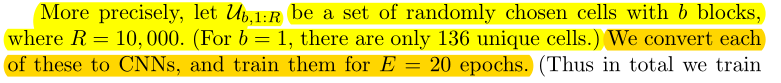2018-ECCV-PNAS-Progressive Neural Architecture Search-论文阅读
PNAS
2018-ECCV-Progressive Neural Architecture Search
- Johns Hopkins University(霍普金斯大学) && Google AI && Stanford
- GitHub:300+ stars
- Citation:504
Motivation
current techniques usually fall into one of two categories: evolutionary algorithms(EA) or reinforcement learning(RL).
Although both EA and RL methods have been able to learn network structures that outperform manually designed architectures, they require significant computational resources.
目前的两种nas方法,EA和RL,存在计算代价高昂的问题
Contribution
we describe a method that requiring 5 times fewer model evaluations during the architecture search.
只需要评估1/5的模型。
We propose to use heuristic search to search the space of cell structures, starting with simple (shallow) models and progressing to complex ones, pruning out unpromising structures as we go.
渐进式的搜索,从浅层网络开始,逐步搜索复杂网络。
Since this process is expensive, we also learn a model or surrogate function(替代函数) which can predict the performance of a structure without needing to training it.
提出一种近似评估模型好坏的评估函数(预测器),直接预测模型性能,而不是从头训练候选网络。
Several advantages:
First, the simple structures train faster, so we get some initial results to train the surrogate quickly.
代理网络比较小,训练速度快(代价可以忽略不计)。
Second, we only ask the surrogate to predict the quality of structures that are slightly different (larger) from the ones it has seen
预测器只需要预测稍微不同的网络。
Third, we factorize(分解) the search space into a product(乘积) of smaller search spaces, allowing us to potentially search models with many more blocks.
将大的搜索空间分解为小的搜索空间的乘积。
we show that our approach is 5 times more efficient than the RL method of [41] in terms of number of models evaluated, and 8 times faster in terms of total compute.
效率相比RL方法提高5倍,总计算量快了8倍。
Method
Search Space
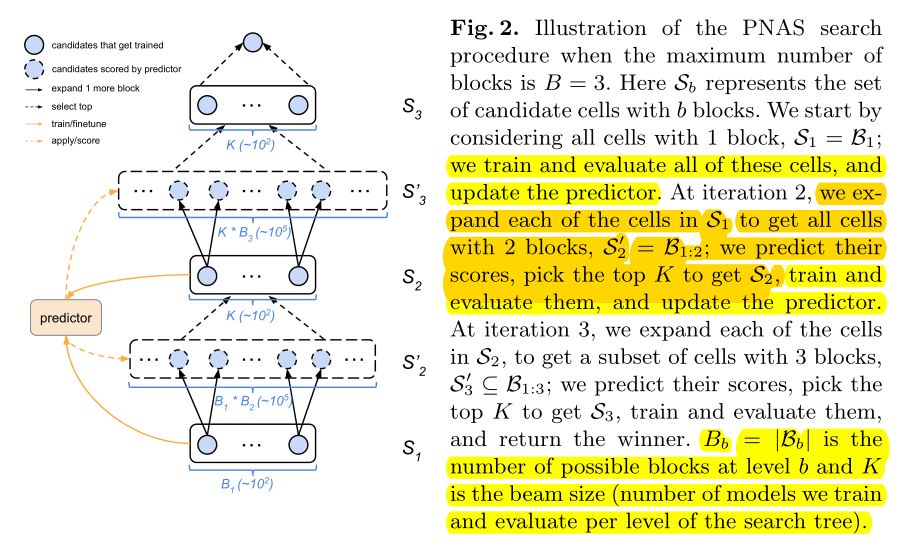
we first learn a cell structure, and then stack this cell a desired number of times, in order to create the final CNN.
