大数据系列之分布式计算批处理引擎MapReduce实践-排序
清明刚过,该来学习点新的知识点了。
上次说到关于MapReduce对于文本中词频的统计使用WordCount。如果还有同学不熟悉的可以参考博文大数据系列之分布式计算批处理引擎MapReduce实践。
博文发表后很多同学私下反映对于MapReduce的处理原理没有了解到。在这篇博文中楼主与大家交流下MapReduce的数据处理原理及MR中各角色的职责。
文末还有示例代码讲解。。
1.MapReduce中的数据流动
- 最简单的过程: map - reduce
- 定制了partitioner以将map的结果送往指定reducer的过程: map - partition - reduce
- 增加了在本地先进行一次reduce(优化)的过程: map - combine - partition - reduce
2.Partition的概念和使用
得到map产生的记录后,他们该分配给哪些reducer来处理呢?hadoop默认是根据散列值来派发,但是实际中,这并不能很高效或者按照我们要求的去执行任务。例如,经过partition处理后,一个节点的reducer分配到了20条记录,另一个却分配到了10W万条,试想,这种情况效率如何。又或者,我们想要处理后得到的文件按照一定的规律进行输出,假设有两个reducer,我们想要最终结果中part-00000中存储的是”h”开头的记录的结果,part-00001中存储其他开头的结果,这些默认的partitioner是做不到的。所以需要我们自己定制partition来选择reducer。自定义partitioner很简单,只要自定义一个类,并且继承Partitioner类,重写其getPartition方法就好了,在使用的时候通过调用Job的setPartitionerClass指定一下即可。
3.MapReduce基于key的全排序的原理
如何使用mapreduce来做全排序?最简单的方法就是使用一个partition,因为一个partition对应一个reduce的task,然而reduce的输入本来就是对key有序的,所以很自然地就产生了一个全排序文件。但是这种方法在处理大型文件时效率极低,因为一台机器必须处理所有输出文件,从而完全丧失了mapreduce所提供的并行架构的优势。
如果是分多个partition呢,则只要确保partition是有序的就行了。首先创建一系列排好序的文件;其次,串联这些文件(类似于归并排序);最后得到一个全局有序的文件。比如有1000个1-10000的数据,跑10个ruduce任务,如果进行partition的时候,能够将在1-1000中数据的分配到第一个reduce中,1001-2000的数据分配到第二个reduce中,以此类推。即第n个reduce所分配到的数据全部大于第n-1个reduce中的数据。这样,每个reduce出来之后都是有序的了,我们只要concat所有的输出文件,变成一个大的文件,就都是有序的了。
这时候可能会有一个疑问,虽然各个reduce的数据是按照区间排列好的,但是每个reduce里面的数据是乱序的啊?当然不会,不要忘了排序是MapReduce的天然特性 — 在数据达到reducer之前,mapreduce框架已经对这些数据按key排序了。
但是这里又有另外一个问题,就是在定义每个partition的边界的时候,可能会导致每个partition上分配到的记录数相差很大,这样数据最多的partition就会拖慢整个系统。我们期望的是每个partition上分配的数据量基本相同,hadoop提供了采样器帮我们预估整个边界,以使数据的分配尽量平均。
在Hadoop中,patition我们可以用TotalOrderPartitioner替换默认的分区,然后将采样的结果传给他,就可以实现我们想要的分区。在采样时,可以使用hadoop的几种采样工具,如RandomSampler,InputSampler,IntervalSampler。
关于上述过程,在《Hadoop权威指南》中有具体的讲解,其中一张图可以帮助我们更好地理解在排序操作中hadoop在map和reduce阶段所做的事:
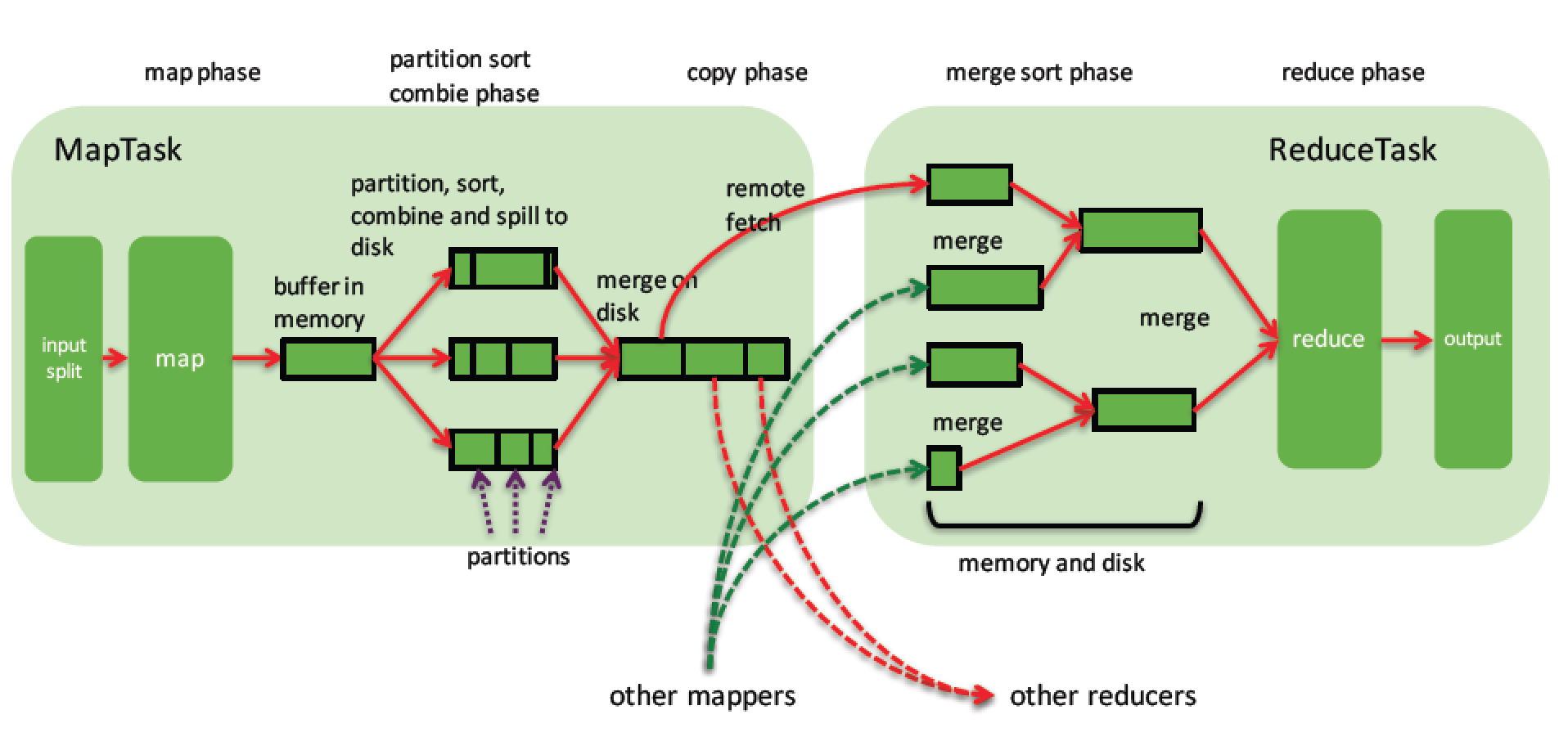
以上文字取自网上某些博文内容。。仅供参考。。。
4.下面介绍下一个代码示例。
MapReduceExample 一组数据按照年龄分区,区内按照成绩倒序排序
#数据内容见data/person.csv,如下
#编号,姓名,年龄,性别,成绩
