CPM(Cluster Percolation method)派系过滤算法
一、概念
(1)完全子图/全耦合网络/k-派系:所有节点全部两两相连
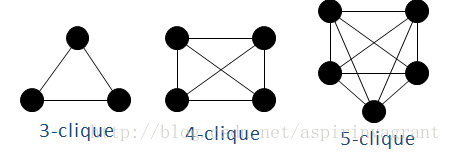
图1
这些全耦合网络也成为派系,k-派系表示该全耦合网络的节点数目为k
1)k-派系相邻:两个不同的k-派系共享k-1个节点,认为他们相邻
2)k-派系连通:一个k-派系可以通过若干个相邻的k-派系到达另一个k-派系,则称这两个k-派系彼此联通
二、思路
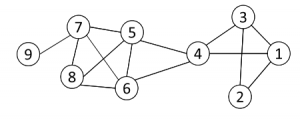
图2
1- first find all cliques of size k in the graph
第一步首先找到网络中大小为K的完全子图,例如图2中k=3的完全子图有{1, 2, 3} {1, 3, 4} {4, 5, 6} {5, 6, 7} {5, 6, 8} {5, 7, 8} {6, 7, 8}
2- then create graph where nodes are cliques of size k
第二步将每个完全子图定义为一个节点,建立一个重叠矩阵
a=[3 2 0 0 0 0 0;
2 3 1 0 0 0 0;
0 1 3 2 2 1 1;
0 0 2 3 2 2 2;
0 0 2 2 3 2 2;
0 0 1 2 2 3 2;
0 0 1 2 2 2 3 ]
3- add edges if two nodes (cliques) share k-1 common nodes
第三步将重叠矩阵变成社团邻接矩阵,其中重叠矩阵中对角线小于k,非对角线小于k-1的元素全置为0
a=[1 1 0 0 0 0 0;
1 1 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 1 1 1 0 0;
0 0 1 1 1 1 1;
0 0 1 1 1 1 1;
0 0 0 1 1 1 1;
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 ]
4- each connected component is a community
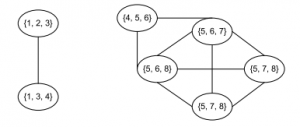
画出派系图,如上所示
从图中可以看出包含了两个社区{1,2,3,4}和{4,5,6,7,8},节点4属于两个社区的重叠节点
三、代码实现
R实现代码和Java实现代码可在GitHub网站上下载,R下载地址
https://github.com/angelosalatino/CliquePercolationMethod-R
四、References
Palla, G., Derényi, I., Farkas, I., & Vicsek, T. (2005). Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society. Nature, 435(7043), 814-818.
注意事项:
CPM算法不适用于稀疏矩阵,K的取值对结果影响不大,一般实验证明4-6为最佳
2017年4.16更新
用matlab算法实现,其中做了一点小变动,k是最小派系范围,寻找的是大于等于k的完全子图数,得到结果与上述描述结果一致,节点4是重叠节点
function [components,cliques,CC] = k_clique(k,M)
% k-clique algorithm for detecting overlapping communities in a network
% as defined in the paper "Uncovering the overlapping
% community structure of complex networks in nature and society" -
% G. Palla, I. Derényi, I. Farkas, and T. Vicsek - Nature 435, 814–818 (2005)
%
% [X,Y,Z] = k_clique(k,A)
%
% Inputs:
% k - clique size
% A - adjacency matrix
%
% Outputs:
% X - detected communities
% Y - all cliques (i.e. complete subgraphs that are not parts of larger
% complete subgraphs)
% Z - k-clique matrix
%
% Author : Anh-Dung Nguyen
% Email : anh-dung.nguyen@isae.fr % The adjacency matrix of the example network presented in the paper
% M = [1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1;
% 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1;
% 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0;
% 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0;
% 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0;
% 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0;
% 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1;
% 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1;
% 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1;
% 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1]; nb_nodes = size(M,1); % number of nodes % Find the largest possible clique size via the degree sequence:
% Let {d1,d2,...,dk} be the degree sequence of a graph. The largest
% possible clique size of the graph is the maximum value k such that
% dk >= k-1
degree_sequence = sort(sum(M,2) - 1,'descend');
max_s = 0;
for i = 1:length(degree_sequence)
if degree_sequence(i) >= i - 1
max_s = i;
else
