Cocos2dLua3.17.2集成FairyGUI之 lua绑定 (二)
上一章中将fairyGUI集成到C++工程,由于本人使用的是cocoslua,还需要将C++的绑定到lua中使用,本章记录一下过程,由于是过了一段时间,有些步骤忘记了,大概记录一下,诸位大大做个临时参考吧
1 打开\cocos2d-x-3.17.2\tools\tolua文件夹,创建一个py脚本,FairyGUIgenbindings.py.仿照genbingings.py写入代码:
#!/usr/bin/python # This script is used to generate luabinding glue codes.
# Android ndk version must be ndk-r9b. import sys
import os, os.path
import shutil
import ConfigParser
import subprocess
import re
from contextlib import contextmanager def _check_ndk_root_env():
''' Checking the environment NDK_ROOT, which will be used for building
''' try:
NDK_ROOT = os.environ['NDK_ROOT']
except Exception:
print "NDK_ROOT not defined. Please define NDK_ROOT in your environment."
sys.exit(1) return NDK_ROOT def _check_python_bin_env():
''' Checking the environment PYTHON_BIN, which will be used for building
''' try:
PYTHON_BIN = os.environ['PYTHON_BIN']
except Exception:
print "PYTHON_BIN not defined, use current python."
PYTHON_BIN = sys.executable return PYTHON_BIN class CmdError(Exception):
pass @contextmanager
def _pushd(newDir):
previousDir = os.getcwd()
os.chdir(newDir)
yield
os.chdir(previousDir) def _run_cmd(command):
ret = subprocess.call(command, shell=True)
if ret != 0:
message = "Error running command"
raise CmdError(message) def main(): cur_platform= '??'
llvm_path = '??'
ndk_root = _check_ndk_root_env()
# del the " in the path
ndk_root = re.sub(r"\"", "", ndk_root)
python_bin = _check_python_bin_env() platform = sys.platform
if platform == 'win32':
cur_platform = 'windows'
elif platform == 'darwin':
cur_platform = platform
elif 'linux' in platform:
cur_platform = 'linux'
else:
print 'Your platform is not supported!'
sys.exit(1) x86_llvm_path = ""
x64_llvm_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(ndk_root, 'toolchains/llvm/prebuilt', '%s-%s' % (cur_platform, 'x86_64')))
if not os.path.exists(x64_llvm_path):
x86_llvm_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(ndk_root, 'toolchains/llvm/prebuilt', '%s' % (cur_platform)))
if not os.path.exists(x86_llvm_path):
x86_llvm_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(ndk_root, 'toolchains/llvm/prebuilt', '%s-%s' % (cur_platform, 'x86'))) if os.path.isdir(x64_llvm_path):
llvm_path = x64_llvm_path
elif os.path.isdir(x86_llvm_path):
llvm_path = x86_llvm_path
else:
print 'llvm toolchain not found!'
print 'path: %s or path: %s are not valid! ' % (x86_llvm_path, x64_llvm_path)
sys.exit(1) x86_gcc_toolchain_path = ""
x64_gcc_toolchain_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(ndk_root, 'toolchains/arm-linux-androideabi-4.9/prebuilt', '%s-%s' % (cur_platform, 'x86_64')))
if not os.path.exists(x64_gcc_toolchain_path):
x86_gcc_toolchain_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(ndk_root, 'toolchains/arm-linux-androideabi-4.9/prebuilt', '%s' % (cur_platform)))
if not os.path.exists(x86_gcc_toolchain_path):
x86_gcc_toolchain_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(ndk_root, 'toolchains/arm-linux-androideabi-4.9/prebuilt', '%s-%s' % (cur_platform, 'x86'))) if os.path.isdir(x64_gcc_toolchain_path):
gcc_toolchain_path = x64_gcc_toolchain_path
elif os.path.isdir(x86_gcc_toolchain_path):
gcc_toolchain_path = x86_gcc_toolchain_path
else:
print 'gcc toolchain not found!'
print 'path: %s or path: %s are not valid! ' % (x64_gcc_toolchain_path, x86_gcc_toolchain_path)
sys.exit(1) project_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..', '..'))
cocos_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(project_root, ''))
cxx_generator_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(project_root, 'tools/bindings-generator')) # save config to file
config = ConfigParser.ConfigParser()
config.set('DEFAULT', 'androidndkdir', ndk_root)
config.set('DEFAULT', 'clangllvmdir', llvm_path)
config.set('DEFAULT', 'gcc_toolchain_dir', gcc_toolchain_path)
config.set('DEFAULT', 'cocosdir', cocos_root)
config.set('DEFAULT', 'cxxgeneratordir', cxx_generator_root)
config.set('DEFAULT', 'extra_flags', '') conf_ini_file = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'userconf.ini')) print 'generating userconf.ini...'