1,Alice,23,female,45
2,Bob,34,male,89
3,Chris,67,male,97
4,Kristine,38,female,53
5,Connor,25,male,27
6,Daniel,78,male,95
7,James,34,male,79
8,Alex,52,male,69
9,Nancy,7,female,98
10,Adam,9,male,37
11,Jacob,7,male,23
12,Mary,6,female,93
13,Clara,87,female,72
14,Monica,56,female,92
#项目要求#
1.将数据按照年龄段分区
0至20岁为第一区,
20至50岁为第二区,
50以上为第三区。
2.将各区的数据按照分数倒序排序输出
#输出结果如下#
分区1:part-r-00000
9,Nancy,female,7 98
12,Mary,female,6 93
10,Adam,male,9 37
11,Jacob,male,7 23
分区2:part-r-00001
2,Bob,male,34 89
7,James,male,34 79
4,Kristine,female,38 53
1,Alice,female,23 45
5,Connor,male,25 27
分区3:part-r-00002
3,Chris,male,67 97
6,Daniel,male,78 95
14,Monica,female,56 92
13,Clara,female,87 72
8,Alex,male,52 69
4.1 解决思路
描述一下MapReduce处理数据的大概简单流程:首先,MapReduce框架通过getSplit方法实现对原始文件的切片之后,每一个切片对应着一个map task,inputSplit输入到Map函数进行处理,中间结果经过环形缓冲区的排序compareTo(T),然后分区、自定义二次排序(如果有的话)和合并,再通过shuffle操作将数据传输到reduce task端,reduce端也存在着缓冲区,数据也会在缓冲区和磁盘中进行合并排序等操作,然后对数据按照Key值进行分组,然后每次处理完一个分组之后就会去调用一次reduce函数,最终输出结果。
4.2 具体解决思路
A.Map端处理:单行数据拆分,对于拆分后的数据按成绩分数进行排序,MapReduce框架不管是默认排序或者是自定义排序都只是对Key值进行排序,现在的情况是这些数据不是key值,怎么办?其实我们可以将原始数据的Key值和其对应的数据组合成一个新的Key值,然后新的Key值对应的还是之前的数字。那么我们就可以将原始数据的map输出变成类似下面的数据结构:
{[1,Alice,23,female], 45}
{[2,Bob,34,male], 89}
{[3,Chris,67,male], 97}
{[4,Kristine,38,female],53}
{[5,Connor,25,male],27}
{[6,Daniel,78,male],95}
{[7,James,34,male],79}
{[8,Alex,52,male],69}
{[9,Nancy,7,female],98}
{[10,Adam,9,male],37}
{[11,Jacob,7,male],23}
{[12,Mary,6,female],93}
{[13,Clara,87,female],72}
{[14,Monica,56,female],92}
B.Partition分区操作:项目要求按照年龄进行分区,这里我们需要自定义一个分区处理器,因为我的目标不是想将所有的数据传到同一个reduce中,而是想将年龄分区后的数据放在同一个reduce中进行分组合并,所以我们需要根据新key值中的第三个字段来自定义一个分区处理器。通过分区操作后,得到的数据流如下:
partition1: 0~20
{[9,Nancy,7,female],98}
{[10,Adam,9,male],37}
{[11,Jacob,7,male],23}
{[12,Mary,6,female],93} partition2:20~50
{[1,Alice,23,female], 45}
{[2,Bob,34,male], 89}
{[4,Kristine,38,female],53}
{[5,Connor,25,male],27}
{[7,James,34,male],79} partition3:50~
{[3,Chris,67,male], 97}
