CUDA-GPU编程
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/augusdi/article/details/12833235 第二节
新建NVIDIA项目:
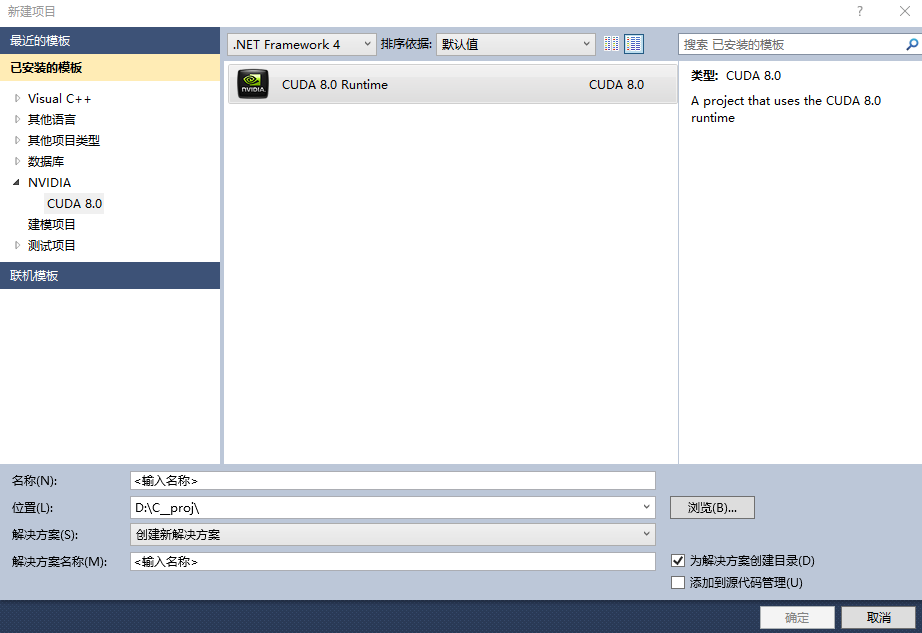
新建项目及会生成一个简单的代码demo,计算矩阵的加法,如下(main中加了一些显示显卡性能的打印):
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h" #include <stdio.h> cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size); __global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b)
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
} int main()
{
const int arraySize = ;
const int a[arraySize] = { , , , , };
const int b[arraySize] = { , , , , };
int c[arraySize] = { }; // Add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!");
return ;
} printf("{1,2,3,4,5} + {10,20,30,40,50} = {%d,%d,%d,%d,%d}\n",
c[], c[], c[], c[], c[]); // cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and
// tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!");
return ;
} int deviceCount;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&deviceCount);
int dev;
for (dev = ; dev < deviceCount; dev++)
{
cudaDeviceProp deviceProp;
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProp, dev);
if (dev == )
{
if (/*deviceProp.major==9999 && */deviceProp.minor = &&deviceProp.major==)
printf("\n"); }
printf("\nDevice%d:\"%s\"\n", dev, deviceProp.name);
printf("Total amount of global memory %u bytes\n", deviceProp.totalGlobalMem);
printf("Number of mltiprocessors %d\n", deviceProp.multiProcessorCount);
printf("Total amount of constant memory: %u bytes\n", deviceProp.totalConstMem);
printf("Total amount of shared memory per block %u bytes\n", deviceProp.sharedMemPerBlock);
printf("Total number of registers available per block: %d\n", deviceProp.regsPerBlock);
printf("Warp size %d\n", deviceProp.warpSize);
printf("Maximum number of threada per block: %d\n", deviceProp.maxThreadsPerBlock);
printf("Maximum sizes of each dimension of a block: %d x %d x %d\n", deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[],
deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[],
deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[]);
printf("Maximum size of each dimension of a grid: %d x %d x %d\n", deviceProp.maxGridSize[], deviceProp.maxGridSize[], deviceProp.maxGridSize[]);
printf("Maximum memory pitch : %u bytes\n", deviceProp.memPitch);
printf("Texture alignmemt %u bytes\n", deviceProp.texturePitchAlignment);
printf("Clock rate %.2f GHz\n", deviceProp.clockRate*1e-6f);
}
printf("\nTest PASSED\n"); getchar();
return ;
} // Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size)
{
int *dev_a = ;
int *dev_b = ;
int *dev_c = ;
cudaError_t cudaStatus; // Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
} // Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) .
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
} cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
} cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
} // Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
} cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
} // Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element.
addKernel<<<, size>>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b); // Check for any errors launching the kernel
cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
goto Error;
} // cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns
// any errors encountered during the launch.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
} // Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
} Error:
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b); return cudaStatus;
}
CUDA-GPU编程的更多相关文章
- 《CUDA并行程序设计:GPU编程指南》
<CUDA并行程序设计:GPU编程指南> 基本信息 原书名:CUDA Programming:A Developer’s Guide to Parallel Computing with ...
