10 STL-list
重新系统学习c++语言,并将学习过程中的知识在这里抄录、总结、沉淀。同时希望对刷到的朋友有所帮助,一起加油哦!
生命就像一朵花,要拼尽全力绽放!死磕自个儿,身心愉悦!
写在前面,本篇章主要介绍STL中常用容器list。
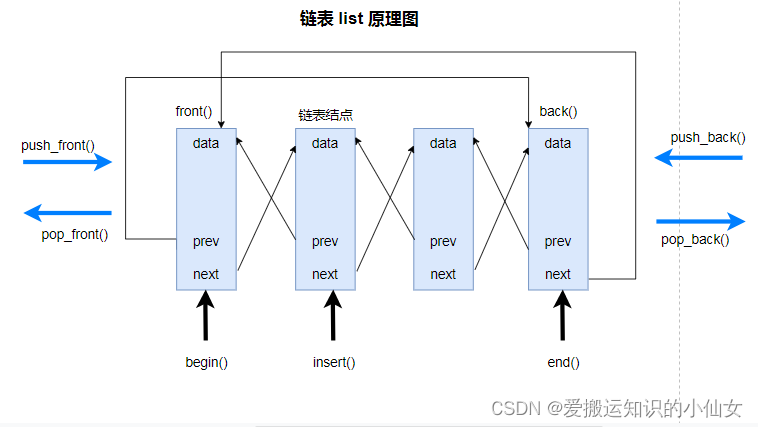
1.1 list基本概念
功能:将数据进行链式存储。
链表list 的数据存储:是非连续的,数据元素的前后顺序是通过链表中的指针链接来 实现的。
链表的组成: 由一系列的结点组成。
结点的组成:
- 一个数据域,用来存储数据元素。
- 一个指针域,用来存储上一个和下一个结点地址。
链表是一个双向循环链表。 因为指针域可以存储上一个和下一个结点地址,第一个结点的的prev指针指向的是最后一个结点的地址,最后一个结点的next指针指向的第一个结点的地址,使得头尾结点可以相互访问。
链表的迭代器:
由于链表的存储方式不是连续的内存空间,因此链表中的迭代器只支持前移和后移,属于双向迭代器。不是随机迭代器。
 编辑
编辑
list的优点:
- 存储不是连续的,采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出。
- 插入和删除非常方便,修改指针域即可,不需要移动大量元素。
- 插入和删除都不会造成原有list迭代器失效,这在vector不成立。
list的缺点:
- 灵活,但是空间和时间消耗大。(指针域造成空间消耗大)(在遍历时需要根据指针来判断下一个结点,时间消耗大)
1.2 list构造函数
函数原型:
- list<T> lst; //list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:
- list(beg, end); //构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
- list(n, elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
- list(const list& lst); //拷贝构造函数。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
// list<T> lst; //list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:
// list(beg, end); //构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
// list(n, elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
// list(const list& lst); //拷贝构造函数。
void printList(const list<int>& l) {
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
list<int> l;
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(2);
l.push_front(3);
l.push_front(4);
printList(l);
list<int> l2(l.begin(), l.end());
printList(l2);
list<int> l3(l2);
printList(l3);
list<int>l4(10, 3);
printList(l4);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.3 list赋值和交换
函数原型:
- size(); //返回容器中元素的个数empty(); //判断容器是否为空
- resize(num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& l) {
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
//assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
list<int> l1;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
l1.push_back(i);
}
printList(l1);
list<int>l2;
l2.assign(l1.begin(), l1.end());
printList(l2);
//assign(n, elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
l2.assign(10, 3);
printList(l2);
//list& operator=(const list & lst); //重载等号操作符
list<int> l3;
l3 = l2;
printList(l3);
//swap(lst); //将lst与本身的元素互换。
l1.swap(l3);
cout << "互换后的:" << endl;
printList(l1);
printList(l3);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.4 list大小操作
函数原型:
- size(); //返回容器中元素的个数
- empty(); //判断容器是否为空
- resize(num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
//size(); //返回容器中元素的个数
//empty(); //判断容器是否为空
//resize(num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。
// //如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
//resize(num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。
// //如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
void printList(const list<int>& l) {
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
//assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
list<int> l1;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
l1.push_back(i);
}
printList(l1);
if (l1.empty()) {
cout << "l1 为空" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "l1 不为空" << endl;
cout << "l1 size(): " << l1.size() << endl;
}
l1.resize(10);
printList(l1);
l1.resize(20,6);
printList(l1);
l1.resize(3);
printList(l1);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出:
0 1 2 3 4
l1 不为空
l1 size(): 5
0 1 2 3 4 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 4 0 0 0 0 0 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
0 1 2
1.5 list插入和删除
函数原型:
- push_back(elem); //在容器尾部加入一个元素
- pop_back(); //删除容器中最后一个元素
- push_front(elem); //在容器开头插入一个元素
- pop_front(); //从容器开头移除第一个元素
- insert(pos, elem); //在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
- insert(pos, n, elem); //在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。
- insert(pos, beg, end); //在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。
- clear(); //移除容器的所有数据