{[6,Daniel,78,male],95}
{[8,Alex,52,male],69}
{[13,Clara,87,female],72}
{[14,Monica,56,female],92}
C.自定义排序操作:分区操作完成之后,我调用自己的自定义排序器对新的Key值按照成绩分数进行排序。 排序后的数据流结果如下:
partition1: 0~20
{[9,Nancy,7,female],98}
{[12,Mary,6,female],93}
{[10,Adam,9,male],37}
{[11,Jacob,7,male],23} partition2:20~50
{[2,Bob,34,male], 89}
{[7,James,34,male],79}
{[4,Kristine,38,female],53}
{[1,Alice,23,female], 45}
{[5,Connor,25,male],27} partition3:50~
{[3,Chris,67,male], 97}
{[6,Daniel,78,male],95}
{[14,Monica,56,female],92}
{[13,Clara,87,female],72}
{[8,Alex,52,male],69}
D.Reducer操作:经过Shuffle处理之后,数据传输到Reducer端输出。
4.2 代码
A.代码结构如下
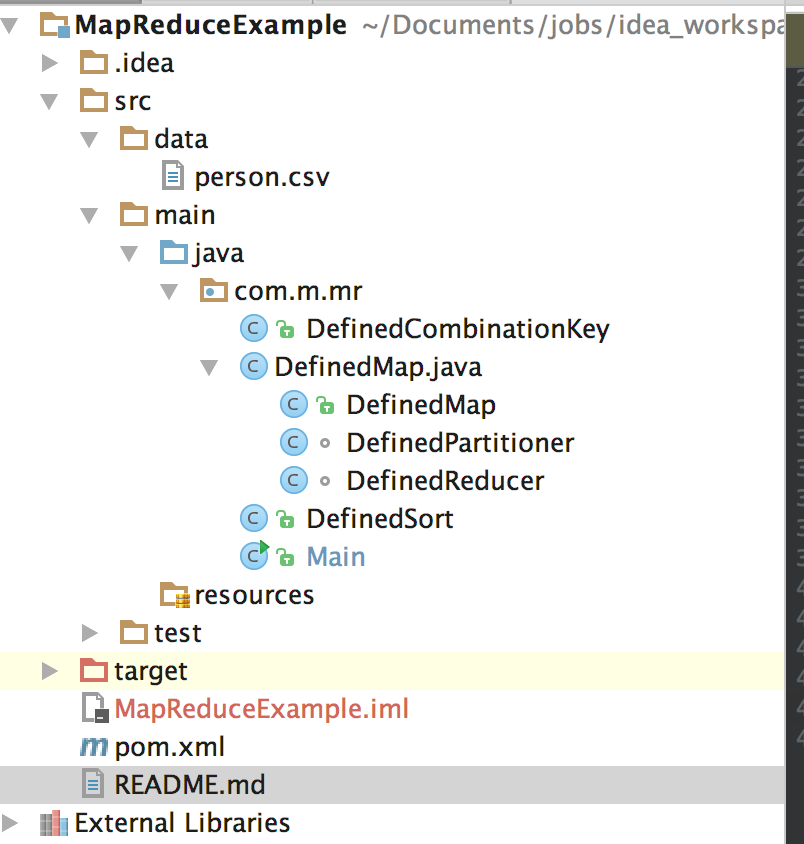
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.</modelVersion> <groupId>mapReduceDemo</groupId>
<artifactId>mapReduceDemo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <repositories>
<repository>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</repository>
</repositories> <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-yarn-client</artifactId>
<version>2.7.</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId>
<version>2.7.</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-mapreduce-client-jobclient</artifactId>
<version>2.7.</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> <build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-dependency-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>copy-dependencies</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>copy-dependencies</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<excludeScope>provided</excludeScope>
<outputDirectory>${project.build.directory}/lib</outputDirectory>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
B.Main.java 入口
package com.m.mr; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner; /**
* 操作person.csv文件
*/
public class Main extends Configured implements Tool { public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != ) {
System.err.println("Usage: AgePartition <input> <output>");