with open(conf_ini_file, 'w') as configfile:
config.write(configfile) # set proper environment variables
if 'linux' in platform or platform == 'darwin':
os.putenv('LD_LIBRARY_PATH', '%s/libclang' % cxx_generator_root)
if platform == 'win32':
path_env = os.environ['PATH']
os.putenv('PATH', r'%s;%s\libclang;%s\tools\win32;' % (path_env, cxx_generator_root, cxx_generator_root)) try: tolua_root = '%s/tools/tolua' % project_root
output_dir = '%s/cocos/scripting/lua-bindings/auto' % project_root cmd_args = {
'cocos2dx_fairygui.ini' : ('cocos2dx_fairygui', 'lua_cocos2dx_fairygui_auto'), \
}
target = 'lua'
generator_py = '%s/generator.py' % cxx_generator_root
for key in cmd_args.keys():
args = cmd_args[key]
cfg = '%s/%s' % (tolua_root, key)
print 'Generating bindings for %s...' % (key[:-4])
command = '%s %s %s -s %s -t %s -o %s -n %s' % (python_bin, generator_py, cfg, args[0], target, output_dir, args[1])
_run_cmd(command) print '---------------------------------'
print 'Generating lua bindings succeeds.'
print '---------------------------------' except Exception as e:
if e.__class__.__name__ == 'CmdError':
print '---------------------------------'
print 'Generating lua bindings fails.'
print '---------------------------------'
sys.exit(1)
else:
raise # -------------- main --------------
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
新建cocos2dx_fairygui.ini文件写入代码
[cocos2dx_fairygui]
# the prefix to be added to the generated functions. You might or might not use this in your own
# templates
prefix = cocos2dx_fairygui # create a target namespace (in javascript, this would create some code like the equiv. to `ns = ns || {}`)
# all classes will be embedded in that namespace
target_namespace = fgui android_headers = android_flags = -target armv7-none-linux-androideabi -D_LIBCPP_DISABLE_VISIBILITY_ANNOTATIONS -DANDROID -D__ANDROID_API__= -gcc-toolchain %(gcc_toolchain_dir)s --sysroot=%(androidndkdir)s/platforms/android-/arch-arm -idirafter %(androidndkdir)s/sources/android/support/include -idirafter %(androidndkdir)s/sysroot/usr/include -idirafter %(androidndkdir)s/sysroot/usr/include/arm-linux-androideabi -idirafter %(clangllvmdir)s/lib64/clang/5.0/include -I%(androidndkdir)s/sources/cxx-stl/llvm-libc++/include clang_headers =
clang_flags = -nostdinc -x c++ -std=c++ -fsigned-char -U__SSE__ cocos_headers = -I%(cocosdir)s -I%(cocosdir)s/cocos -I%(cocosdir)s/../libfairygui/Classes -I%(cocosdir)s/cocos/platform/android -I%(cocosdir)s/external cocos_flags = -DANDROID cxxgenerator_headers = # extra arguments for clang
extra_arguments = %(android_headers)s %(clang_headers)s %(cxxgenerator_headers)s %(cocos_headers)s %(android_flags)s %(clang_flags)s %(cocos_flags)s %(extra_flags)s # what headers to parse
headers = %(cocosdir)s/../libfairygui/Classes/FairyGUI.h %(cocosdir)s/../libfairygui/Classes/FairyGUIMacros.h # what classes to produce code for. You can use regular expressions here. When testing the regular
# expression, it will be enclosed in "^$", like this: "^Menu*$".
classes = UIPackage GRoot GObject GComponent UIEventDispatcher GImage GMovieClip GTextField GRichTextField GTextInput GGraph GLoader GGroup GButton GComboBox GProgressBar GSlider GScrollBar GList Window PopupMenu UIObjectFactory GObjectPool DragDropManager FairyGUIMacros EventContext JoystickModule Transition GController ScrollPane InputEvent # what should we skip? in the format ClassName::[function function]
# ClassName is a regular expression, but will be used like this: "^ClassName$" functions are also
# regular expressions, they will not be surrounded by "^$". If you want to skip a whole class, just
# add a single "*" as functions. See bellow for several examples. A special class name is "*", which
# will apply to all class names. This is a convenience wildcard to be able to skip similar named
# functions from all classe/s. skip =
#skip = UIEventDispatcher::[^addEventListener$ ^removeEventListener$ ^hasEventListener$],
# GObject::[^addClickListener$ removeClickListener getData],
# GComponent::[^constructFromResource$],
# Transition::[^play$ setup],
# UIObjectFactory::[setPackageItemExtension],
# GController::[setup],
# EventContext::[getData] rename_functions = rename_classes = # for all class names, should we remove something when registering in the target VM?