先学习cell结构,再堆叠cell到目标层数。
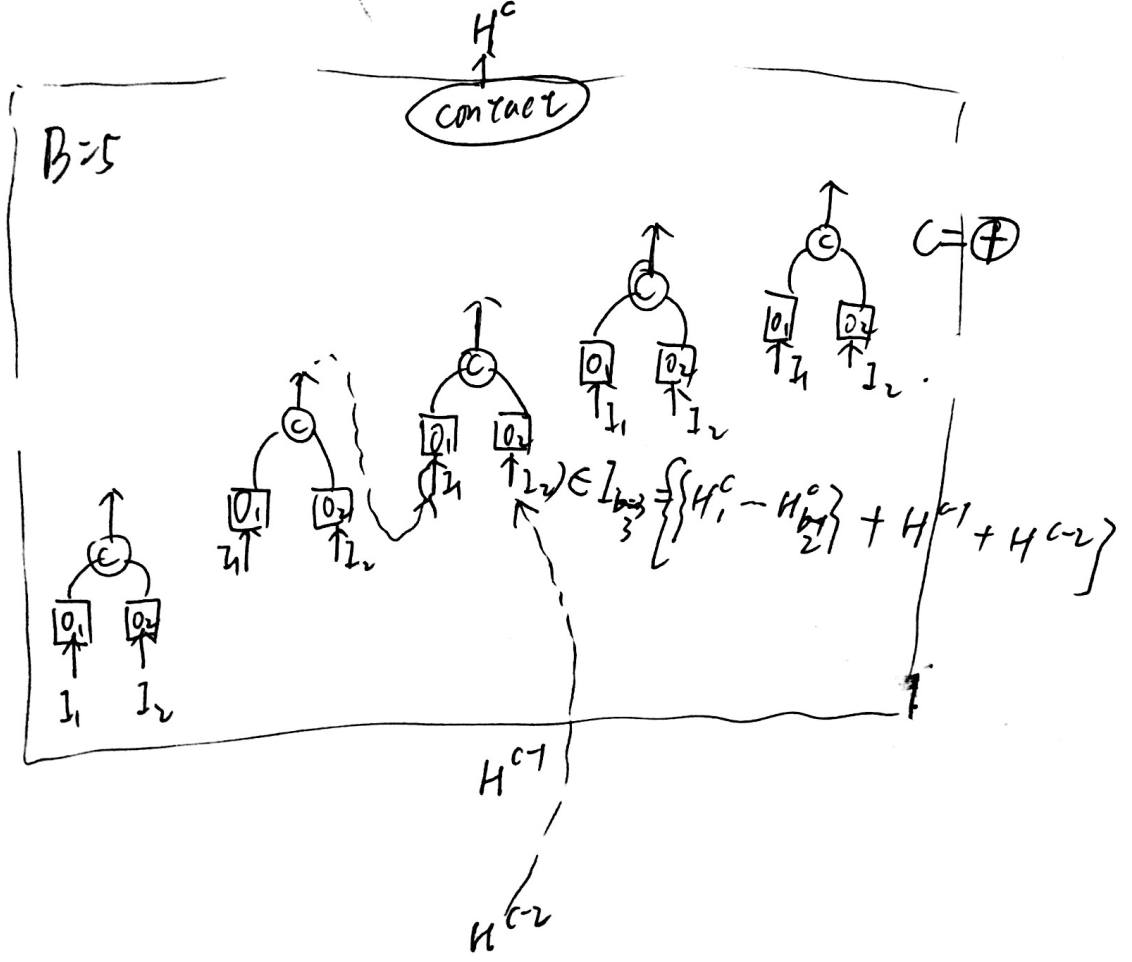
一个cell接收HxWxF的tensor,如果cell的stride=1,输出HxWxF的tensor,如果stride=2,输出H/2 x W/2 x 2F的tensor。
一个cell由B个block组成,每个block有2个input和1个output,每个block可以用一个五元组表示\(\left(I_{1}, I_{2}, O_{1}, O_{2}, C\right)\),第c个cell的输出表示为\(H^c\),第c个cell的第b个block的输出表示为\(H^c_b\)。
每个block的输入为当前cell中,在 {此block之前所有block的输出} 和 {上一个cell的输出,上上个cell的输出} 的集合。
Operator的选择空间有8种操作。
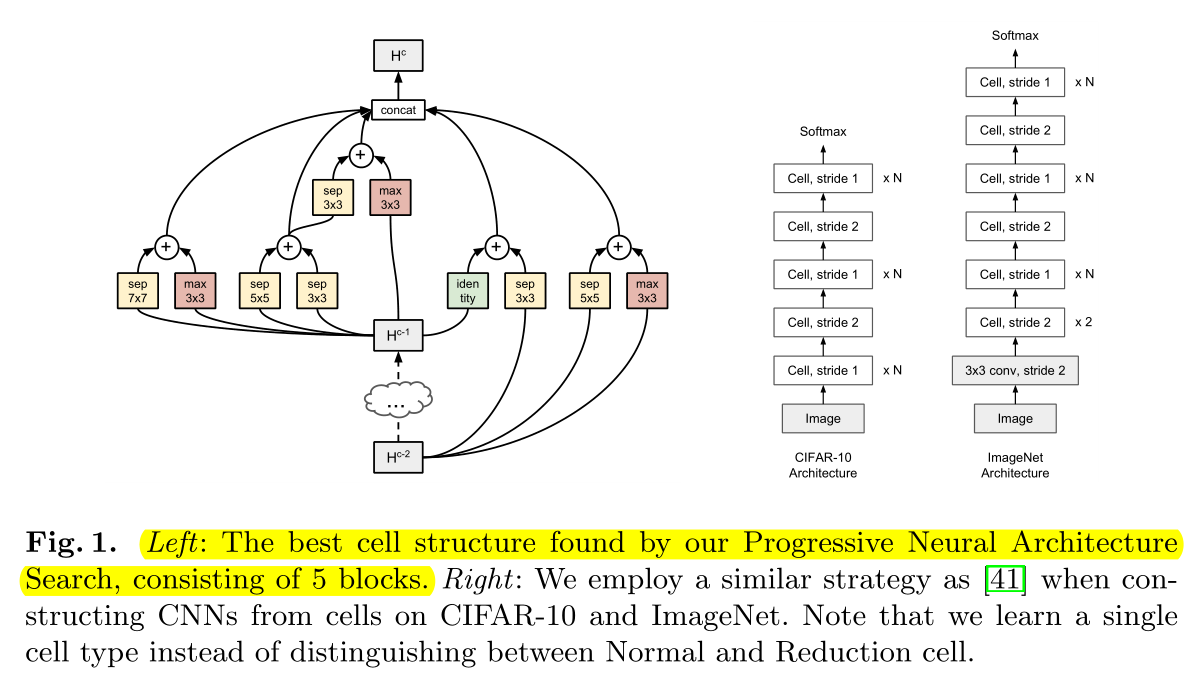
we stack a predefined number of copies of the basic cell (with the same structure, but untied weights 不继承权重 ), using either stride 1 or stride 2, as shown in Figure 1 (right).
找到最佳cell结构后,堆叠预定义的层数,构成右边的完整网络,不继承权重(重新训练)。
The number of stride-1 cells between stride-2 cells is then adjusted accordingly with up to N number of repeats.
Normal cell(stride=1)的数量,取决于N(超参)。
we only use one cell type (we do not distinguish between Normal and Reduction cells, but instead emulate a Reduction cell by using a Normal cell with stride 2),
我们没有区分normal cell 和Reduction cell,仅将Normal cell的stride设置为2作为Reduction cell。
Progressive Neural Architecture Search
