linearlayout-weight 属性作用
今天用到了weight的属性,现在就把这个属性的具体意义记录一下。也是参考网上的讲解,只不过自己验证了一下而已
参考自 http://blog.csdn.net/jincf2011/article/details/6598256
我们首先看一下网上对它的总结
在layout_width設置為fill_parent的時候,layout_weight所代表的是你的控件要優先盡可能的大,但這個大是有限度的,即fill_parent.
在layout_width設置為wrap_content的時候,layout_weight所代表的是你的控件要優先盡可能的小,但這個小是有限度的,即wrap_content.
layout_height 同 layout_width.
下面我们看一下验证结果
1.xml布局如下
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" > <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" > <LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ll"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/bt0"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/bt1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:clickable="false"
android:text="click fase" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:clickable="false"
android:longClickable="false"
android:text="long fasle" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/bt2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="long click true" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#0000ff" > <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="long click true" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>
其实就是写了两个linearlayout,第一个控件非常多(不妨称之为l1),会超出屏幕,第二个就含有一个button(l2)
1.当我们没有使用weight的时候
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/l1"
android:background="#ff0000" > <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/l2"
android:background="#0000ff" >
结果
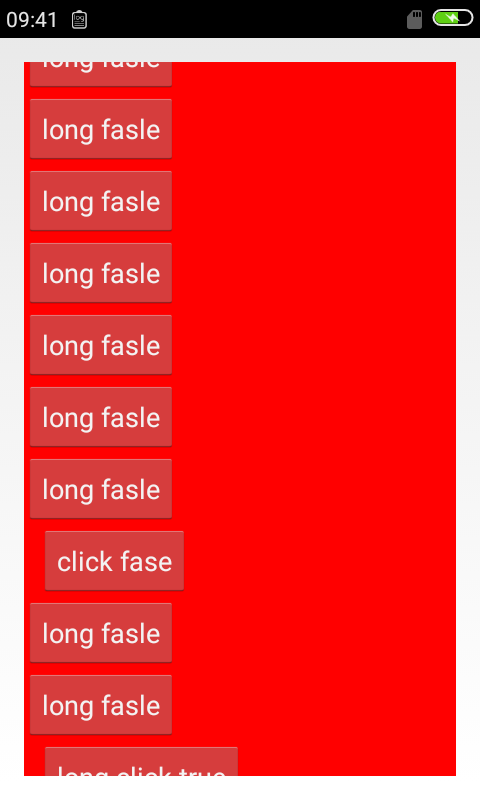