ToolRunner.printGenericCommandUsage(System.out);
System.exit();
} Configuration conf = getConf();
//conf.set(RegexMapper.GROUP,"female");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[]));
Path output = new Path(args[]);
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
if (fs.exists(output)) {
fs.delete(output, true);
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, output);
job.setJarByClass(Main.class);
job.setMapperClass(DefinedMap.class);
//设置map的输出key和value类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(DefinedCombinationKey.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setReducerClass(DefinedReducer.class);
//设置reduce的输出key和value类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//自定义分区策略
job.setPartitionerClass(DefinedPartitioner.class);
//自定义排序策略,在自定义组合键重写方法compareTo时若自定义排序策略与之相同可以省略自定义排序策略。最终结果以自定义排序策略为主
job.setSortComparatorClass(DefinedSort.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks();//reducer num = partition num return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? : ;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int res = ToolRunner.run(new Configuration(), new Main(), args);
System.exit(res);
}
}
C. DefinedMap.java {自定义分区器 class DefinedPartitioner,class Map, class Reducer}
package com.m.mr; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator; /**
* @author mengfanzhu
* @Package com.m.mr
* @Description: 自定义 map处理
* @date 17/4/7 14:04
*/
public class DefinedMap extends Mapper<Object, Text, DefinedCombinationKey, IntWritable> {
DefinedCombinationKey combinationKey=new DefinedCombinationKey();
Text sortName = new Text();
IntWritable score = new IntWritable(); @Override
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// no,name, age, gender, score
String[] arr = value.toString().split(",");
score.set(Integer.parseInt(arr[]));
sortName.set(arr[]+","+arr[]+","+arr[]+","+arr[]);
combinationKey.setFirstKey(sortName);
