Java之——利用Comparator接口对多个排序条件进行处理
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/l1028386804/article/details/56513205
一、需求
假设现在有个如此的需求:需要对一个这样的雇员列表进行排序,排序规则如下:
1、首先级别最高的排在前面,
2、如果级别相等,那么按工资排序,工资高的排在前面,
3、如果工资相当则按入职年数排序,入职时间最长的排在前面。
雇员对象包含级别、工资和入职年份,代码如下:
- package
import
/**
- * 雇员信息
- * @author liuyazhuang
- *
- */
publicclassimplementsprivatestaticfinallong
* ID
- */
publicint* 级别
- */
publicint* 工资
- */
publicint* 入职年数
- */
publicintpublicint
returnpublicvoidint
thispublicint
returnpublicvoidint
thispublicint
returnpublicvoidint
thispublicint
returnpublicvoidint
thispublicintintintint
this
this
this
this}
二、实现Comparator接口
这里我们实现Java.util.Comparator接口,用于对雇员列表进行排序,代码如下:
- package
import
import
/**
- * 核心排序类
- * @author liuyazhuang
- *
- */
publicclassimplements - publicint
int; - int
if) { - ) ? : -;
- else
- if) {
- ) ? : -;
- else
- if) {
- ) ? : -;
- return
}
三、验证排序结果
下面用一个单元测试,来验证排序结果是否正确
- package
import
import
importimport
import
import/**
- * 测试排序类
- *
- * @author liuyazhuang
- *
- */
publicclass - publicvoidthrows
newnew, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new, , , ));
- new
); - );
- for
, employee.getId(), employee.getLevel(), employee.getSalary(), - );
- }
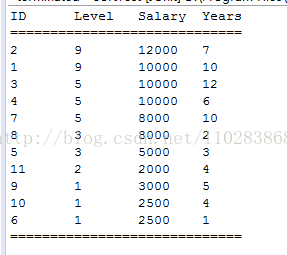
运行结果:
四、附录
java.util.Comparator接口源代码
- /*
- * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
- * contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
- * this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
- * The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
- * (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
- * the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
- *
- * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- *
- * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
- * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
- * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
- * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
- * limitations under the License.
- */
package
/**
- * A {@code Comparator} is used to compare two objects to determine their ordering with
- * respect to each other. On a given {@code Collection}, a {@code Comparator} can be used to
- * obtain a sorted {@code Collection} which is <i>totally ordered</i>. For a {@code Comparator}
- * to be <i>consistent with equals</i>, its {code #compare(Object, Object)}
- * method has to return zero for each pair of elements (a,b) where a.equals(b)
- * holds true. It is recommended that a {@code Comparator} implements
- * {@link java.io.Serializable}.
- *
- * @since 1.2
- */
publicinterface* Compares the two specified objects to determine their relative ordering. The ordering
- * implied by the return value of this method for all possible pairs of
- * {@code (lhs, rhs)} should form an <i>equivalence relation</i>.
- * This means that
- * <ul>
- * <li>{@code compare(a,a)} returns zero for all {@code a}</li>
- * <li>the sign of {@code compare(a,b)} must be the opposite of the sign of {@code
- * compare(b,a)} for all pairs of (a,b)</li>
- * <li>From {@code compare(a,b) > 0} and {@code compare(b,c) > 0} it must
- * follow {@code compare(a,c) > 0} for all possible combinations of {@code
- * (a,b,c)}</li>
- * </ul>
- *
- * @param lhs
- * an {@code Object}.
- * @param rhs
- * a second {@code Object} to compare with {@code lhs}.
- * @return an integer < 0 if {@code lhs} is less than {@code rhs}, 0 if they are
- * equal, and > 0 if {@code lhs} is greater than {@code rhs}.
- * @throws ClassCastException
- * if objects are not of the correct type.
- */
publicint* Compares this {@code Comparator} with the specified {@code Object} and indicates whether they
- * are equal. In order to be equal, {@code object} must represent the same object
- * as this instance using a class-specific comparison.
- * <p>
- * A {@code Comparator} never needs to override this method, but may choose so for
- * performance reasons.
- *
- * @param object
- * the {@code Object} to compare with this comparator.
- * @return boolean {@code true} if specified {@code Object} is the same as this
- * {@code Object}, and {@code false} otherwise.