break;
end
end cliques = cell(0);
% Find all s-size kliques in the graph
for s = max_s:-1:3
M_aux = M;
% Looping over nodes
for n = 1:nb_nodes
A = n; % Set of nodes all linked to each other
B = setdiff(find(M_aux(n,:)==1),n); % Set of nodes that are linked to each node in A, but not necessarily to the nodes in B
C = transfer_nodes(A,B,s,M_aux); % Enlarging A by transferring nodes from B
if ~isempty(C)
for i = size(C,1)
cliques = [cliques;{C(i,:)}];
end
end
M_aux(n,:) = 0; % Remove the processed node
M_aux(:,n) = 0;
end
end % Generating the clique-clique overlap matrix
CC = zeros(length(cliques));
for c1 = 1:length(cliques)
for c2 = c1:length(cliques)
if c1==c2
CC(c1,c2) = numel(cliques{c1});
else
CC(c1,c2) = numel(intersect(cliques{c1},cliques{c2}));
CC(c2,c1) = CC(c1,c2);
end
end
end % Extracting the k-clique matrix from the clique-clique overlap matrix
% Off-diagonal elements <= k-1 --> 0
% Diagonal elements <= k --> 0
CC(eye(size(CC))==1) = CC(eye(size(CC))==1) - k;
CC(eye(size(CC))~=1) = CC(eye(size(CC))~=1) - k + 1;
CC(CC >= 0) = 1;
CC(CC < 0) = 0; % Extracting components (or k-clique communities) from the k-clique matrix
components = [];
for i = 1:length(cliques)
linked_cliques = find(CC(i,:)==1);
new_component = [];
for j = 1:length(linked_cliques)
new_component = union(new_component,cliques{linked_cliques(j)});
end
found = false;
if ~isempty(new_component)
for j = 1:length(components)
if all(ismember(new_component,components{j}))
found = true;
end
end
if ~found
components = [components; {new_component}];
end
end
end function R = transfer_nodes(S1,S2,clique_size,C)
% Recursive function to transfer nodes from set B to set A (as
% defined above) % Check if the union of S1 and S2 or S1 is inside an already found larger
% clique
found_s12 = false;
found_s1 = false;
for c = 1:length(cliques)
for cc = 1:size(cliques{c},1)
if all(ismember(S1,cliques{c}(cc,:)))
found_s1 = true;
end
if all(ismember(union(S1,S2),cliques{c}(cc,:)))
found_s12 = true;
break;
end
end
end if found_s12 || (length(S1) ~= clique_size && isempty(S2))
% If the union of the sets A and B can be included in an
% already found (larger) clique, the recursion is stepped back
% to check other possibilities
R = [];
elseif length(S1) == clique_size;
% The size of A reaches s, a new clique is found
if found_s1
R = [];
else
R = S1;
end
else
% Check the remaining possible combinations of the neighbors
% indices
if isempty(find(S2>=max(S1),1))
R = [];
else
R = [];
for w = find(S2>=max(S1),1):length(S2)
S2_aux = S2;
S1_aux = S1;
S1_aux = [S1_aux S2_aux(w)];
S2_aux = setdiff(S2_aux(C(S2(w),S2_aux)==1),S2_aux(w));
R = [R;transfer_nodes(S1_aux,S2_aux,clique_size,C)];
end
end
end
end
end
CPM(Cluster Percolation method)派系过滤算法的更多相关文章
- win7下使用Taste实现协同过滤算法
如果要实现Taste算法,必备的条件是: 1) JDK,使用1.6版本.需要说明一下,因为要基于Eclipse构建,所以在设置path的值之前要先定义JAVA_HOME变量. 2) Maven,使用2 ...
- SVD++:推荐系统的基于矩阵分解的协同过滤算法的提高
1.背景知识 在讲SVD++之前,我还是想先回到基于物品相似的协同过滤算法.这个算法基本思想是找出一个用户有过正反馈的物品的相似的物品来给其作为推荐.其公式为:
- GBDT(Gradient Boosting Decision Tree)算法&协同过滤算法
GBDT(Gradient Boosting Decision Tree)算法参考:http://blog.csdn.net/dark_scope/article/details/24863289 理 ...
