【并查集专题】【HDU】
PS:做到第四题才发现 2,3题的路径压缩等于没写
How Many Tables
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 14542 Accepted Submission(s): 7132
One important rule for this problem is that if I tell you A knows B, and B knows C, that means A, B, C know each other, so they can stay in one table.
For example: If I tell you A knows B, B knows C, and D knows E, so A, B, C can stay in one table, and D, E have to stay in the other one. So Ignatius needs 2 tables at least.
follow. Each line consists of two integers A and B(A!=B), that means friend A and friend B know each other. There will be a blank line between two cases.
2
5 3
1 2
2 3
4 5 5 1
2 5
2
4
裸的并查集没什么好说的
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#define oo 0x13131313
using namespace std;
int N,M;
int Set[1001];
int ans;
void YCL()
{
ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<=N;i++)
Set[i]=i;
}
int find(int x)
{
if(x!=Set[x])
Set[x]=find(Set[x]);
return Set[x];
}
int Union(int a,int b)
{
int a1=find(a);
int b1=find(b);
if(a1!=b1)
{
Set[a1]=b1;
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
void input()
{
cin>>N>>M;
int a,b;
YCL();
for(int i=1;i<=M;i++)
{
cin>>a>>b;
if(Union(a,b))
ans++;
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
input();
cout<<N-ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
小希的迷宫
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 27792 Accepted Submission(s): 8589
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0 8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0 3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0 -1 -1
Yes
Yes
No
几点注意:
1.不止要判环,还要判断是否是一棵树,而不是多棵树
2.注意0 0 //,1 1 0 0 这样的数据
3.编号非连续的,所以开个数组存编号
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#define oo 0x13131313
using namespace std;
int father[100001];
int A[200001];
int Max=-1,tot=0;
int find(int x)
{
if(x!=father[x])
father[x]=find(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
int Union(int a,int b)
{
int a1=find(a);
int a2=find(b);
if(a1==a2) return 0;
else father[a1]=a2;
return 1;
}
void init()
{
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
}
void YCL()
{
for(int i=1;i<=100000;i++)
{
father[i]=i;
}
}
int main()
{
// init();
int a,b,OK=1;
while(1)
{
YCL();
OK=1;Max=-1;tot=0;
while(cin>>a>>b)
{
if(a==-1&&b==-1) return 0;
else if(a==0&&b==0) {break;}
else if(OK)
if(Union(a,b)==0) OK=0;
A[++tot]=a;
A[++tot]=b;
}
if(OK==1) {
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
if(find(father[A[i]])!=find(father[A[1]])) OK=0;
if(OK==1) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Is It A Tree?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 15095 Accepted Submission(s): 3342
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
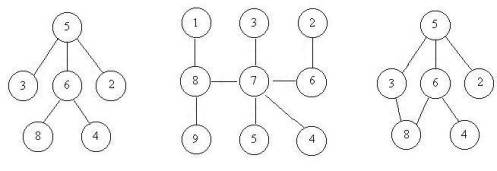
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
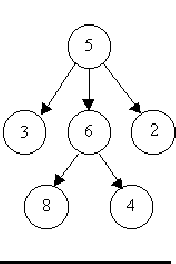
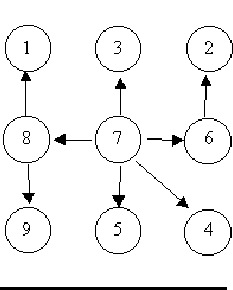
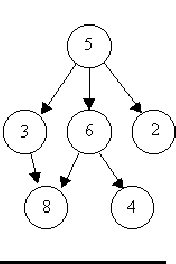
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
Case 1 is a tree.
Case 2 is a tree.
Case 3 is not a tree.