Many previous approaches directly search in the space of full cells, or worse, full CNNs.
之前的方法直接搜索完整的cell结构,更糟糕的是整个cnn。
While this is a more direct approach, we argue that it is difficult to directly navigate in an exponentially large search space, especially at the beginning where there is no knowledge of what makes a good model.
尽管这种方式很直接,但搜索空间太大,而且一开始我们没有任何先验知识指导我们在巨大的搜索空间往哪个方向搜索。
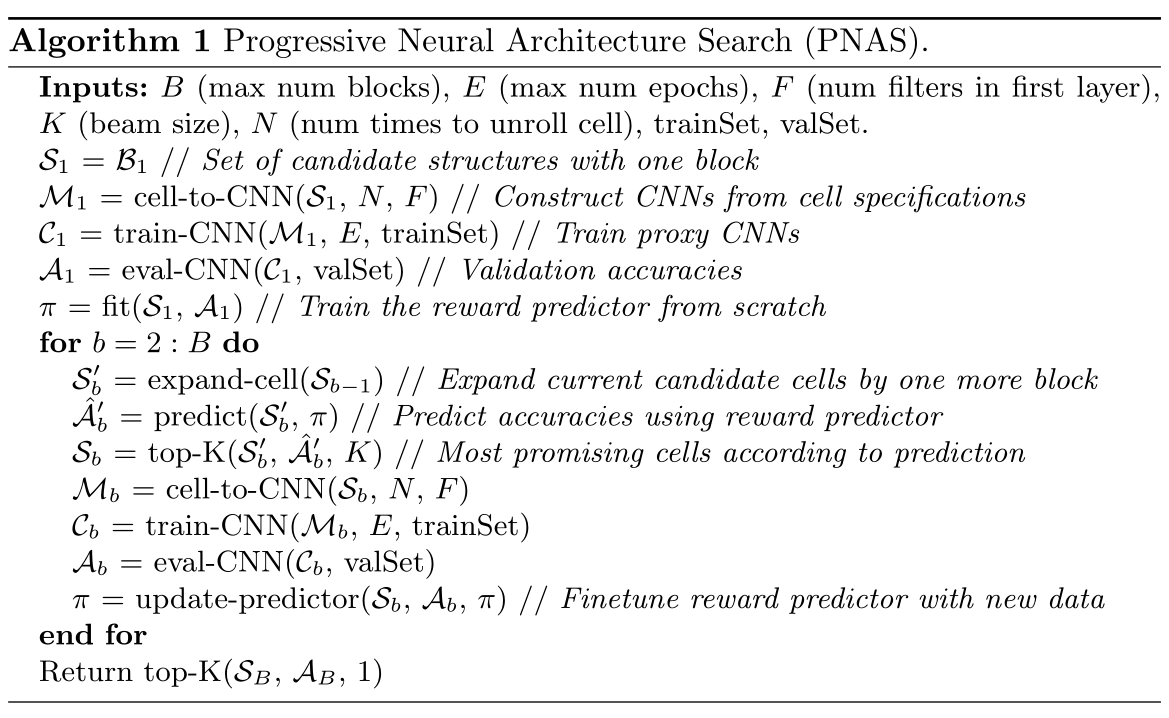
从每个cell含有1个block开始搜索。训练所有可能的\(B_1\),用\(B_1\)训练预测器,然后将\(B_1\)展开为\(B_2\)。
训练所有可能的\(B_2\)代价太大,我们使用预测器来评估所有\(B_2\)-cell的性能并选出最佳的K个\(B_2\)-cell,重复此过程(用选出来K个\(B_2\)-cell训练预测器,将选出的K个\(B_2\)-cell展开为\(B_3\),再用预测器选出最佳的K个...)。
Performance Prediction with Surrogate Model
Requirement of Predictor:
- Handle variable-sized inputs(接受可变输入)
- Correlated with true performance(预测值与真实值得相关性)
- Sample efficiency(简单高效)
- The requirement that the predictor be able to handle variable-sized strings immediately suggests the use of an RNN.
Two Predictor method
RNN and MLP(多层感知机)
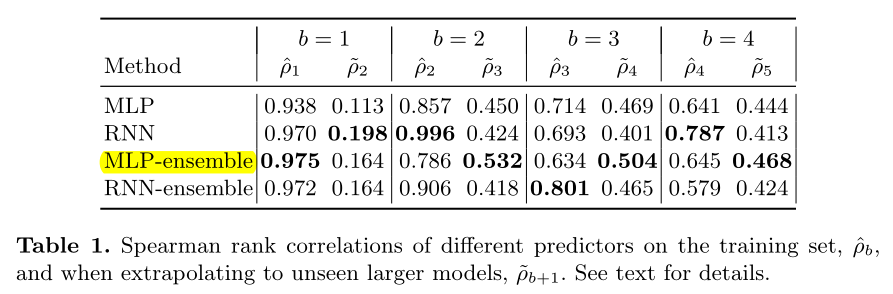
