理解java容器底层原理--手动实现LinkedList
Node
java 中的 LIinkedList 的数据结构是链表,而链表中每一个元素是节点。
我们先定义一下节点:
package com.xzlf.collection;
public class Node {
Node previous; // 上一个节点
Node next; // 下一个节点
Object element; // 元素数据
public Node(Object element) {
super();
this.element = element;
}
public Node(Node previous, Node next, Object element) {
super();
this.previous = previous;
this.next = next;
this.element = element;
}
}
版本一:基础版本
先创建一个类,完成链表的创建、添加元素、然后重写toString() 方法:
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
测试:
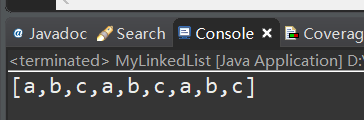
版本二:增加get() 方法
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 增加get方法
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList2 {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public Object get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp.element;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList2 list = new MyLinkedList2();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.get(1));
System.out.println(list.get(4));
}
}
测试:
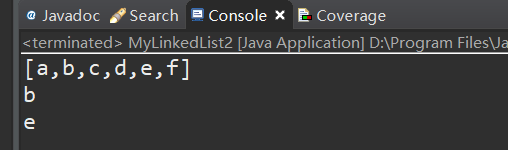
版本三:增加remove() 方法
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 增加remove
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList3 {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public Object get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
tmp = getNode(index);
return tmp == null ? null : tmp.element;
}
public void remove(int index) {
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node up = tmp.previous;
Node down = tmp.next;
if (tmp != null) {
if (up != null) {
up.next = down;
}
if (down != null) {
down.previous = up;
}
// 被删元素是第一个时
if(index == 0) {
first = down;
}
// 被删元素是最后一个时
if(index == size - 1) {
last = up;
}
size--;
}
}
public Node getNode(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList3 list = new MyLinkedList3();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(2);
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(0);// 删除第一个元素
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(3);// 删除最后一个元素
System.out.println(list);
}
}
测试:
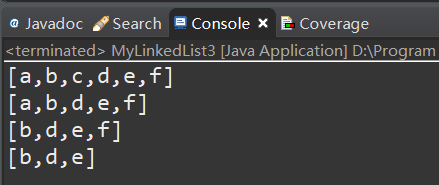
版本四:插入节点
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 插入节点
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList4 {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public void add(int index, Object obj) {
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node newNode = new Node(obj);
if(tmp != null) {
Node up = tmp.previous;
up.next = newNode;
newNode.previous = up;
newNode.next = tmp;
tmp.previous = newNode;
}
}
public Object get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
tmp = getNode(index);
return tmp == null ? null : tmp.element;
}
public void remove(int index) {
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node up = tmp.previous;
Node down = tmp.next;
if (tmp != null) {
if (up != null) {
up.next = down;
}
if (down != null) {
down.previous = up;
}
// 被删元素是第一个时
if(index == 0) {
first = down;
}
// 被删元素是最后一个时
if(index == size - 1) {
last = up;
}
size--;
}
}
public Node getNode(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList4 list = new MyLinkedList4();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
System.out.println(list);
list.add(1, "hello");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
测试:
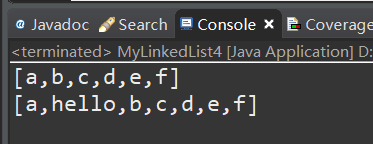
版本五:增加泛型,小的封装
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 增加泛型,小的封装
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList5<E> {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(E element) {
Node node = new Node(element);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkRange(index);
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node newNode = new Node(element);
if(tmp != null) {
Node up = tmp.previous;
up.next = newNode;
newNode.previous = up;
newNode.next = tmp;
tmp.previous = newNode;
size++;
}
}
private void checkRange(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
}
public E get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
checkRange(index);
tmp = getNode(index);
return tmp == null ? null : (E) tmp.element;
}
public void remove(int index) {
checkRange(index);
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node up = tmp.previous;
Node down = tmp.next;
if (tmp != null) {
if (up != null) {
up.next = down;
}
if (down != null) {
down.previous = up;
}
// 被删元素是第一个时
if(index == 0) {
first = down;
}
// 被删元素是最后一个时
if(index == size - 1) {
last = up;
}
size--;
}
}
private Node getNode(int index) {
checkRange(index);
Node tmp = null;
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList5<String> list = new MyLinkedList5<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
System.out.println(list);
list.add(1, "hello");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.get(1));
}
}
测试:
现在我们在编辑上使用add() 方法后已经提示要插入String类型的数据了:
以上代码测试运行结果:
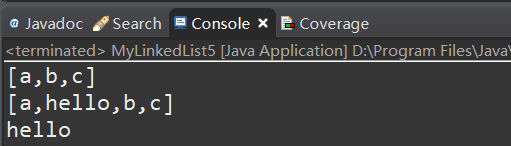
以上代码可能还有部分细节上的bug,不过作为理解LinkedList数据结构的练习应该够用了。
理解java容器底层原理--手动实现LinkedList的更多相关文章
- 理解java容器底层原理--手动实现HashMap
HashMap结构 HashMap的底层是数组+链表,百度百科找了张图: 先写个链表节点的类 package com.xzlf.collection2; public class Node { int ...
