Quality of Service (QoS) in LTE
Background: Why we need QoS ?
There are premium subscribers who always want to have better user experience on their 4G LTE device. These users are willing to pay more for high bandwidth and better network access on their devices. Not only the subscribers but some services itself need better priority handling in the network (e.g. VoIP call). To be able to full fill this, QOS plays the key role. QOS defines priorities for certain customers / services during the time of high congestion in the network
3GPP definition for QoS
between UE and PDN Gateway and is applied to a set of bearers. 'Bearer'
is basically a virtual concept and is a set of network configuration to
provide special treatment to set of traffic e.g. VoIP packets
are prioritized by network compared to web browser traffic.
In LTE, QoS is applied on Radio bearer, S1 bearer and S5/S8 bearer, collectively called as EPS bearer as shown in figure below.

bearer types and properties associated with each bearer
through hierarchical chart as shown below. First there are two types of
Bearer, i.e. Dedicated bearer and Default bearer. There is at-least one
default bearer established when UE is attached to LTE network while
dedicated bearer is always established when there is need to provide QoS
to specific service (like VoIP, video etc). Please go through the
article Default and Dedicated Bearer which hopefully will help to explain the concept in more detail.
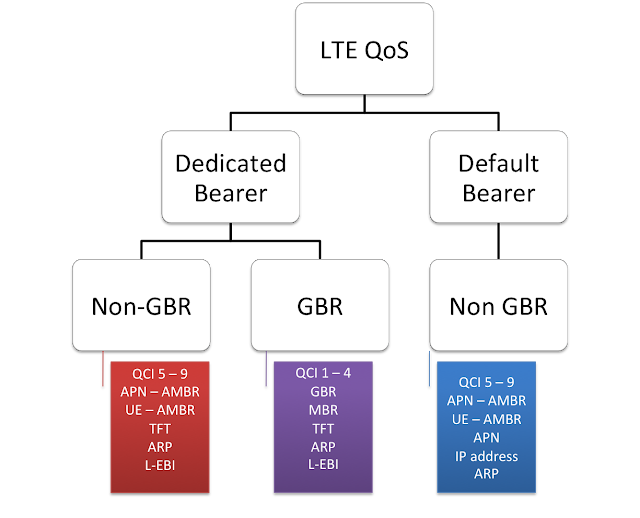
maximum bit rate is the maximum allowed total non-GBR throughput to
specific APN. It is specified interdependently for uplink an downlink
can only be non-GBR type. Some other important terms associated with
each bearer type are discussed below:
retention priority is basically used for deciding whether new bearer
modification or establishment request should be accepted considering the
current resource situation.
is always associated with dedicated bearer and while default bearer may
or may not have TFT. As mentioned earlier, dedicated bearer provides QoS
to special service or application and TFT defines rules so that UE and
Network knows which IP packet should be sent on particular dedicated
bearer. It usually has rules on the basis of IP packet
destination/source or protocol used.
EPS bearer ID. As I discussed in previous article about dedicated and
default bearer, we know that each dedicated bearer is always linked to
one of default bearers. L-EBI tells Dedicated bearer which default
bearer it is attached to.
bearer is attached to some PDN network and has its own IP address while
dedicated bearer does not need this since it is linked to default
bearer.
associated with all bearers i.e. QoS class of identifier (QCI).This
parameter basically defines IP level packets characteristics as shown
below
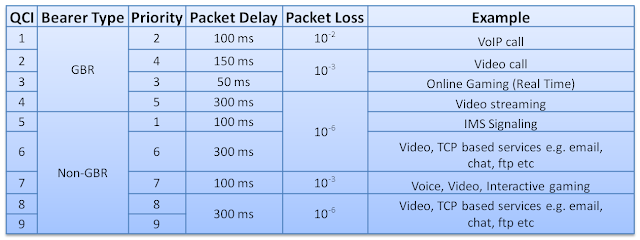
Default bearer 1: Used for signaling messages (sip signaling) related to IMS network. It uses qci 5
Dedicated bearer: Used for VoLTE VoIP traffic. It uses qci 1 and is linked to default bearer 1
Default bearer 2: Used for all other smartphone traffic (video, chat, email, browser etc), assuming qci 9 is used here
associated with IMS PDN and has specific IP address. It has throughput
limitations defined in terms of A-AMBR and UE-AMBR. Since it has qci 5
which means that its IP packets has the highest priority over other IP
packets and maximum delay as 100ms between UE and PGW with packet loss
percentage up to 10-6
internet PDN and has specific IP. It has throughput limitations defined
in terms of A-AMBR and UE-AMBR as well. Since it has qci 9 which means
that its IP packets has the lowest priority over other IP packets and
maximum delay possible as 300ms between UE and PGW with packet loss
percentage up to 10-6
Default bearer 1 with L-EBI and it also has TFT which basically defines
which IP packets should be allowed to travel on this bearer. It has
throughput limitations defined in terms of MBR and GBR. Since it is
using QCI 1, the IP packets traveling on this bearer have the second
highest priority. The maximum delay possible to IP packets on this
bearer is 100 ms and the percentage of packet loss will be under 10-2
Quality of Service (QoS) in LTE的更多相关文章
- [转] Quality Of Service In OpenStack
http://tropicaldevel.wordpress.com/2013/07/15/quality-of-service-in-openstack/ In this post I will b ...
