Hadoop学习之路(十九)MapReduce框架排序
流量统计项目案例
样本示例
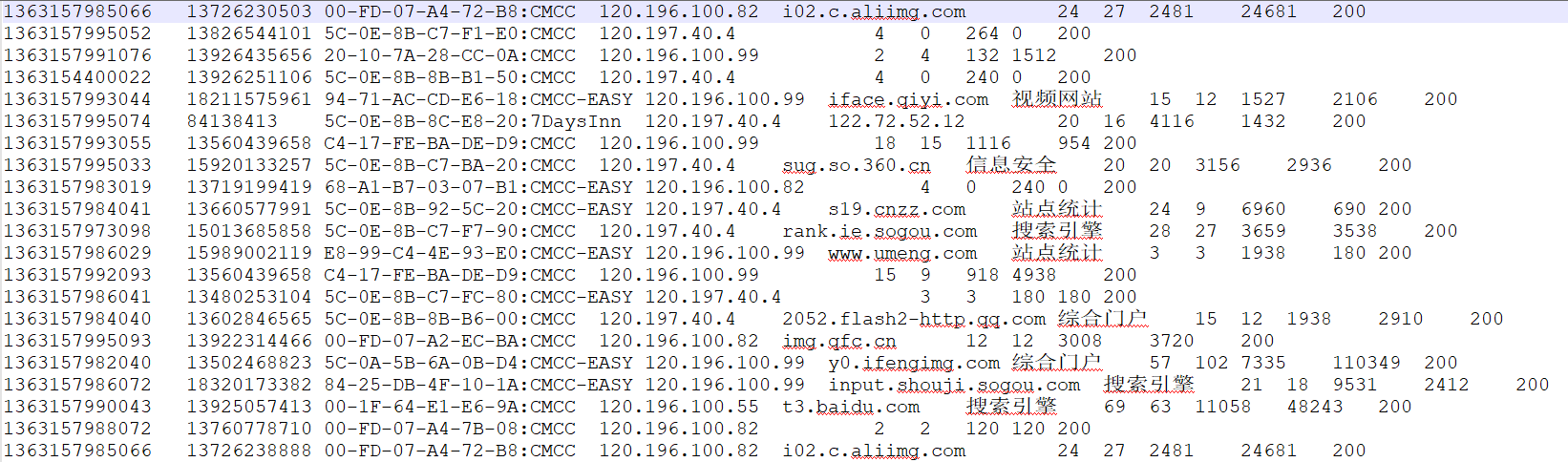

需求
1、 统计每一个用户(手机号)所耗费的总上行流量、总下行流量,总流量
2、 得出上题结果的基础之上再加一个需求:将统计结果按照总流量倒序排序
3、 将流量汇总统计结果按照手机归属地不同省份输出到不同文件中
第一题
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /**
* 第一题:统计每一个用户(手机号)所耗费的总上行流量、总下行流量,总流量
*/ public class FlowSumMR { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "FlowSumMR");
job.setJarByClass(FlowSumMR.class); job.setMapperClass(FlowSumMRMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowSumMRReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/input/"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/output_sum")); boolean isDone = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(isDone ? 0 : 1);
} public static class FlowSumMRMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ /**
* value = 1363157993044 18211575961 94-71-AC-CD-E6-18:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99
* iface.qiyi.com 视频网站 15 12 1527 2106 200
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\t"); String outkey = split[1]; String outValue = split[8] + "\t" + split[9]; context.write(new Text(outkey), new Text(outValue)); }
} public static class FlowSumMRReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int upFlow = 0;
int downFlow = 0;
int sumFlow = 0; for(Text t : values){
String[] split = t.toString().split("\t"); int upTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
int downTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[1]); upFlow+=upTempFlow;
downFlow += downTempFlow;
} sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow; context.write(key, new Text(upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + sumFlow));
}
}
}
第二题
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import comg.ghgj.mr.pojo.FlowBean; /**
* 需求: 第二个题目,就是对第一个题目的结果数据,进行按照总流量倒叙排序
*
*
*/
public class FlowSortMR { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "FlowSumMR");
job.setJarByClass(FlowSortMR.class); job.setMapperClass(FlowSortMRMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowSortMRReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/output_sum"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/output_sort_777")); boolean isDone = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(isDone ? 0 : 1); } public static class FlowSortMRMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, NullWritable>{ /**
* value = 13602846565 26860680 40332600 67193280
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\t"); FlowBean fb = new FlowBean(split[0], Long.parseLong(split[1]), Long.parseLong(split[2])); context.write(fb, NullWritable.get());
} } public static class FlowSortMRReducer extends Reducer<FlowBean, NullWritable, FlowBean, NullWritable>{ @Override
protected void reduce(FlowBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException { for(NullWritable nvl : values){
context.write(key, nvl);
} } }
}
FlowBean.java
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; /**
* 第一,定义好属性
* 第二,定义好属性的getter 和 setter方法
* 第三,定义好构造方法(有参,无参)
* 第四:定义好toString();
*
*
* 详细解释:
*
* 如果一个自定义对象要作为key 必须要实现 WritableComparable 接口, 而不能实现 Writable, Comparable
*
* 如果一个自定义对象要作为value,那么只需要实现Writable接口即可
*/
public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean>{
//public class FlowBean implements Comparable<FlowBean>{ private String phone;
private long upFlow;
private long downFlow;
private long sumFlow;
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public long getUpFlow() {
return upFlow;
}
public void setUpFlow(long upFlow) {
this.upFlow = upFlow;
}
public long getDownFlow() {
return downFlow;
}
public void setDownFlow(long downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