combinationKey.setSecondKey(score);
context.write(combinationKey, score);
}
} /**
* 自定义分区 按照年龄段分区
*/
class DefinedPartitioner extends Partitioner<DefinedCombinationKey,IntWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(DefinedCombinationKey key, IntWritable value, int n) {
if (n == ) {
return ;
}
String[] arr = key.getFirstKey().toString().split(",");
int age = Integer.parseInt(arr[]);
if (age <= ) {
return ;
} else if (age <= ) {
return % n;
} else {
return % n;
}
}
}
/**
* 自定义reducer处理
*/
class DefinedReducer extends Reducer<DefinedCombinationKey, IntWritable, Text, Text> { StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
Text sore=new Text(); @Override
protected void reduce(DefinedCombinationKey key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
sb.delete(, sb.length());
Iterator<IntWritable> it=values.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
sb.append(it.next()+",");
} if (sb.length()>) {
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-);
}
sore.set(sb.toString());
context.write(key.getFirstKey(),sore);
}
}
D . 自定义二次排序策略 DefinedSort
package com.m.mr; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; /**
* @author mengfanzhu
* @Description: 自定义排序策略
* @date 17/4/7 13:04
*/
public class DefinedSort extends WritableComparator {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefinedSort.class);
public DefinedSort() {
super(DefinedCombinationKey.class,true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable combinationKeyOne,
WritableComparable CombinationKeyOther) {
logger.info("---------enter DefinedComparator flag---------"); DefinedCombinationKey c1 = (DefinedCombinationKey) combinationKeyOne;
DefinedCombinationKey c2 = (DefinedCombinationKey) CombinationKeyOther; logger.info("---------out DefinedComparator flag---------");
return c2.getSecondKey().get()-c1.getSecondKey().get();//0,负数,正数
}
}
E. DefinedCombinationKey.java 自定义组合键
package com.m.mr; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException; /**