- Quality of Service 0, 1 & 2
来自:http://www.hivemq.com/blog/mqtt-essentials-part-6-mqtt-quality-of-service-levels Quality of Servi ...
- Quality of service
w https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quality_of_service Quality of service (QoS) is the overall performan ...
- MQTT协议QoS服务质量 (Quality of Service 0, 1 & 2)概念学习
什么是 QoS ? QoS (Quality of Service) 是发送者和接收者之间,对于消息传递的可靠程度的协商. QoS 的设计是 MQTT 协议里的重点.作为专为物联网场景设计的协议,MQ ...
- neutron qos Quality of Service
Quality of Service advanced service is designed as a service plugin. The service is decoupled from t ...
- [译]Ocelot - Quality of Service
原文 可以针对每个ReRoute设置对下游服务的熔断器circuit breaker.这部分是通过Polly实现的. 将下面的配置添加到一个ReRoute下面去. "QoSOptions&q ...
- Default Bearer, Dedicated Bearer... What exactly is bearer ?
Default Bearer, Dedicated Bearer... What exactly is bearer ? While trying to get a better understa ...
- LTE QOS
http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=ziFIkdKaC7MU2RY-bTOp2bt87WFPw5_02bqmYs5W6w4ktOfPHEcWesK1U2T7YiyXjVSM ...
- Information Centric Networking Based Service Centric Networking
A method implemented by a network device residing in a service domain, wherein the network device co ...
随机推荐
- 给JZ2440开发板重新分区
转自:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzAxNTAyOTczMw==&mid=2649328035&idx=1&sn=7d3935cc05d3 ...
- jQuery对象和DOM对象的互换
Dom 对象:指的是普通的 JavaScript 对象 jQuery对象:是包装 Dom 对象后产生的对象. 一:JQuery 对象和 Dom 对象 在使用 JQuery 过程中,我们一般(也是绝大多 ...
- Python函数(十一)-生成器
首先看一下什么是列表生成式 >>> [i*2 for i in range(10)] [0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18] >>> ...
- sharepoint Foundation 2013安装过程
安装完必备软件后,便可安装sharepoint Foundation 2013
- 仿QQ底部切换(Fragment + Radio)
第一步: activity_main.xml 布局文件 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/ ...
- 六种获取配置properties文件的方法
总结一下六种获取配置properties文件的方法,代码如下: package com.xujingyang.test ; import java.io.BufferedInputStream ; i ...
- 树莓派 Learning 002 装机后的必要操作 --- 06 共用键鼠 之 windows和树莓派
树莓派 装机后的必要操作 - 使用Synergy软件 共用键鼠 之 windows和树莓派 我的树莓派型号:Raspberry Pi 2 Model B V1.1 装机系统:NOOBS v1.9.2 ...
- java File基本操作,以及递归遍历文件夹
java 的文件操作,相对来说是比较重要的,无论是编写CS还是BS程序,都避免不了要与文件打交道,例如读写配置文件等.虽然现在很多框架都直接帮你做好了这一步! java.io.File 底层是调用与c ...
- ASP.NET jquery 获取服务器控件ID
一般方法: jQuery("#txtUserName").val(); 如果页面加载了母版页或者自定义控件:该页面的ID有可能会被篡改(可能是因为避免控件ID冲突的机制),因此强烈 ...
- Log4NET的日志框架的使用
日志信息分类 1.等级由低到高:debug<info<warn<Error<Fatal; 2.区别: debug 级别最低,可以随意的使用于任何觉得有利于在调试时更详细的了解系 ...