很容易猜到,l1会充满整个屏幕,并把l2挤出去
2.当我们对了l1使用weight的时候
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/l1"
android:background="#ff0000" > <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/l2"
android:background="#0000ff" >
结果
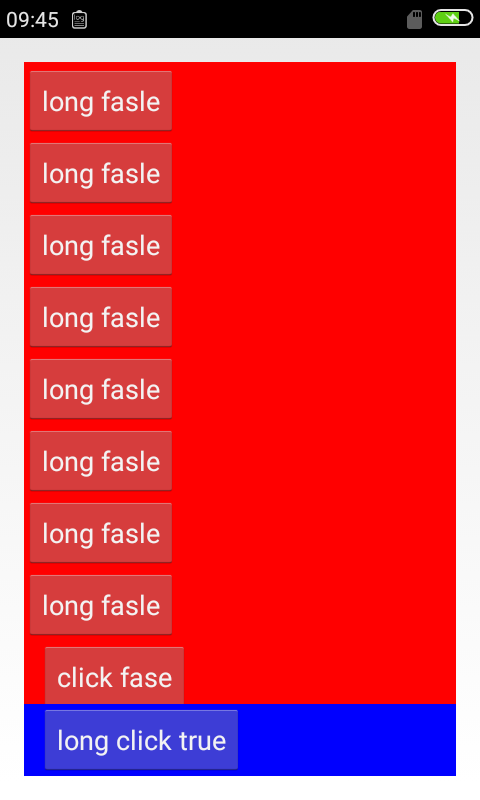
我们发现,这时候,l1会尽可能占据控空间,但是会给l2留出空间显示
3.当我们给两个linearlayout都添加weight属性的时候
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" android:id="@+id/l1"
android:background="#ff0000" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" android:id="@+id/l2"
android:background="#0000ff" >
结果

这时候,权重虽然都是1.感觉还是有优先级的,仍然是先让l1满足自身的最小wrap,假如这时候我们把两个height都设置为0dp,看 下结果

因为这时候没有所谓满足最小wrap(变为0了),所以权重又开始起到均分空间的作用了
4.我们继续更改下
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="5" android:id="@+id/l1"
android:background="#ff0000" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" android:id="@+id/l2"
android:background="#0000ff" >
结果
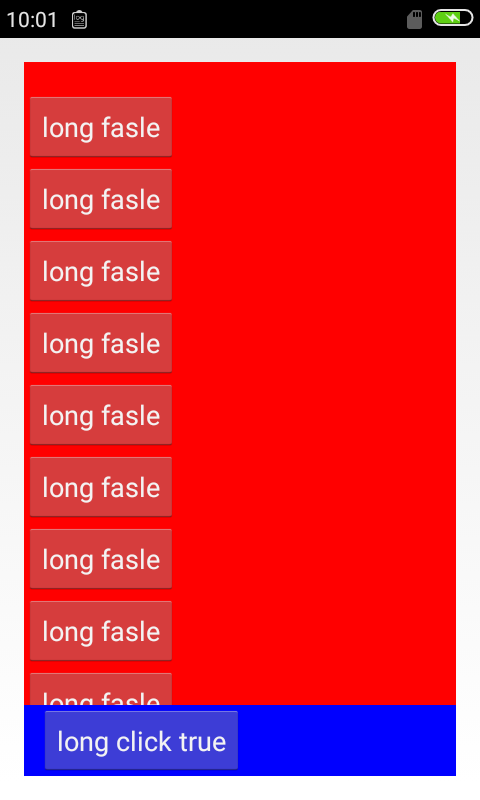
到此,我们基本上就验证了开始结论的正确性。至于match_parent的情况,这里不再说明了。
最后我们看下android:weightSum 属性
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:weightSum="2"
android:orientation="vertical" > <ScrollView
android:id="@+id/l1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
>
结果
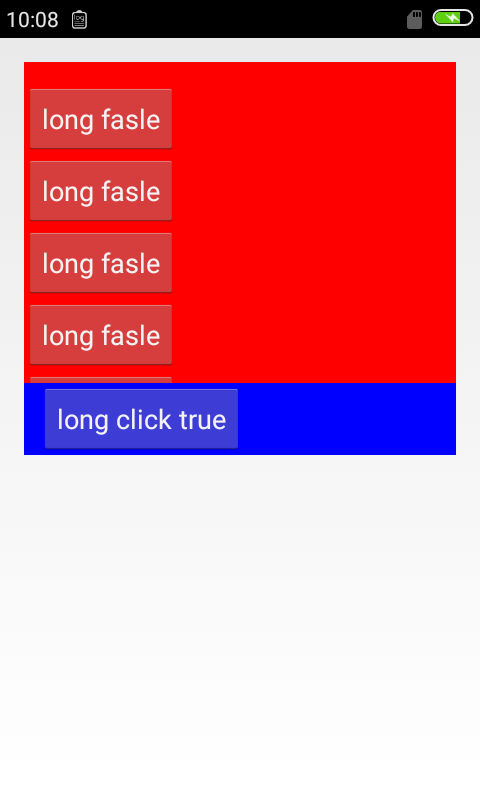
我们看到l1占据了父容器的一半。其实这条属性的意义已经体现出来了,就是把一个linearlayout的权重比例固定,可以理解为分成了2份,而它的子控件(l1)通过weight获得了1份
linearlayout-weight 属性作用的更多相关文章
- weight属性你用的真的6嘛?
相信大家在日常开发中一定使用过weight这个属性,它的作用一个是权重,另一个就是渲染优先级,但是你真的能很6的使用它嘛?如果不是,那么请继续往下看!!! 我们知道,当weight起到不同作用的时候, ...