- 理解java容器底层原理--手动实现HashSet
HashSet的底层其实就是HashMap,换句话说HashSet就是简化版的HashMap. 直接上代码: package com.xzlf.collection2; import java.uti ...
- 理解java容器底层原理--手动实现ArrayList
为了照顾初学者,我分几分版本发出来 版本一:基础版本 实现对象创建.元素添加.重新toString() 方法 package com.xzlf.collection; /** * 自定义一个Array ...
- (前篇:NIO系列 推荐阅读) Java NIO 底层原理
出处: Java NIO 底层原理 目录 1.1. Java IO读写原理 1.1.1. 内核缓冲与进程缓冲区 1.1.2. java IO读写的底层流程 1.2. 四种主要的IO模型 1.3. 同步 ...
- Java面试底层原理
面试发现经常有些重复的面试问题,自己也应该学会记录下来,最好自己能做成笔记,在下一次面的时候说得有条不紊,深入具体,面试官想必也很开心.以下是我个人总结,请参考: HashSet底层原理:(问了大几率 ...
- 10分钟看懂, Java NIO 底层原理
目录 写在前面 1.1. Java IO读写原理 1.1.1. 内核缓冲与进程缓冲区 1.1.2. java IO读写的底层流程 1.2. 四种主要的IO模型 1.3. 同步阻塞IO(Blocking ...
- java容器HashMap原理
1.为什么需要HashMap 前面我们说了ArrayList和LinkedList,它们对容器内的对象都能实现增.删.改.查.遍历等操作, 并且对应不同的情况,我们可以选择不同的List,用以提高效率 ...
- 魔鬼在细节,理解Java并发底层之AQS实现
jdk的JUC包(java.util.concurrent)提供大量Java并发工具提供使用,基本由Doug Lea编写,很多地方值得学习和借鉴,是进阶升级必经之路 本文从JUC包中常用的对象锁.并发 ...
- Java 容器源码分析之 LinkedList
概览 同 ArrayList 一样,LinkedList 也是对 List 接口的一种具体实现.不同的是,ArrayList 是基于数组来实现的,而 LinkedList 是基于双向链表实现的.Lin ...
随机推荐
- Redis数据结构——quicklist
之前的文章我们曾总结到了Redis数据结构--链表和Redis数据结构--压缩列表这两种数据结构,他们是Redis List(列表)对象的底层实现方式.但是考虑到链表的附加空间相对太高,prev 和 ...
- [noip模拟赛]虫洞holes<SPFA>
虫洞(holes.cpp/c/pas) [题目描述] N个虫洞,M条单向跃迁路径.从一个虫洞沿跃迁路径到另一个虫洞需要消耗一定量的燃料和1单位时间.虫洞有白洞和黑洞之分.设一条跃迁路径两端的虫洞质量差 ...
- lly的数列询问(最小生成树 + 思维)
lly的数列询问 Description 这个问题很简单,lly lly lly给你一些提示,让你试着确定长度为n n n的数列A [1] A [2] ... A [n]的值,但是他想尽一切办法为大家 ...
- C++中的字符串切片操作
string str = "hello"; str.substr(0,2); //输出"he", 表示[0,2)
- web font各浏览器兼容问题以及格式
语法: @font-face { font-family: <identifier>; src: <fontsrc> [, <fontsrc>]*; <fon ...
- django->基本操作和新建项目常用配置
一.安装django pip install django==2.1.5 -U #安装django/升级最新版本 二.创建.启动django项目 django-admin startproject m ...
- MODIS系列之NDVI(MOD13Q1)一:数据下载(一)基于插件
引言: 写MODIS数据处理这个系列文章的初衷,主要是为了分享本人处理MODIS数据方面的一些经验.鉴于网上对这方面系统性的总结还比较少,我搜集资料时也是走了许多的弯路,因此希望通过此文让初学者能够更 ...
- AJ学IOS 之微博项目实战(10)微博cell中图片的显示以及各种填充模式简介
AJ分享,必须精品 :一效果 如果直接设置会有拉伸等等的状况,这里主要介绍图片显示的一些细节 二:代码 代码实现其实很简单,微博当中用了一个photos来存放九宫格这些图片,然后用了一个photo类来 ...
- AJ整理问题之:内存堆栈
内存 数据在内存中的存放 在计算机中,运行的应用程序的数据都是保存在内存中的. 不同类型的数据,保存的内存区域不同,其中包括: 1:栈区(stack)由编译器自动分配并释放,一半存放函数的参数值,局部 ...
- Mybatis-项目结构
源文件:https://github.com/569844962/Mybatis-Learn/blob/master/doc/Mybatis%E6%95%B4%E4%BD%93%E6%9E%B6%E6 ...