- Spark机器学习之协同过滤算法
Spark机器学习之协同过滤算法 一).协同过滤 1.1 概念 协同过滤是一种借助"集体计算"的途径.它利用大量已有的用户偏好来估计用户对其未接触过的物品的喜好程度.其内在思想是相 ...
- Collaborative Filtering(协同过滤)算法详解
基本思想 基于用户的协同过滤算法是通过用户的历史行为数据发现用户对商品或内容的喜欢(如商品购买,收藏,内容评论或分享),并对这些喜好进行度量和打分.根据不同用户对相同商品或内容的态度和偏好程度计算用户 ...
- 【机器学习笔记一】协同过滤算法 - ALS
参考资料 [1]<Spark MLlib 机器学习实践> [2]http://blog.csdn.net/u011239443/article/details/51752904 [3]线性 ...
- 吴恩达机器学习笔记58-协同过滤算法(Collaborative Filtering Algorithm)
在之前的基于内容的推荐系统中,对于每一部电影,我们都掌握了可用的特征,使用这些特征训练出了每一个用户的参数.相反地,如果我们拥有用户的参数,我们可以学习得出电影的特征. 但是如果我们既没有用户的参数, ...
- Spark机器学习(11):协同过滤算法
协同过滤(Collaborative Filtering,CF)算法是一种常用的推荐算法,它的思想就是找出相似的用户或产品,向用户推荐相似的物品,或者把物品推荐给相似的用户.怎样评价用户对商品的偏好? ...
- 亚马逊 协同过滤算法 Collaborative filtering
这节课时郭强的三维课.他讲的是MAYA和max .自己对这个也不怎么的感兴趣.而且这个课感觉属于数字媒体.自己对游戏,动画,这些东西一点都不兴趣,比如大一的时候刚开学的时候,张瑞的数字媒体的导论课.还 ...
随机推荐
- 2018.06.30 BZOJ 3932: [CQOI2015]任务查询系统(主席树)
3932: [CQOI2015]任务查询系统 Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MB Description 最近实验室正在为其管理的超级计算机编制一套任务管理 ...
- UVa 11464 Even Parity (二进制法枚举)
题意:给你一个n*n的01矩阵,让你把最少的0变成1,使得每个元素的上,下,左,右的元素(如果有的话)之和均为偶数. 析:最好想的的办法就是暴力,就是枚举每个数字是变还是不变,但是...时间复杂度也太 ...
- HDU 1756 Cupid's Arrow (几何问题,判定点在多边形内部)
题意:中文的么,自己看喽. 析:很容易明白是判定点是不是在多边形内部,一般是向量来判定,我一开始用点在向量的右侧,因为是顺时针给的,只要点全在外侧或边上, 就可以,暴力一下就ok.由于这个是浮点数,一 ...
- 学习前端的菜鸡对JS的call,apply,bind的通俗易懂理解
call,apply,bind 在JavaScript中,call.apply和bind是Function对象自带的三个方法,都是为了改变函数体内部 this 的指向. a ...
- i9-9900k烤机
新装机一台,记录烤机参数 硬件配置: cpu: i9-9900k 主板:技嘉Z390 AORUS PRO WIFI 内存:海盗船ddr4 3200 显卡:技嘉gtx1080ti 硬盘:三星970Pro ...
- gorename: easy refactoring tool for Golang[转]
To inaugurate this attempt of blog, I’ll talk about gorename a small but incredibly useful tool I ju ...
- linux 各项配置汇总
DNS配置 linux动态地址无需配置DNSlinux配置静态地址时,需要重新设置DNS,DNS的地址为:自己所用网络商的DNS地址,其中DNS地址还分区域例如:电信 江苏南京dns:218.2.13 ...
- java基础-day4
第04天 java基础语法 今日内容介绍 u Random u 数组 第1章 Random 1.1 产生整数随机数 1.1.1 Random的使用步骤 我们想产生1~100(包含1 ...
- java web前端easyui(layout+tree+双tabs)布局+树+2个选项卡tabs
1.列出要实现的样式: 2.实现的代码: 分三大部分: 1):页面主体部分:mian.vm <html> <head> <title>Ks UI</title ...
- 集合(四)HashMap
之前的List,讲了ArrayList.LinkedList,最后讲到了CopyOnWriteArrayList,就前两者而言,反映的是两种思想: (1)ArrayList以数组形式实现,顺序插入.查 ...