- erase(beg, end); //删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
- erase(pos); //删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
- remove(elem); //删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& l) {
for (auto item : l) {
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
list<int> l1;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//push_back(elem);//在容器尾部加入一个元素
l1.push_back(i);
}
//push_front(elem);//在容器开头插入一个元素
l1.push_front(5);
printList(l1);// 5 0 1 2 3 4
//pop_front();//从容器开头移除第一个元素
l1.pop_front();
printList(l1);// 0 1 2 3 4
//pop_back();//删除容器中最后一个元素
l1.pop_back();
printList(l1);// 0 1 2 3
//insert(pos, elem);//在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
l1.insert(l1.begin(), 100);
printList(l1);// 100 0 1 2 3
//insert(pos, n, elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。
l1.insert(l1.end(), 3, 200);
printList(l1);//100 0 1 2 3 200 200 200
//insert(pos, beg, end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。
l1.insert(l1.begin(), l1.begin(), l1.end());
printList(l1);//100 0 1 2 3 200 200 200 100 0 1 2 3 200 200 200
//erase(beg, end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
l1.erase(l1.begin(), ++l1.begin());
printList(l1);//0 1 2 3 200 200 200 100 0 1 2 3 200 200 200
//erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
l1.erase(++l1.begin());
printList(l1);//0 2 3 200 200 200 100 0 1 2 3 200 200 200
//remove(elem);//删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
l1.remove(200);
printList(l1);//0 2 3 100 0 1 2 3
//clear();//移除容器的所有数据
l1.clear();
printList(l1);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.6 list数据存取
函数原型:
- front(); //返回第一个元素
- back(); //返回最后一个元素
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
void test() {
list<int> l;
l.push_back(1);
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(3);
l.push_back(4);
// l[0]; // 错误
// l.at(0); // 错误
// 原因:list本质是双向迭代器,不是随机迭代器,不支持随机访问,不是连续线性存储。
cout << "first item: " << l.front() << endl;
cout << "last item: " << l.back() << endl;
list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();
it++;// 支持双向
it++++;
it--;
//it = it + 1;//不支持随机访问 即便是+1;
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.7 list反转和排序
函数原型:
- reverse(); 反转链表
- sort(); 链表排序,默认升序
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& l) {
for (auto item : l) {
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool myCompare(int v1, int v2) {
// 降序 就让第一个数 > 第二个数
return v1 > v2;
}
void test() {
list<int> l;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
l.push_back(i);
}
printList(l);
l.reverse();
printList(l);
//所有不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,不可以用标准算法
// 不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,内部会提供对应的算法
//sort(l.begin(), l.end());
//使用容器内部算法排序 sort排序,默认升序
l.sort();
cout << "升序:" << endl;
printList(l);
l.sort(myCompare);
cout << "降序:" << endl;
printList(l);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.8 list排序案例
需求描述:
自定义person类,包含姓名、年龄、升高属性。
排序规则,按照年龄升序,若年龄相同,按照身高降序。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
Person(string name,int age,int height) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
this->m_height=height;
}
string m_name;
int m_age;
int m_height;
};
bool myCompare(Person& p1, Person& p2) {
// 年龄相同 按照升高降序
if (p1.m_age == p2.m_age) {
return p1.m_height > p2.m_height;
}
else {
//按照年龄 升序
return p1.m_age < p2.m_age;
}
}
void printPerson(const list<Person>& l) {
for (auto item : l) {
cout << "name: " << item.m_name
<< " age: " << item.m_age
<< " height: " << item.m_height
<< endl;
}
}
void test() {
Person p1("echo", 20, 150);
Person p2("lisa", 25, 170);
Person p3("mesa", 20, 160);
list<Person> l;
l.push_back(p1);
l.push_back(p2);
l.push_back(p3);
printPerson(l);
l.sort(myCompare);
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
printPerson(l);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
10 STL-list的更多相关文章
- 学习激动人心的C++ 11
1->创建7个Thread,跑个非常大的循环.观察CPU void func(string &name) { ;i<0xFFFFFFFF;i++) { //cout << ...