However, since the sample size is very small, we fit an ensemble of 5 predictors, We observed empirically that this reduced the variance of the predictions.
由于样本很简单,因此集成5个预测器(RNN-ensemble,MLP-ensemble),可以减少方差。
Experiments
Performance of the Surrogate Predictors
we train the predictor on the observed performance of cells with up to b blocks, but we apply it to cells with b+1 blocks.
在{B=b}上训练,在{B=b+1}的集合上预测。
We therefore consider predictive accuracy both for cells with sizes that have been seen before (but which have not been trained on), and for cells which are one block larger than the training data.
同时考虑在{B=b}的未训练的cell集合上的预测准确率,和{B=b+1}的cell集合上的预测准确率。
在所有{B=b}的cell集合中随机选择10k个作为数据集\(U_{b,1 :R}\),训练20个epochs。
randomly select K = 256 models (each of size b) from \(U_{b,1 :R}\)to generate a training set \(S_{b,t,1:K}\);
从数据集U中随机选择256个作为每轮的训练集S。
一共会训练20*256=5120个数据点。
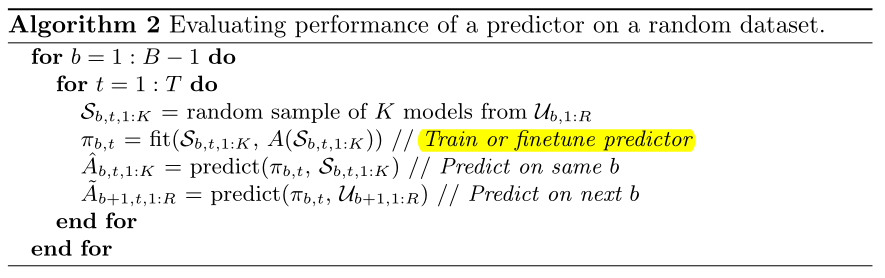
We now use this random dataset to evaluate the performance of the predictors using the pseudocode(伪代码) in Algorithm 2, where A(H) returns the true validation set accuracies of the models in some set H.