* @author mengfanzhu
* @Description:
* @date 17/4/7 13:01
*/
public class DefinedCombinationKey implements WritableComparable<DefinedCombinationKey> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefinedCombinationKey.class);
private Text firstKey;
private IntWritable secondKey;
public DefinedCombinationKey() {
this.firstKey = new Text();
this.secondKey = new IntWritable();
}
public Text getFirstKey() {
return this.firstKey;
}
public void setFirstKey(Text firstKey) {
this.firstKey = firstKey;
}
public IntWritable getSecondKey() {
return this.secondKey;
}
public void setSecondKey(IntWritable secondKey) {
this.secondKey = secondKey;
}
public void readFields(DataInput dateInput) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.firstKey.readFields(dateInput);
this.secondKey.readFields(dateInput);
}
public void write(DataOutput outPut) throws IOException {
this.firstKey.write(outPut);
this.secondKey.write(outPut);
}
/**
* 自定义比较策略
* 注意:该比较策略用于mapreduce的第一次默认排序,也就是发生在map阶段的sort小阶段,
* 发生地点为环形缓冲区(可以通过io.sort.mb进行大小调整)
*/
public int compareTo(DefinedCombinationKey definedCombinationKey) {
logger.info("-------CombinationKey flag-------");
return this.secondKey.compareTo(definedCombinationKey.getSecondKey()); } }
说明:
1.在自定义组合键的时候,我们需要特别注意,一定要实现WritableComparable接口,并且实现compareTo方法的比较策略。这个用于mapreduce的第一次默认排序,也就是发生在map阶段的sort小阶段,发生地点为环形缓冲区(可以通过io.sort.mb进行大小调整),但是其对我们最终的二次排序结果是没有影响的。我们二次排序的最终结果是由我们的自定义比较器决定的。
2.在此示例代码中写了自定义组合键的compareTo对于score进行正序,在自定义比较器中对score进行倒序。用来分析MR的工作原理。
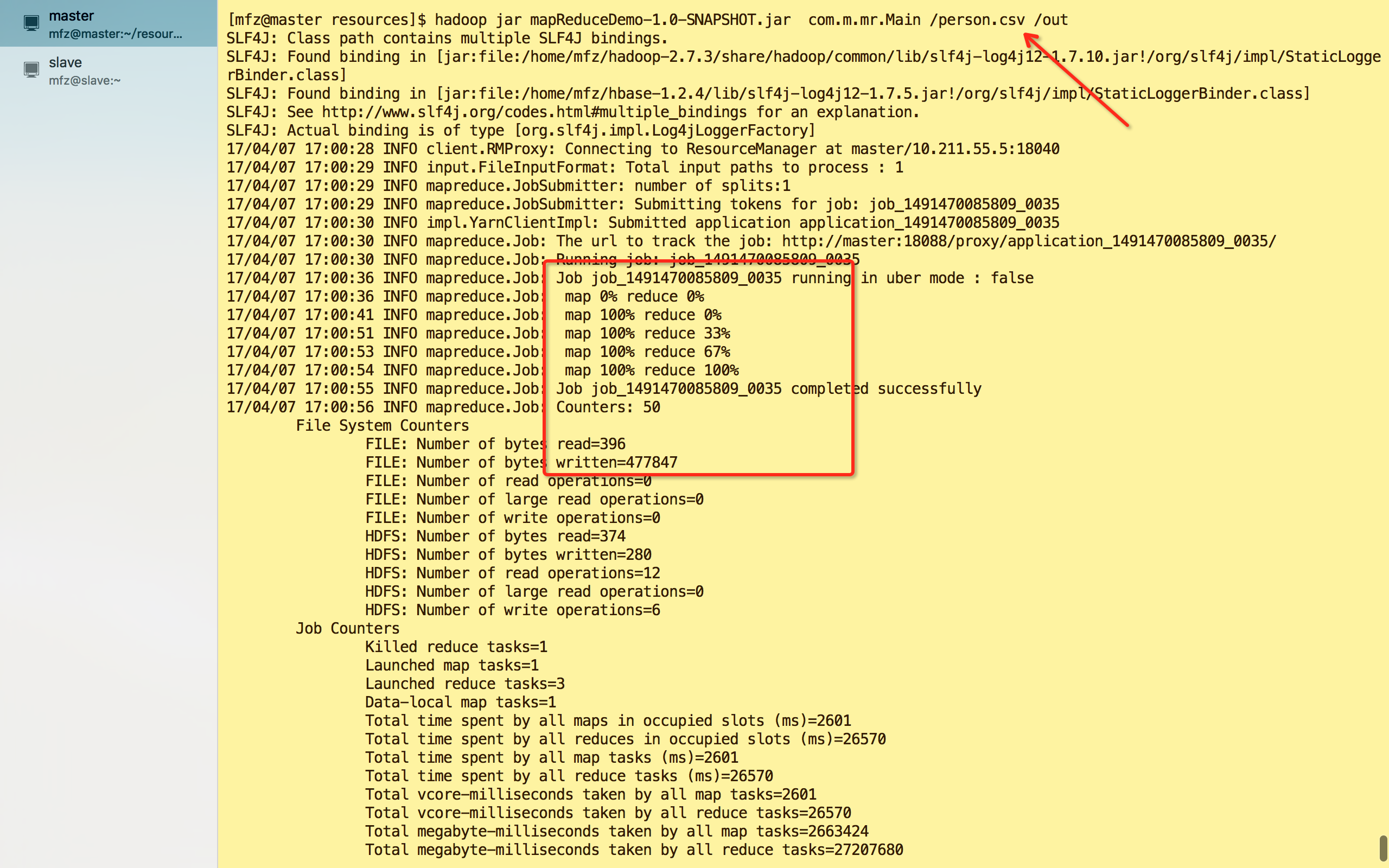
F.打包运行。maven :mvn clean package
hadoop jar mapReduceDemo-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.m.mr.Main /person.csv /out

完~
数据及代码包见
代码示例已上传至GitHub,https://github.com/fzmeng/MapReduceExample
大数据系列之分布式计算批处理引擎MapReduce实践-排序的更多相关文章
- 大数据系列之分布式计算批处理引擎MapReduce实践
关于MR的工作原理不做过多叙述,本文将对MapReduce的实例WordCount(单词计数程序)做实践,从而理解MapReduce的工作机制. WordCount: 1.应用场景,在大量文件中存储了 ...