}
public long getSumFlow() {
return sumFlow;
}
public void setSumFlow(long sumFlow) {
this.sumFlow = sumFlow;
}
public FlowBean(String phone, long upFlow, long downFlow, long sumFlow) {
super();
this.phone = phone;
this.upFlow = upFlow;
this.downFlow = downFlow;
this.sumFlow = sumFlow;
}
public FlowBean(String phone, long upFlow, long downFlow) {
super();
this.phone = phone;
this.upFlow = upFlow;
this.downFlow = downFlow;
this.sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow;
}
public FlowBean() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return phone + "\t" + upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + sumFlow;
} /**
* 把当前这个对象 --- 谁掉用这个write方法,谁就是当前对象
*
* FlowBean bean = new FlowBean();
*
* bean.write(out) 把bean这个对象的四个属性序列化出去
*
* this = bean
*/
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub out.writeUTF(phone);
out.writeLong(upFlow);
out.writeLong(downFlow);
out.writeLong(sumFlow); } // 序列化方法中的写出的字段顺序, 一定一定一定要和 反序列化中的 接收顺序一致。 类型也一定要一致 /**
* bean.readField();
*
* upFlow =
*/
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub phone = in.readUTF();
upFlow = in.readLong();
downFlow = in.readLong();
sumFlow = in.readLong(); } /**
* Hadoop的序列化机制为什么不用 java自带的实现 Serializable这种方式?
*
* 本身Hadoop就是用来解决大数据问题的。
*
* 那么实现Serializable接口这种方式,在进行序列化的时候。除了会序列化属性值之外,还会携带很多跟当前这个对象的类相关的各种信息
*
* Hadoop采取了一种全新的序列化机制;只需要序列化 每个对象的属性值即可。
*/ /*@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
value = in.readLong();
} @Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(value);
}*/ /**
* 用来指定排序规则
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean fb) { long diff = this.getSumFlow() - fb.getSumFlow(); if(diff == 0){
return 0;
}else{
return diff > 0 ? -1 : 1;
} }
}
第三题
package comg.ghgj.mr.flow; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.ProvincePartitioner; public class FlowPartitionerMR { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "FlowSumMR");
job.setJarByClass(FlowPartitionerMR.class); job.setMapperClass(FlowPartitionerMRMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowPartitionerMRReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); /**
* 非常重要的两句代码
*/
job.setPartitionerClass(ProvincePartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(10); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:\\bigdata\\flow\\input"));
Path outputPath = new Path("E:\\bigdata\\flow\\output_ptn2");
if(fs.exists(outputPath)){
fs.delete(outputPath, true);
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath); boolean isDone = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(isDone ? 0 : 1);
} public static class FlowPartitionerMRMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ /**
* value = 13502468823 101663100 1529437140 1631100240
*/
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\t"); String outkey = split[1];
String outValue = split[8] + "\t" + split[9]; context.write(new Text(outkey), new Text(outValue)); }
} public static class FlowPartitionerMRReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int upFlow = 0;
int downFlow = 0;
int sumFlow = 0; for(Text t : values){
String[] split = t.toString().split("\t"); int upTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
int downTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[1]); upFlow+=upTempFlow;
downFlow += downTempFlow;
} sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow; context.write(key, new Text(upFlow + "\t" + downFlow + "\t" + sumFlow));
}
}
}
Hadoop学习之路(十九)MapReduce框架排序的更多相关文章
- Hadoop 学习笔记 (十) MapReduce实现排序 全局变量
一些疑问:1 全排序的话,最后的应该sortJob.setNumReduceTasks(1);2 如果多个reduce task都去修改 一个静态的 IntWritable ,IntWritable会 ...