remove_prefix = # classes for which there will be no "parent" lookup
classes_have_no_parents = # base classes which will be skipped when their sub-classes found them.
base_classes_to_skip = # classes that create no constructor
# Set is special and we will use a hand-written constructor
abstract_classes = ArmatureDataManager Manifest # Determining whether to use script object(js object) to control the lifecycle of native(cpp) object or the other way around. Supported values are 'yes' or 'no'.
script_control_cpp = no
2修改cocos2d-x-3.17.2\tools\bindings-generator\targets\lua\conversions.yaml里的ns_map:下添加fairygui的命名空间"fairygui::": "fgui."
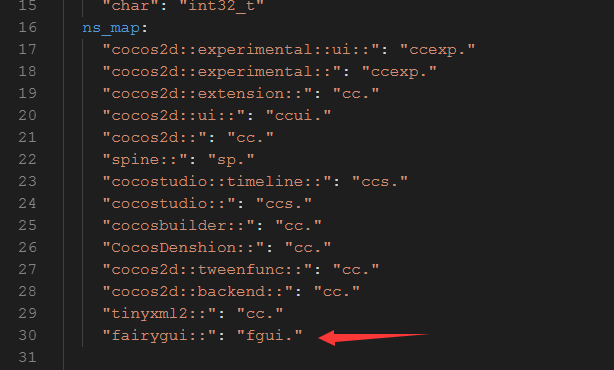
以及在中间to_native:和底部from_native:
to_native:
"Margin": "ok &= luaval_to_margin(tolua_S, ${arg_idx}, &${out_value}, ${lua_namespaced_class_name}:${func_name})"
from_native:
"Margin": "margin_to_luaval(tolua_S, ${in_value})"
2 命令行执行 FairyGUIgenbindings.py. 要用python2版本。执行后在cocos2d-x-3.17.2\cocos\scripting\lua-bindings\auto文件夹下会生成

两个文件。在C++工程中导入两个文件。
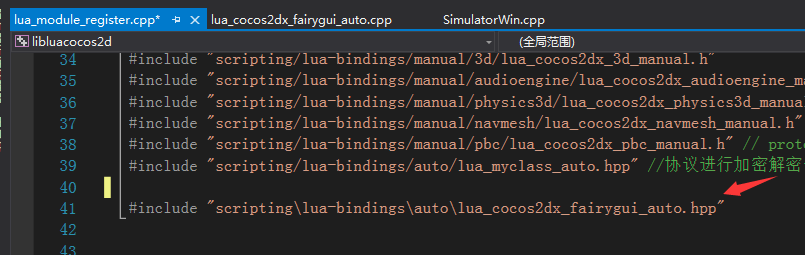
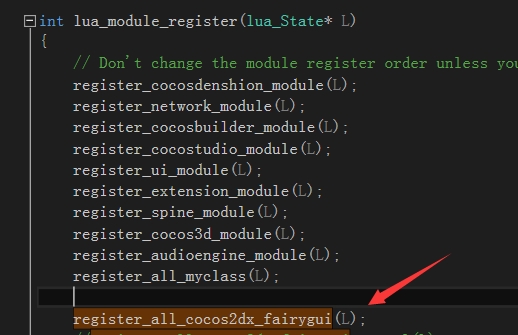
3 在lua_module_register中include头文件并注册
4,编译运行
5 成功截图
lua测试代码(直接用的fairy的demo资源)

注释:过程中可能会遇到一些问题,由于我是好些天前集成的,遇到的一些问题都忘记截图了,以上只是大体的流程。
放上一点test的 lua 代码:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MSzsX78rZKPV2TQrVWxsmg
提取码:nh5i
Cocos2dLua3.17.2集成FairyGUI之 lua绑定 (二)的更多相关文章
- Cocos2dLua3.17.2集成FairyGUI(一)
版本说明:使用cocos2d-lua3.17.2版本 FairyGUI下载好链接地址是:https://github.com/fairygui/FairyGUI-cocos2dx 首先创建cocos项 ...