A(H) 返回cell的集合H训练后真实的准确率。
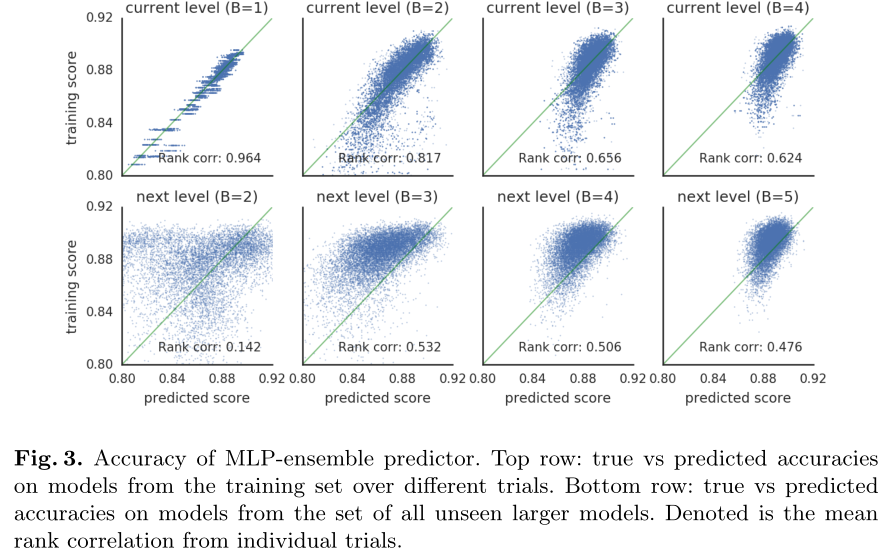
当B=b时,训练集为所有{B=b}的cell的一个子集,第一行为在所有{B=b}的cell的训练集(256*20=5120)上的预测结果和真实结果的相关性,
第二行为在所有{B=b+1}的cell的数据集(10k)上的预测结果和真实结果的相关性。
We see that the predictor performs well on models from the training set, but not so well when predicting larger models. However, performance does increase as the predictor is trained on more (and larger) cells.
预测器在训练集{B=b}上表现良好,但在较大的数据集{B=b+1}上表现不够好,但随着b的增加,越来越好。
We see that for predicting the training set, the RNN does better than the MLP, but for predicting the performance on unseen larger models (which is the setting we care about in practice), the MLP seems to do slightly better.
RNN方法的预测器在训练集{B=b}上表现更好,MLP在较大的数据集{B=b+1}上表现更好(我们关心的)
Conclusion
The main contribution of this work is to show how we can accelerate the search for good CNN structures by using progressive search through the space of increasingly complex graphs
使用渐进式(cell的深度逐渐增加)的搜索加速NAS
combined with a learned prediction function to efficiently identify the most promising models to explore.
使用可学习的预测器来识别潜在的最优网络。(引入P网络来搜索目标网络的最佳结构。eg. 用C网络来搜索B网络的最佳结构,而B网络又是来搜索A网络的最佳结构,套娃)
The resulting models achieve the same level of performance as previous work but with a fraction of the computational cost.
用小代价达到了了SOTA
Appendix
2018-ECCV-PNAS-Progressive Neural Architecture Search-论文阅读的更多相关文章
- 论文笔记:Progressive Neural Architecture Search
Progressive Neural Architecture Search 2019-03-18 20:28:13 Paper:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/conten ...
- 论文笔记:Auto-DeepLab: Hierarchical Neural Architecture Search for Semantic Image Segmentation
Auto-DeepLab: Hierarchical Neural Architecture Search for Semantic Image Segmentation2019-03-18 14:4 ...