注意 这和上面的题有点不一样 是一个有向图
所以要判断入度
否则会出现
判断成树的情况
代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#define oo 0x13131313
using namespace std;
int father[100001];
int A[200001];
int T[200001];
int Max=-1,tot=0;
int find(int x)
{
if(x!=father[x])
father[x]=find(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
int Union(int a,int b)
{
int a1=find(a);
int a2=find(b);
if(a1==a2) return 0;
else father[a1]=a2;
return 1;
}
void init()
{
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
}
void YCL()
{
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
{
father[A[i]]=A[i];
T[A[i]]=0;
}
}
int main()
{
// init();
int a,b,OK=1;
int kk=0;
while(1)
{
kk++;
OK=1;Max=-1;tot=0;
while(cin>>a>>b)
{
if(a<0||b<0) return 0;
else if(a==0&&b==0) {break;}
A[++tot]=a;
A[++tot]=b;
}
YCL();
for(int i=1;i<=tot/2;i++)
{
if(OK)
{
if(Union(A[2*(i-1)+1],A[2*i])==0) OK=0;
T[A[2*i]]++;
}
}
if(OK==1) {
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
{
if(find(father[A[i]])!=find(father[A[1]])) OK=0;
if(T[A[i]]>1) OK=0;
}
if(OK==1) printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",kk);
else printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",kk);
}
else printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",kk);
}
return 0;
}
More is better
Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 327680/102400 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 15588 Accepted Submission(s): 5737
Mr Wang selected a room big enough to hold the boys. The boy who are not been chosen has to leave the room immediately. There are 10000000 boys in the room numbered from 1 to 10000000 at the very beginning. After Mr Wang's selection any two of them who are
still in this room should be friends (direct or indirect), or there is only one boy left. Given all the direct friend-pairs, you should decide the best way.
4
1 2
3 4
5 6
1 6
4
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
4
2HintA and B are friends(direct or indirect), B and C are friends(direct or indirect),
then A and C are also friends(indirect). In the first sample {1,2,5,6} is the result.
In the second sample {1,2},{3,4},{5,6},{7,8} are four kinds of answers.
MAP离散化+路径压缩。。 还一直以为是MAP导致TLE 结果发现是2,3题的路径压缩写错了。。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include<map>
#define oo 0x13131313
using namespace std;
int N;
int father[200000];
int A[200000];
int B[200000];
int num[200000];
map<int,int> Hash;
int tot=0;
int ans=1;
void input()
{
Hash.clear();
tot=0;ans=1;
int a,b;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
B[(2*i-1)]=A[(2*i-1)]=a;
B[(2*i)]=A[(2*i)]=b;
}
}
void CSH()
{
B[0]=-1;
sort(B+1,B+2*N+1);
for(int i=1;i<=2*N;i++)
{
if(B[i]!=B[i-1])
Hash[B[i]]=++tot;
}
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
{
father[i]=i;
num[i]=1;
}
}
int find(int x)
{
if(x!=father[x])
father[x]=find(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
int Union(int a,int b)
{
int a1=find(a);
int b1=find(b);
if(a1==b1) return 0;
else
{
father[a1]=b1;
num[b1]+=num[a1];
if(num[b1]>ans) ans=num[b1];
}
return 1;
}
void solve()
{
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
Union(Hash[A[(2*i-1)]],Hash[A[(2*i)]]);
}
}
void init()
{
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
}
int main()
{
// init();
while(scanf("%d",&N)!=EOF)
{
input();
CSH();
solve();
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
Constructing Roads
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 14672 Accepted Submission(s): 5572
C such that there is a road between A and C, and C and B are connected.
We know that there are already some roads between some villages and your job is the build some roads such that all the villages are connect and the length of all the roads built is minimum.
i and village j.
Then there is an integer Q (0 <= Q <= N * (N + 1) / 2). Then come Q lines, each line contains two integers a and b (1 <= a < b <= N), which means the road between village a and village b has been built.
3
0 990 692
990 0 179
692 179 0
1
1 2
179
给定N条建好路径的最小生成树
1.建好的路径就是权值为0即可,或直接克鲁斯卡尔
附代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#define oo 0x13131313
using namespace std;
struct edge
{
int s,t,w;
};
int father[101];
edge A[20111];
int map[101][101];
int N;
int ans;
int tot=0;
int Q;
int k;
int cmp(const void *i,const void *j)
{
edge *ii=(edge *)i;edge *jj=(edge *)j;
return ii->w-jj->w;
}
void YCL()
{
for(int i=1;i<=101;i++)
{
father[i]=i;
}
}
int find(int x)
{
if(x!=father[x])
father[x]=find(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
int Union(int a,int b)
{
int a1=find(a);
int b1=find(b);
if(a1==b1) return 0;
else
{
father[b1]=a1;
}
return 1;
}
void input()
{
YCL();
int temp,a,b;
ans=0;
tot=0;
k=0;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&map[i][j]);
if(i<j)
{
tot++;
A[tot].s=i;A[tot].t=j;A[tot].w=map[i][j];
}
}
cin>>Q;
for(int i=1;i<=Q;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(Union(a,b))
{
k++;
}
}
}
void solve()
{
int j=1;
qsort(A+1,tot,sizeof(A[1]),cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=N-1-k;i++)
{
while(Union(A[j].s,A[j].t)==0&&j<=tot)
j++;
ans+=A[j].w;
}
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>N)
{
input();
solve();
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
后面还有几道生成树水题就不上了。。
【并查集专题】【HDU】的更多相关文章
- Leetcode之并查集专题-765. 情侣牵手(Couples Holding Hands)
Leetcode之并查集专题-765. 情侣牵手(Couples Holding Hands) N 对情侣坐在连续排列的 2N 个座位上,想要牵到对方的手. 计算最少交换座位的次数,以便每对情侣可以并 ...
