] = u;
rmq[cnt] = dep;
}
}
void LCA_init(int root,int node_num)//查询LCA前的初始化
{
cnt = 0;
dfs(root,root,0);
st.init(2*node_num-1);
}
int query_lca(int u,int v)//查询u,v的lca编号
{
return F[st.query(P[u],P[v])];
}
bool root[MAXN];
int sum[MAXN];
int main()
{
int n,m,num,x,u;
while(~scf(n))
{
init();
mm(sum,0);
mm(root,true);
rep(i,1,n+1)
{
sf("\t%d\t:\t(\t%d\t)",&u,&num);//一种方法
while(num--)
{
int x;
sf("\t%d\t",&x);
addedge(u,x);
addedge(x,u);
root[x]=false;
}
}
int temp;
rep(i,1,n+1)
{
if(root[i])
{
temp=i;break;
}
}
scf(m);
LCA_init(temp,n);
int v;
while(m--)//另一种输入方法
{
while(getchar()!='(') ;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
while(getchar()!=')') ;
sum[query_lca(u,v)]++;
}
rep(i,1,n+1)
{
if(sum[i])
pf("%d:%d\n",i,sum[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
E - Closest Common Ancestors的更多相关文章
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors
传送门 Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 17306 Ac ...
- poj----(1470)Closest Common Ancestors(LCA)
Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 15446 Accept ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors(最近公共祖先 LCA)
POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors(最近公共祖先 LCA) Description Write a program that takes as input a root ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors (LCA,离线Tarjan算法)
Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 13372 Accept ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors (LCA, dfs+ST在线算法)
Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 13370 Accept ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors 【LCA】
任意门:http://poj.org/problem?id=1470 Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000 ...
- poj1470 Closest Common Ancestors [ 离线LCA tarjan ]
传送门 Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 14915 Ac ...
- BNUOJ 1589 Closest Common Ancestors
Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000ms Memory Limit: 10000KB This problem will be judged on PKU ...
- poj——1470 Closest Common Ancestors
Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 20804 Accept ...
- Closest Common Ancestors POJ 1470
Language: Default Closest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissio ...
随机推荐
- golang 特殊知识点
golang 代码不需要分号; 但是又会自己在底层增加;号 ,所以 golang的{左花括号必须在代码的最后一行,而不能在新的一行; golang 代码组织里需要注意 vendor 和 interna ...
- dubbo常见错误
1.dubbo zookeeper注册中心provider的ip地址为内网ip,导致consumer连不上 我用的阿里云的服务器,host默认配置了内网ip,注销或删除即可 vim /etc/host ...
- 【Google设计冲刺】一种适合于创新小组的协作方式
传统的产品闭环是1.产品策划-2.研发-3.上线-4.等待市场反馈,4个步骤.对于一个创新项目来说,试错成本过高,等待周期过长[注释1].那么,有没有一种适合创新项目的协作方式呢?谷歌风投杰克·纳普发 ...
- boost::filesystem经常使用使用方法具体解释
提示: filesystem库提供了两个头文件,一个是<boost/filesystem.hpp>,这个头文件包括基本的库内容.它提供了对文件系统的重要操作. 同一时候它定义了一个类pat ...
- ShrePoint 迁移域控
背景: 客户的AD服务器换掉,重新安装AD,SharePoint服务器重新加入域后,将所有服务账号换成新域的账号. 虽然SP的应用程序采用的是表单认证,但是,用户(包括管理员)访问站点,添加数据的时候 ...
- MySQL技术内幕读书笔记(三)——文件
目录 文件 参数文件 日志文件 套接字文件 pid文件 表结构定义文件 INNODB存储引擎文件 文件 有以下类型文件 参数文件:告诉MYSQL实例启动时在哪里找到数据库文件,并且制定某些初始化参 ...
- python3 + flask + sqlalchemy +orm(1):链接mysql 数据库
1.pycharm中新建一个flask项目 2.按装flask.PyMySQL.flask-sqlalchemy 3.项目下面新建一个config.py 文件 DEBUG = True #dialec ...
- Python分页组件
分页组件的实现: class Pagination(object): """ 自定义分页 """ def __init__(self,cur ...
- “The subscription does not exist” when a distributor primary replica fails over to a replica that does not use the same agent profile
Symptoms Consider the following scenario: In Microsoft SQL Server 2017, you have a distribution agen ...
- 获取CPU序列号的Delphi程序
Unit CPUid; Interface Type TCpuType = (cpu8086, cpu286, cpu386, cpu486, cpuPentium); Function CpuTyp ...