- 小米造最强超分辨率算法 | Fast, Accurate and Lightweight Super-Resolution with Neural Architecture Search
本篇是基于 NAS 的图像超分辨率的文章,知名学术性自媒体 Paperweekly 在该文公布后迅速跟进,发表分析称「属于目前很火的 AutoML / Neural Architecture Sear ...
- Research Guide for Neural Architecture Search
Research Guide for Neural Architecture Search 2019-09-19 09:29:04 This blog is from: https://heartbe ...
- 论文笔记:Fast Neural Architecture Search of Compact Semantic Segmentation Models via Auxiliary Cells
Fast Neural Architecture Search of Compact Semantic Segmentation Models via Auxiliary Cells 2019-04- ...
- 论文笔记系列-Neural Architecture Search With Reinforcement Learning
摘要 神经网络在多个领域都取得了不错的成绩,但是神经网络的合理设计却是比较困难的.在本篇论文中,作者使用 递归网络去省城神经网络的模型描述,并且使用 增强学习训练RNN,以使得生成得到的模型在验证集上 ...
- 论文笔记:ProxylessNAS: Direct Neural Architecture Search on Target Task and Hardware
ProxylessNAS: Direct Neural Architecture Search on Target Task and Hardware 2019-03-19 16:13:18 Pape ...
- 论文笔记:Progressive Differentiable Architecture Search:Bridging the Depth Gap between Search and Evaluation
Progressive Differentiable Architecture Search:Bridging the Depth Gap between Search and Evaluation ...
- (转)Illustrated: Efficient Neural Architecture Search ---Guide on macro and micro search strategies in ENAS
Illustrated: Efficient Neural Architecture Search --- Guide on macro and micro search strategies in ...
随机推荐
- 绕WAF文章收集
在看了bypassword的<在HTTP协议层面绕过WAF>之后,想起了之前做过的一些研究,所以写个简单的短文来补充一下文章里“分块传输”部分没提到的两个技巧. 技巧1 使用注释扰乱分块数 ...
- 为什么要学习微信小程序直播开发?最新的小程序直播介绍和优势分析!
小程序直播的介绍 “小程序直播”是微信提供给开发者的实时视频直播工具,包括直播管理端.主播端和观众端等模块,支持提供常用的用户互动和营销促销工具. 开发者只需在小程序中引入相关代码并在管理后台完成配置 ...
- D. Count the Arrays 计数题
D. Count the Arrays 也是一个计数题. 题目大意: 要求构造一个满足题意的数列. \(n\) 代表数列的长度 数列元素的范围 \([1,m]\) 数列必须有且仅有一对相同的数 存在一 ...
- 【Linux基础总结】Shell 基础编程
Shell 基础编程 重启虚拟机遇到磁盘损坏如何解决 Shell编程中变量的声明.引用及作用域 Shell程序 概述 以文件形式存放批量的Linux命令集合,该文件能够被Shell解释执行,这种文件就 ...
- SpringBoot + SpringCloud的爬坑之旅
1,application.yaml中配置没有生效问题解决 如果配置文件确认没有错误但是没有生效首先是要到编译目录去查看是否被编译过去了,如果没有,请先将项目clean在重启 但是idea启动项目时也 ...
- python 基础应用4
1.列表所有元素全部单独输出 #所有元素全部单独输出 li = [1,2,3,'taibai',[4,5,6,'taibaia']] for i in li: if type(i) == list: ...
- dedecms织梦建站后怎么防止被黑,加强安全漏洞措施?
dedecms织梦建站后怎么防止被黑,加强安全漏洞措施? 很多人反映dedecms织梦网站被黑的情况,因为织梦相对来说漏洞还是挺多的,特别是新建设的站点,有些目录.文件该删的删,权限及安全都要设置,以 ...
- Unity接入友盟分享遇到的坑
最近项目接了一下友盟分享的SDK,中间遇到了几个坑,写下几条注意事项记录一下. 接入之前需要准备友盟开发者账号,相应平台开发者账号(微信.QQ.新浪微博)等... 安卓端: 1.确保 AndroidM ...
- 基于Vue搭建自己的组件库(1)
本项目演示地址:https://husilang.github.io/zm-ui 项目参考文章:从零开始搭建Vue组件库 VV-UI 项目的初衷是学习怎么封装一个基于Vue的UI组件库,顺便记录每个步 ...
- Vue+Vuex实现自动登录 升级版
Vue+Vuex实现自动登录 升级版 之前实现的版本在这里:Vue+Vuex实现自动登录 在之前实现的版本中,如果你进行测试,可以看到在浏览器的local Storage中,确实里面有了我 ...