- * @see Object#hashCode
- * @see Object#equals
- */
publicboolean
}
Java之——利用Comparator接口对多个排序条件进行处理的更多相关文章
- 我的Java开发学习之旅------>Java利用Comparator接口对多个排序条件进行处理
一需求 二实现Comparator接口 三验证排序结果 验证第一条件首先按级别排序级别最高的排在前面 验证第二条如果级别相等那么按工资排序工资高的排在前面 验证第三条如果工资相当则按入职年数排序入职时 ...
- java Comparable 和 Comparator接口区别
Comparable 简介 Comparable 是排序接口. 若一个类实现了Comparable接口,就意味着“该类支持排序”. 即然实现Comparable接口的类支持排序,假设现在存在“实现C ...
- Java Comparable 和 Comparator 接口详解
本文基于 JDK8 分析 Comparable Comparable 接口位于 java.lang 包下,Comparable 接口下有一个 compareTo 方法,称为自然比较方法.一个类只要实现 ...
- 【LeetCode】two num 利用comparable接口 对对象进行排序
题目two num 题意:给定一个整数数组和一个目标值.要求在数组中找到两个数.使得它们的和相加等于目标值.而且返回两个数的下标 思路:1.假设使用暴力,时间复杂度为O(n^2) 2.能够先将全部数进 ...
- java利用Comparator接口对自定义数组排序
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class MySort { public static void main( ...
- java基础-Comparator接口与Collections实现排序算法
java 排序Comparable和Comparator使用 java提供了两个排序用的接口Comparable和Comparator,一般情况下使用区别如下: Comparable 接口用于类的固定 ...
- Java语言利用Collections.sort对Map,List排序
1.main方法包含TreeMap排序1,TreeMap排序2,HashMap排序,List<Integer>排序,List<Bean>排序,List<Map>排序 ...
- Java:Comparator接口
public interface Comparator<T> 接口里面的方法 int compare(T o1, T o2) o1 > o2 返回 1 o1 = o2 返回 0 o1 ...
- java中Comparatable接口和Comparator接口的区别
1.不同类型的排序规则 .自然排序是什么? 自然排序是一种升序排序.对于不同的数据类型,升序规则不一样: BigDecimal BigInteger Byte Double Float Int ...
随机推荐
- yii2项目中运行composer 过程中遇到的问题
问题1: Your requirements could not be resolved to an installable set of packages 则表明 未安装fxp/composer-a ...
- 初识 GitHub
初识 GitHub 一.注册账号 GitHub 官网:https://github.com/ 点击右上角sign up,进行注册,注册界面如下: 填写用户名,邮箱地址,密码,下滑点击绿色按钮:Crea ...
- docker 实践
https://doc.yonyoucloud.com/doc/docker_practice/etcd/etcdctl.html 启动http restful API docker批量映射端口 怎么 ...
- 20145325张梓靖 《网络对抗技术》 MSF基础应用
20145325张梓靖 <网络对抗技术> MSF基础应用 实验内容 掌握metasploit的基本应用方式以及常用的三种攻击方式的思路 主动攻击,即对系统的攻击,不需要被攻击方配合,这里以 ...
- 尚硅谷面试第一季-14Redis持久化类型及其区别
课堂重点: Redis提供了两种不同形式的持久化方案,分别是RDB和AOF. RDB使用Snapshot快照做全量的存储. RDB优缺点: AOF 以日志的方式记录每个写操作,只最佳,不该写文件.增量 ...
- Vue学习【第一篇】:Vue初识与指令
什么是Vue 什么是Vue Vue.js是一个渐进式JavaScript框架它是构建用户界面的JavaScript框架(让它自动生成js,css,html等) 渐进式:vue从小到控制页面中的一个变量 ...
- 浅谈Log4j2日志框架及使用
目录 1.日志框架 2.为什么需要日志接口,直接使用具体的实现不就行了吗? 3.log4j2日志级别 4.log4j2配置文件的优先级 5.对于log4j2配置文件的理解 6.对于Appender的理 ...
- extjs的使用笔记
2006年jack slocum斯洛克姆 基于yui写的扩展前端框架(就是由一些前端可视化组件如表单,树, 表格,等组成的frameset或者叫做 ui engine),叫yui-ext, 后来成熟后 ...
- Docker 使用Dockerfile构建redis镜像
Dockerfile实现: FROM centos: MAINTAINER hongdada "hongdaqi159505@gmail.com" WORKDIR /home RU ...
- SpringBoot 使用jwt进行身份验证
这里只供参考,比较使用jwt方式进行身份验证感觉不好,最不行的就是不能退出 登陆时设定多长过期时间,只能等这个时间过了以后才算退出,服务端只能验证请求过来的token是否通过验证 Code: /** ...