- Hadoop学习之路(九)HDFS深入理解
HDFS的优点和缺点 HDFS的优点 1.可构建在廉价机器上 通过多副本提高可靠性,提供了容错和恢复机制 服务器节点的宕机是常态 必须理性对象 2.高容错性 数据自动保存多个副本,副本丢失后,自动 ...
- 嵌入式Linux驱动学习之路(十九)触摸屏驱动、tslib测试
触摸屏使用流程: 1. 按下产生中断. 2.在中断处理程序中启动AD转换XY坐标. 3.AD转换结束并产生AD中断. 4. 在AD的中断处理函数中上报信息,启动定时器. 5. 定时器时间到后进入中断, ...
- IOS学习之路十九(JSON与Arrays 或者 Dictionaries相互转换)
今天写了个json与Arrays 或者 Dictionaries相互转换的例子很简单: 通过 NSJSONSerialization 这个类的 dataWithJSONObject: options: ...
- salesforce零基础学习(七十九)简单排序浅谈 篇一
我们在程序中经常需要对数据列表进行排序,有时候使用SOQL的order by 不一定能完全符合需求,需要对数据进行排序,排序可以有多种方式,不同的方式针对不同的场景.篇一只是简单的描述一下选择排序,插 ...
- 阿里封神谈hadoop学习之路
阿里封神谈hadoop学习之路 封神 2016-04-14 16:03:51 浏览3283 评论3 发表于: 阿里云E-MapReduce >> 开源大数据周刊 hadoop 学生 s ...
- 《Hadoop学习之路》学习实践
(实践机器:blog-bench) 本文用作博文<Hadoop学习之路>实践过程中遇到的问题记录. 本文所学习的博文为博主“扎心了,老铁” 博文记录.参考链接https://www.cnb ...
- Hadoop学习之路(十五)MapReduce的多Job串联和全局计数器
MapReduce 多 Job 串联 需求 一个稍复杂点的处理逻辑往往需要多个 MapReduce 程序串联处理,多 job 的串联可以借助 MapReduce 框架的 JobControl 实现 实 ...
- Hadoop学习之路(二十)MapReduce求TopN
前言 在Hadoop中,排序是MapReduce的灵魂,MapTask和ReduceTask均会对数据按Key排序,这个操作是MR框架的默认行为,不管你的业务逻辑上是否需要这一操作. 技术点 MapR ...
- Hadoop 学习之路(三)—— 分布式计算框架 MapReduce
一.MapReduce概述 Hadoop MapReduce是一个分布式计算框架,用于编写批处理应用程序.编写好的程序可以提交到Hadoop集群上用于并行处理大规模的数据集. MapReduce作业通 ...
随机推荐
- C#制作手机网站
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> //在 ...
- 添加FB登陆时,需要curl扩展
安装curl扩展遇到一个傻逼问题 [root@xxx openssl]# /usr/local/php/bin/phpizeCannot find config.m4.Make sure that y ...
- 12、springboot注解
@RestController和@Controller import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Elem ...
- js实现栈结构
实现栈结构 //创建栈 function Stack (){ let items = [] this.push = function(element){ items.push(element) } t ...
- sublime Text3汉化和激活注册码
sublimeText3 很不错,前面几天下了vscore学习Node.js,感觉有点懵,今天下载sublimeText3,遇到的一些小问题,在这里说说: 百度云:https://pan.baidu. ...
- CSS实现太极图(3个div实现)
使用三个div实现太极图的步骤如下: HTML部分 <div class="box"> <div class="yin"></di ...
- 【转载】python实例手册
今天写爬虫的时候遇到了问题,在网上不停地查找资料,居然碰到两篇好文章: 1.python实例手册 作者:没头脑的土豆 另一篇在这:shell实例手册 python实例手册 #encoding:ut ...
- 学习使用PRINCE2能带来什么益处?
使用PRINCE2有许多好处.它除了可重复使用.可升级.非常灵活之外,是在成百上千名有经验的项目经理们的帮助下,总结他们多年积累的实践经验和专业技术建立的. PRINCE2 开发于1989年并从此不断 ...
- 瞥了一眼js
JS打开超链接的几种形式1.window.open(''url'') 2.用自定义函数<script>function openWin(tag,obj){obj.target=" ...
- centos ntfs-3g 安装和使用
安装fuse 下载fuse(ntfs-3g依赖fuse):http://vdisk.weibo.com/s/ajww5fZsUq50L?from=page_100505_profile&wvr ...
