Matlab filter常用函数
Filtering and Analysis Functions
Filtering
Filter Analysis
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
|
Casts the coefficients of a |
|
|
Generates a Simulink® filter block corresponding to a |
|
|
Returns the filter order of a |
|
|
Returns the type (1, 2, 3, or 4) of an FIR |
|
|
Returns or plots the frequency response of a |
|
|
Opens the Filter Visualization Tool and displays the magnitude response of a |
|
|
Returns or plots the group delay response of a |
|
|
Returns or plots the impulse response of a |
|
|
Returns the length of the impulse response of a |
|
|
Returns a character array with information about a |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns or plots the phase delay response of a |
|
|
Returns or plots the (unwrapped) phase response of a |
|
|
Casts the coefficients of a |
|
|
Returns the state-space representation of a |
|
|
Returns or plots the step response of a |
|
|
Returns the transfer function representation of a |
|
|
Returns or plots the zero-phase response of a |
|
|
Returns the zero-pole-gain representation of a |
|
|
Displays the poles and zeros of the transfer function represented by a |
1.zero,pole-->transfer function form
[b,a] = zp2tf(zer,pol,1);
fvtool(b,a)

2.transform function-->zero/polo
fvtool(b,a,'Analysis','polezero')

zplane(b,a)

3.Z-transform frequency response of a digital filter.
[h,w] = freqz(b,a,p)
returns the p-point complex frequency response, H(ejω), of the digital filter.
For example, a ninth-order Butterworth lowpass filter with a cutoff frequency of 400 Hz, based on a 2000 Hz sampling frequency, is
[b,a] = butter(9,400/1000);
To calculate the 256-point complex frequency response for this filter, and plot the magnitude and phase with freqz, use
freqz(b,a,256,2000)

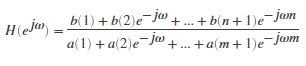
4.filter
Use filter in the form y = filter(d,x) to filter an input signal, x, with a digitalFilter, d, and obtain output data, y.
5.designfilt(https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/signal/ref/designfilt.html)
Use designfilt in the form d = designfilt(resp,Name,Value) to design a digital filter, d, with response type resp. Specify the filter further using a set of Name,Value pairs.
Type d.Coefficients to obtain the coefficients of a digitalFilter, d. For IIR filters, the coefficients are expressed as second-order sections.
Lowpass IIR Filter
Design a lowpass IIR filter with order 8, passband frequency 35 kHz, and passband ripple 0.2 dB. Specify a sample rate of 200 kHz. Visualize the magnitude response of the filter. Use it to filter a 1000-sample random signal.
lpFilt = designfilt('lowpassiir','FilterOrder',8, ...
'PassbandFrequency',35e3,'PassbandRipple',0.2, ...
'SampleRate',200e3);
fvtool(lpFilt)

dataIn = randn(1000,1);
dataOut = filter(lpFilt,dataIn);
Output the filter coefficients, expressed as second-order sections.
sos = lpFilt.Coefficients
sos = 4×6
0.2666 0.5333 0.2666 1.0000 -0.8346 0.9073
0.1943 0.3886 0.1943 1.0000 -0.9586 0.7403
0.1012 0.2023 0.1012 1.0000 -1.1912 0.5983
0.0318 0.0636 0.0318 1.0000 -1.3810 0.5090
Bandpass FIR Filter
Design a 20th-order bandpass FIR filter with lower cutoff frequency 500 Hz and higher cutoff frequency 560 Hz. The sample rate is 1500 Hz. Visualize the magnitude response of the filter. Use it to filter a random signal containing 1000 samples.
bpFilt = designfilt('bandpassfir','FilterOrder',20, ...
'CutoffFrequency1',500,'CutoffFrequency2',560, ...
'SampleRate',1500);
fvtool(bpFilt)