- 大数据系列4:Yarn以及MapReduce 2
系列文章: 大数据系列:一文初识Hdfs 大数据系列2:Hdfs的读写操作 大数据谢列3:Hdfs的HA实现 通过前文,我们对Hdfs的已经有了一定的了解,本文将继续之前的内容,介绍Yarn与Yarn ...
- 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive命令使用及JDBC连接
Hive系列博文,持续更新~~~ 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive原理 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive安装 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive中分区Partition如何使用 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive命令使用 ...
- 大数据系列之并行计算引擎Spark介绍
相关博文:大数据系列之并行计算引擎Spark部署及应用 Spark: Apache Spark 是专为大规模数据处理而设计的快速通用的计算引擎. Spark是UC Berkeley AMP lab ( ...
- 大数据系列之并行计算引擎Spark部署及应用
相关博文: 大数据系列之并行计算引擎Spark介绍 之前介绍过关于Spark的程序运行模式有三种: 1.Local模式: 2.standalone(独立模式) 3.Yarn/mesos模式 本文将介绍 ...
- 批处理引擎MapReduce编程模型
批处理引擎MapReduce编程模型 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. MapReduce是一个经典的分布式批处理计算引擎,被广泛应用于搜索引擎索引构建,大规模数据处理 ...
- 批处理引擎MapReduce内部原理
批处理引擎MapReduce内部原理 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.MapReduce作业生命周期 MapReduce作业作为一种分布式应用程序,可直接运行在H ...
- 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive原理
Hive系列博文,持续更新~~~ 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive原理 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive安装 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive中分区Partition如何使用 大数据系列之数据仓库Hive命令使用 ...
- 批处理引擎MapReduce应用案例
批处理引擎MapReduce应用案例 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. MapReduce能够解决的问题有一个共同特点:任务可以被分解为多个子问题,且这些子问题相对独立 ...
随机推荐
- Objective-C 语言特点/特性
Objective-C中 1.所有的类都必须继承自NSObject. 2.所有对象都是指针的形式. 3.用self代替this. 4.使用id代替void*. 5.使用nil表示NULL, 6.只支持 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (14) - 深入搜索系列之全文搜索
ElasticSearch 2 (14) - 深入搜索系列之全文搜索 摘要 在看过结构化搜索之后,我们看看怎样在全文字段中查找相关度最高的文档. 全文搜索两个最重要的方面是: 相关(relevance ...
- PAT 甲级 1030 Travel Plan
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805464397627392 A traveler's map gives ...
- PHP后台支付的开发:微信支付和支付宝支付
关于支付的流程之类的就不做解释,大家可以自行搜索! 微信支付 项目前提:本人用的是tp框架,PHP语言下载到微信平台提供的微信支付接口文件,放在了tp第三方类库vendor,命名为WxpayAPI, ...
- Node.js & SSR
Node.js & SSR nest.js https://github.com/nestjs/nest next.js 中文文档 https://nextjs.org/learn/ Grap ...
- Spring之AOP注解配置
1.导入相应jar包 2.引入约束并配置XML文件 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xm ...
- 一本通1628X-factor Chain
1628:X-factor Chain 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 524288 KB [题目描述] 原题来自 POJ 3421 输入正整数 x,求 x 的大于 1 的因子 ...
- Cat VS Dog HDU - 3829 (最大独立集 )
Cat VS Dog Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 125536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- BZOJ1492 货币兑换 CDQ分治优化DP
1492: [NOI2007]货币兑换Cash Time Limit: 5 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MB Description 小Y最近在一家金券交易所工作.该金券交易所只发行交 ...
- C/C++ Bug记录
链接错误解决方法 1. 检查库是否链接正确 2. 库的顺序是否合理(如果库之间有依赖关系的话) 3. 检查obj文件是否存在既有C编译的,也有C++编译的,如果存在,用extern "C&q ...