- Leetcode之并查集专题-684. 冗余连接(Redundant Connection)
Leetcode之并查集专题-684. 冗余连接(Redundant Connection) 在本问题中, 树指的是一个连通且无环的无向图. 输入一个图,该图由一个有着N个节点 (节点值不重复1, 2 ...
- ZR并查集专题
ZR并查集专题 并查集,作为一个基础算法,对于初学者来说,下面的代码是维护连通性的利器 return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = getf(fa[x]); 所以,但是这对并查集的 ...
- 【带权并查集】HDU 3047 Zjnu Stadium
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3047 [题意] http://blog.csdn.net/hj1107402232/article/detail ...
- 【进阶——种类并查集】hdu 1829 A Bug's Life (基础种类并查集)TUD Programming Contest 2005, Darmstadt, Germany
先说说种类并查集吧. 种类并查集是并查集的一种.但是,种类并查集中的数据是分若干类的.具体属于哪一类,有多少类,都要视具体情况而定.当然属于哪一类,要再开一个数组来储存.所以,种类并查集一般有两个数组 ...
- 并查集问题hdu 1232
Problem Description 某省调查城镇交通状况,得到现有城镇道路统计表,表中列出了每条道路直接连通的城镇.省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个城镇间都可以实现交通(但不一定有直接的道 ...
- 【并查集】HDU 1325 Is It A Tree?
推断是否为树 森林不是树 空树也是树 成环不是树 数据: 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 1 0 0 1 2 2 3 4 5 0 0 2 5 0 0 ans: no ...
- 克鲁斯卡尔(并查集)hdu 1233
还是畅通工程 Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Sub ...
- 并查集专题: HDU1232畅通工程
畅通工程 Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submi ...
随机推荐
- 2. QT窗体间值的传递
一.主窗体与子窗体传参 方法有很多,这里介绍一种通过重载子窗体的构造函数实现主窗体参数传入到子窗体,并通过QT信号和槽的机制实现子窗口到主窗口值的传递. 主和子窗体的设置如下: 主要实现功能为: 1 ...
- [跟我学Spring学习笔记][DI配置与使用]
DI 依赖和依赖注入 定义 传统的依赖一般指"类之间的关系",那先让我们复习一下类之间的关系: 泛化:表示类与类之间的继承关系.接口与接口之间的继承关系: 实现:表示类对接口的实现 ...
- UISegmentedControl判断点击第几项
UISegmentedControl 关于UISegmentedControl判断当前点击的是第几项,找了很久,终于再老外的博客上找到了,在委托中 UISegmentedControl *Seg=se ...
- Centos6架设GIT服务,windows客户端使用TortoiseGit加载KEYGEN连接GIT服务器
前几天得空,想起前一阵学了GIT还没好好实践,就在虚拟机中安装测试了一下,并简单记录了CENTOS6中GIT安装,ssh-keygen生成,客户端使用TortoiseGit加载KEYGEN连接GIT服 ...
- Oracle CASE WHEN 用法介绍[Z]
Oracle CASE WHEN 用法介绍 1. CASE WHEN 表达式有两种形式 --简单Case函数 CASE sex WHEN '1' THEN '男' WHEN '2' THEN '女' ...
- iOS nav加角标
写一个类别加上就可以啦 #import "UIBarButtonItem+Badge.h" #import "BadgeView.h" #import < ...
- Masonry的一些使用。
除了等距的有问题(懒得改了),其他用过挺正常的,我自己也是刚使用,有问题还请海涵. 地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1boyxu8Z
- HttpClient中异步方法的同步调用
在System.Net.Http中,提供了使用Http与远程服务器通讯的httpClient,但是里面都是异步方法,有时候我们并不需要使用异步操作.这个时候可以使用如下的方式来进行同步调用. clas ...
- Code Review中应该关注的点
Magic number/string If statement, you should always use single line or brackets Provide default valu ...
- javascript版1024游戏源码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content ...