dataIn = randn(1000,1);
dataOut = filter(bpFilt,dataIn);
Output the filter coefficients.
b = bpFilt.Coefficients
b = 1×21 -0.0113 0.0067 0.0125 -0.0445 0.0504 0.0101 -0.1070 0.1407 -0.0464 -0.1127 0.1913 -0.1127 -0.0464 0.1407 -0.1070 0.0101 0.0504 -0.0445 0.0125 0.0067 -0.0113 ⋯
6.fvtool
fvtool(b,a)
fvtool(sos)
fvtool(d)
fvtool(b1,a1,b2,a2,...,bN,aN)
fvtool(sos1,sos2,...,sosN)
fvtool(Hd)
fvtool(Hd1,Hd2,...,HdN)
h = fvtool(...)
Use fvtool to visualize a digitalFilter, d.
Matlab filter常用函数的更多相关文章
- MATLAB中常用函数及语法
zeros() 1 zeros(n):n*n 全零矩阵 2 zeros(m,n):m*n全零矩阵 3 zeros(d1,d2,d3……dn):生成 d1*d2*d3*……*dn 全零矩阵或数组. 4 ...
- matlab 图像常用函数
Canny function [ canny ] = canny( rgb ) temp=rgb2gray(rgb); canny=edge(temp,'canny'); end 灰度 temp=rg ...
- 【Matlab】常用函数
1.取整函数 ceil(x)返回不小于x的最小整数值.floor(x)返回不大于x的最大整数值.round(x)返回x的四舍五入整数值.
- Matlab GUI设计中的一些常用函数
Matlab GUI常用函数总结 % — 文件的打开.读取和关闭% — 文件的保存% — 创建一个进度条% — 在名为display的axes显示图像,然后关闭% — 把数字转化为时间格式% — ch ...
- matlab进阶:常用功能的实现,常用函数的说明
常用功能的实现 获取当前脚本所在目录 current_script_dir = fileparts(mfilename('fullpath')); % 结尾不带'/' 常用函数的说明 bsxfun m ...
- matlab 常用函数
Matlab常用函数 Matlab的内部常数 eps 浮点相对精度 pi 圆周率 exp 自然对数的底数e i 或j 虚数单位 Inf或 inf 无穷大 Matlab概率密度函数 ...
- Matlab常用函数集锦
ndims(A)返回A的维数size(A)返回A各个维的最大元素个数length(A)返回max(size(A))[m,n]=size(A)如果A是二维数组,返回行数和列数nnz(A)返回A中非0元素 ...
- MATLAB算术运算符和常用函数
1 算术运算符 Matlab中的算术运算符按优先级由高到低为: (1) ^ 幂 (2) * 乘 / 右除(正常除) ...
- MATLAB常用函数
Matlab的内部常数 pi 圆周率 exp(1) 自然对数的底数e i 或j 虚数单位 Inf或 inf ...
随机推荐
- 【剑指Offer】24、二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目描述 输入一颗二叉树的根节点和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径.路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径.(注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大 ...
- 积分题1之来自G.Han的一道积分题
今天,收到G.Han的提问,第一个是计算积分 \[\int_0^{\infty}{\frac{\ln x}{(x^2+1)^n}dx}\]顿时不明觉厉,然后在宝典<Table of Integr ...
- 两个html页面之间传值
参考网址:https://blog.csdn.net/csdn_ds/article/details/78393564?locationNum=8&fps=1
- jQuery 滚动条和浏览器窗口事件
滚动条事件 // 实时监听元素的滚动事件 $(window).scroll(function(){ ... }); $(window).scrollLefft(); // 获取滚动条位置 $(wind ...
- python3.6安装lxml库
好像是在python3.5之后,安装了lxml也无法使用etree 为了就解决这个问题使用如下方法: 1.下载lxml的wheel文件,下载地址:https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~go ...
- SVM-支持向量机(三)SVM回归与原理
SVM回归 我们之前提到过,SVM算法功能非常强大:不仅支持线性与非线性的分类,也支持线性与非线性回归.它的主要思想是逆转目标:在分类问题中,是要在两个类别中拟合最大可能的街道(间隔),同时限制间隔侵 ...
- 2020牛客寒假算法基础集训营1 J. 缪斯的影响力 (矩阵快速幂/费马小定理降幂)
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/200658 f(n) = f(n-1) * f(n-2) * ab ,f的第一项是x,第二项是y. 试着推出第三项是x·y·a ...
- webpack之 plugin(插件)
plugin plugin是插件的意思,通常用来对某个现有的架构就行拓展 webpack中的插件,就是对webpack现有功能的各种扩展,比如打包优化,文件压缩等 loader和plugin区别 lo ...
- CSS伪类before,after制作左右横线中间文字效果
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- JDBC未知列
Exception in thread "main" com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4. MySQLSyntaxErrorException: Unk ...