- 开源基于lua gc管理c++对象的cocos2dx lua绑定方案
cocos2dx目前lua对应的c++对象的生命周期管理,是基于c++析构函数的,也就是生命周期可能存在不一致,比如c++对象已经释放,而lua对象还存在,如果这时候再使用,会有宕机的风险,为此我开发 ...
- cocos2d-x lua绑定解析
花了几天时间看了下cocos2d-x lua绑定那块,总算是基本搞明白了,下面分三部分解析lua绑定: 一.lua绑定主要用到的底层函数 lua绑定其本质就是有一个公用的lua_Stack来进行C和L ...
- cocos2dx的lua绑定
一.cocos2dx对tolua++绑定的修正 A.c对lua回调函数的引用 在使用cocos2dx编写游戏时,我们经常会设置一些回调函数(时钟.菜单选择等).如果采用脚本方式编写游戏的话,这些回调函 ...
- cocos2dx lua 绑定之二:手动绑定自定义类中的函数
cococs2dx 3.13.1 + vs2013 + win10 1.首先按照<cocos2dx lua 绑定之一:自动绑定自定义类>绑定Student类 2.在Student类中增加一 ...
- Cocos2d-x v3.3 lua绑定c++类方法总结
网上有很多cocos2d-x lua绑定c++类的接口教程,这篇文章也是总结他们的经验. 其中重点参考了 http://cn.cocos2d-x.org/tutorial/show?id=1295, ...
- 使用cocos2d脚本生成lua绑定
这几天要老大要求把DragonBones移到cocos2dx 3.0 里边,并且绑定lua使用接口.因为刚学lua,使用的引擎也刚从2.2改为3.0,各种不熟悉,折腾了好几天才弄完,有空了总结一下 这 ...
- cocos2dx lua 绑定之一:自动绑定自定义类中的函数
cococs2dx 3.13.1 + vs2013 + win10 1.首先定义C++类Student 在cocos2d-x\cocos文件夹下新建一个user_define的文件夹放置两个文件. 注 ...
- quick-cocos2d-x 创建自定义lua绑定c++类
内容主要参考 “在quick-cocos2d-x中添加自定义的类给lua使用” ( http://www.codeo4.cn/archives/746) 1. quick-coco2d-x 使用 to ...
随机推荐
- Python记:列表方法略记
- 在PDB级别中如何切换或重建UNDO表空间
Oracle 12.1版本中,UNDO表空间仅存在CDB级别(共享UNDO),来自于AskScuti博客园. Oracle 12.2版本开始,UNDO表空间同时可以存在每个PDB级别(本地UNDO). ...
- Python3标准库:string通用字符串操作
1. string:通用字符串操作 string模块在很早的Python版本中就有了.以前这个模块中提供的很多函数已经移植为str对象的方法,不过这个模块仍保留了很多有用的常量和类来处理str对象. ...
- util之Set
1.定义: Set<Integer>set = new TreeSet<Integer>(); 注意: TreeSet 是二差树实现的,Treeset中的数据是自动排好序的,不 ...
- STL初探
关于STL的一些东西 感言: 学C++不学STL函数库的人可能都是... 有点问题 头文件<algorithm>的一些东西 sort,快排: 这是个初学者必需掌握的东西,及其好用,因为方( ...
- MVC HTML辅助方法
HTML辅助方法(HTML Helper)用来辅助产生HTML,在开发View的时候会面对许多HTML标签,处理这些HTML标签非常繁琐,为了降低View的复杂度,可以使用HTML辅助方法帮助你产生一 ...
- Python入门1 —— 初识Python
一:Python介绍 1.Python是什么? Python是一门编程语言,编程语言是一门语言. 语言就是一个事物与另一个事物沟通的工具. 而编程语言则是人与计算机沟通的介质. 2.为什么要跟计算机沟 ...
- 路飞-celery框架
Celery 官方 Celery 官网:http://www.celeryproject.org/ Celery 官方文档英文版:http://docs.celeryproject.org/en/la ...
- windows 下安装memcache拓展
Windows下安装memcached (linux 接下来会继续 学习) 以管理员身份进入CMD 模式,具体方法:C:/windows/system32 管理员身份打开cmd.exe memcach ...
- SparkStreaming个人记录
一.SparkStreaming概述 SparkStreaming是一种构建在Spark基础上的实时计算框架,它扩展了Spark处理大规模流式数据的能力,以吞吐量高和容错能力强著称. SparkStr ...