- android LinearLayout android:layout_weight 作用,固定比例
android 中的 LinearLayout 是线性布局有水平布局horizontal 垂直布局vertical .本文针对 水平布局horizontal 布局的weight属性做一个标记,以免 ...
- Android开发技巧一--weight属性实现视图的居中(半)显示
面试时,一位面试官问到:“如果我想讲按钮居中显示,并且占据其父视图宽度的一半,应该怎么做到呢?”即实现这种效果: 我们使用weightSum属性和layout_weight属性实现这一要求: < ...
- Android Hack1 使用weight属性实现视图的居中显示
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wuyudong/p/5898403.html,转载请注明源地址. 如果要实现如下图所示的将按钮居中显示,并且占据父视图的一半,无论屏幕是否旋转 ...
- Android weight属性详解
android:layout_weight是一个经常会用到的属性,它只在LinearLayout中生效,下面我们就来看一下: 当我们把组件宽度设置都为”match_parent”时: <Butt ...
- android gravity属性 和 weight属性
来看这个布局文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:and ...
- 关于weight属性使用的一些细节
之前被这个属性困扰过好久,今天一个偶然的机会,终于把这个搞清楚了,现在与大家分享一下. 假设我们要在一个LinearLayout布局中显示两个按钮,button1和button2,button2的宽度 ...
- Android——android weight 属性(百度)
LinearLayout 在androidUI布局中使用非常多,它其中有个很方便又很有意思的属性 weight ,这个属性理解起来不是那么简单的,而真正理解了又觉得非常简单! 下面就通过一个例子来说明 ...
- 【转】android gravity属性 和 weight属性
有点忘记这两个属性了,复习一下. 来看这个布局文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <Linea ...
随机推荐
- SharePoint UserProfileService 接口列表 注解
Remove Leader 除去领袖 Add Leader 加领袖 Get leaders 获得管理员 Get Profile Scherna Get Profile Scherna Names ...
- vue 中使用querySelect 封装的万能选择器
function query (el) { if (typeof el === 'string') { var selector = el; el = document.querySelector(e ...
- 51Nod 和为k的连续区间
一整数数列a1, a2, ... , an(有正有负),以及另一个整数k,求一个区间[i, j],(1 <= i <= j <= n),使得a[i] + ... + a[j] = k ...
- Qihoo 360 altas 实践
Qihoo 360 altas 实践 简介 Atlas是由 Qihoo 360公司Web平台部基础架构团队开发维护的一个基于MySQL协议的数据中间层项目.它在MySQL官方推出的MySQL-Prox ...
- [APIO2014]回文串 后缀自动机_Manancher_倍增
Code: // luogu-judger-enable-o2 #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstr ...
- 四舍五入VS银行家舍入法
在学习python的时候,遇见了一个颠覆了我传统观念的四舍五入. 看下面,round()的结果和我们以前根深蒂固的四舍五入是不同的. >>> round(0.5) 0 >> ...
- rsync---远程数据同步工具
rsync命令是一个远程数据同步工具,可通过LAN/WAN快速同步多台主机间的文件.rsync使用所谓的“rsync算法”来使本地和远程两个主机之间的文件达到同步,这个算法只传送两个文件的不同部分,而 ...
- Java排序算法(二):简单选择排序
[基本思想] 在要排序的一组数中.选出最小的一个数与第一个位置的数交换:然后在剩下的数中再找出最小的与第二个位置的数交换,如此循环至倒数第二个数和最后一个数比較为止. 算法关键:找到最小的那个数.并用 ...
- 网页加速之Chromium 预载入 Prerendering
前一篇博文已经介绍通过prefetch预先载入网页的资源来提升网页载入速度,以下我们一起来看一下网页加速之chromium prerendering.在介绍prerendering之前,先介绍两个概念 ...
- Java中发送http的get、post请求
近期做项目中,须要把消息通过中间件的形式通过http请求的方式推送给第三方,因此用到了http协议,小编花费了一个多小时.对于http协议中的post和get请求,封装了一个工具类.以下与大家分享一下 ...