- GPU编程自学4 —— CUDA核函数运行参数
深度学习的兴起,使得多线程以及GPU编程逐渐成为算法工程师无法规避的问题.这里主要记录自己的GPU自学历程. 目录 <GPU编程自学1 -- 引言> <GPU编程自学2 -- CUD ...
- GPU编程自学3 —— CUDA程序初探
深度学习的兴起,使得多线程以及GPU编程逐渐成为算法工程师无法规避的问题.这里主要记录自己的GPU自学历程. 目录 <GPU编程自学1 -- 引言> <GPU编程自学2 -- CUD ...
- GPU编程自学2 —— CUDA环境配置
深度学习的兴起,使得多线程以及GPU编程逐渐成为算法工程师无法规避的问题.这里主要记录自己的GPU自学历程. 目录 <GPU编程自学1 -- 引言> <GPU编程自学2 -- CUD ...
- 【OpenCV & CUDA】OpenCV和Cuda结合编程
一.利用OpenCV中提供的GPU模块 目前,OpenCV中已提供了许多GPU函数,直接使用OpenCV提供的GPU模块,可以完成大部分图像处理的加速操作. 基本使用方法,请参考:http://www ...
- CUDA 标准编程模式
前言 本文将介绍 CUDA 编程的基本模式,所有 CUDA 程序都基于此模式编写,即使是调用库,库的底层也是这个模式实现的. 模式描述 1. 定义需要在 device 端执行的核函数.( 函数声明前加 ...
- 第一篇:GPU 编程技术的发展历程及现状
前言 本文通过介绍 GPU 编程技术的发展历程,让大家初步地了解 GPU 编程,走进 GPU 编程的世界. 冯诺依曼计算机架构的瓶颈 曾经,几乎所有的处理器都是以冯诺依曼计算机架构为基础的.该系统架构 ...
- GPU 编程入门到精通(五)之 GPU 程序优化进阶
博主因为工作其中的须要,開始学习 GPU 上面的编程,主要涉及到的是基于 GPU 的深度学习方面的知识.鉴于之前没有接触过 GPU 编程.因此在这里特地学习一下 GPU 上面的编程. 有志同道合的小伙 ...
- mpi和cuda混合编程的正确编译
针对大数据的计算,很多程序通过搭建mpi集群进行加速,并取得了很好的效果.算法内部的加速,当前的并行化趋势是利用GPU显卡进行算法加速.针对并行性非常好的算法,GPU加速效果将远大于集群带来的加速效果 ...
- GPU编程--宏观理解篇(1)
GPU编程与CPU编程最大的不同可以概括为以下两点: "The same program is executed on many data elements in parallel" ...
随机推荐
- kafka+spark-streaming实时推荐系统性能优化笔记
1) --conf spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled=false 如果正在使用的是CDH的Spark,修改这个配置为false:开源的Spark版本则默认是false. ...
- NOIP2015 提高组合集
NOIP 2015 提高组 合集 D1 T1 神奇的幻方 题目让你干啥你就干啥,让你咋走你就咋走就完事儿了 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio& ...
- 玲珑杯 ACM Round #10
A 题意:给长度为n的序列染黑白色,要求连续的黑的格子数量<=a,连续的白的格子数量<=b,问方案总数,有多个询问 分析:递推 注意数据范围,是可以O(n)做的,所以可以直接递推 B 题意 ...
- sql-server-storage-internals
https://www.simple-talk.com/sql/database-administration/sql-server-storage-internals-101/
- MYSQL常用的性能指标
(1) QPS(每秒Query量) QPS = Questions(or Queries) / seconds mysql > show global status like 'Questio ...
- 设计模式:浅析 抽象工厂、工厂方法、简单(静态)工厂 java实现
----简单工厂 (也叫静态工厂模式):一个抽象产品抽象出多个详细产品类.一个详细工厂类 代码: //抽象产品角色 public interface Car{ public void drive(); ...
- JAVA学习第四十一课 — 泛型的基本应用(一)
泛型是JDK1.5以后出现的安全机制,简化机制,提高安全性 泛型的长处 1.将执行时出现的问题ClassCastException转移到了编译时期 2.避免了强制转换的麻烦 <>在当操作的 ...
- w3m命令行模式浏览网页
w3m是一个基于文本的网页浏览器,支持多种操作系统,在命令行终端可以很好的支持中文.即使在没有鼠标支持的情况下也可以检查网页的输出. 我们一般用Ubuntu的X Windows来看图形界面的东西,有没 ...
- 2017iOS开发最新的打包测试步骤(亲测)
最近也是忙着修改项目,今天把最近遇到的问题和知识给大家分享一下. 有时候我们需要将我们的项目发给测试组进行bug测试,这时候我们就需要把自己的项目打包,生成一个二维码或者链接的形式,给测试组,接下来就 ...
- 【BZOJ 2160】 拉拉队排练
[题目链接] https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2160 [算法] 先简化题意 : 给定一个字符串,求最长的k个奇回文子串长度的乘积 先 ...