- c++高质量编程手册
怡化主管强烈要求我读这本书.... 笔记尚未完成,持续更新呗.. 第1章 高质量软件开发之道 1.1 软件质量基本概念 1.1.1 如何理解软件的质量:功能性和非公能性 1.1.2 提高软件质量的基本 ...
- C++ 11 snippets , 1
1->创建7个Thread,跑个非常大的循环.观察CPU void func(string &name) { ;i<0xFFFFFFFF;i++) { //cout << ...
- ignitius and princess 2(全排列)
A - Ignatius and the Princess II Now our hero finds the door to the BEelzebub feng5166. He opens the ...
- 我要好offer之 C++大总结
0. Google C++编程规范 英文版:http://google-styleguide.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/cppguide.xml 中文版:http://zh-g ...
- CMS系统简介(从简介到使用)
CMS系统简介 1.简介 CMS是Content Management System的缩写,意为"内容管理系统". 在中国互联网的发展历程中,一直以来默默地为中国站长提供动力的CM ...
- c++ 性能优化策略
c++ 性能优化策略 作者:D_Guco 来源:CSDN 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/D_Guco/article/details/75729259 1 关于继承:不可否认良好的 ...
- 【10.11校内测试】【优先队列(反悔贪心)】【莫队】【stl的应用??离线处理+二分】
上次做过类似的题,原来这道还要简单些?? 上次那道题是每天可以同时买进卖出,所以用两个优先队列,一个存买进,一个存卖出(供反悔的队列). 这道题实际上用一个就够了???但是不好理解!! 所以我还是用了 ...
- 10.3 c++ STL 初步
#include<Windows.h>#include<iostream>#include<algorithm> // sort swap min ma ...
- STL 小白学习(10) map
map的构造函数 map<int, string> mapS; 数据的插入:用insert函数插入pair数据,下面举例说明 mapStudent.insert(pair<, &qu ...
随机推荐
- 注解@DependsOn解析
作用 @DependsOn注解可以定义在类和方法上,意思是我这个组件要依赖于另一个组件,也就是说被依赖的组件会比该组件先注册到IOC容器中. 在哪里被解析 解析的地方在 ComponentScanAn ...
- Kratos漫游指南 1 - 概览
您好,地球人,欢迎来到Kratos漫游指南. 对于刚开始研究Kratos框架的开发者来说,目前的文档有些零散,这与我们的模块化设计有一些关系,不过Don't panic,从这篇文章开始,我将试图打破这 ...
- Springboot配置文件参数使用docker-compose实现动态配置
文章总结; Springboot配置文件中的一些参数可以写成变量的形式,具体变量的值可以从docker-compose.yml文件中设置来获取 在yml文件中,通过${Envirment_variab ...
- django-compressor安装失败
报错日志: Installing collected packages: rcssmin, django-compressor Running setup.py install for rcssmin ...
- 1_requests基础用法
requests模块的基本使用 什么是requests模块? Python中封装好的一个基于网络请求的模块 requests模块的作用? 用来模拟浏览器发请求 requests模块的环境安装: pip ...
- 局域网内搭建CentOS PHP 环境
首先我们找到一台已经搭建好的CentOS,IP地址我就不说啦. 我们需要用到的几个工具,一个是SecureCRT用于远程连接,还有一个用于文件上传和下载就是filezilla 准备好了之后,我们就可以 ...
- MyBatis之ResultMap的association和collection标签详解
一.前言 MyBatis 创建时的一个思想是:数据库不可能永远是你所想或所需的那个样子. 我们希望每个数据库都具备良好的第三范式或 BCNF 范式,可惜它们并不都是那样. 如果能有一种数据库映射模式, ...
- Mysql单表访问方法,索引合并,多表连接原理,基于规则的优化,子查询优化
参考书籍<mysql是怎样运行的> 非常推荐这本书,通俗易懂,但是没有讲mysql主从等内容 书中还讲解了本文没有提到的子查询优化内容, 本文只总结了常见的子查询是如何优化的 系列文章目录 ...
- HTTP缺点有哪些,如何解决
前言 大家好,我是蜗牛,在上一篇中,我们介绍了不同版本的HTTP区别和发展背景,这篇文章我们来聊聊HTTP的缺点,HTTP缺点大致总结有以下三点: 通信使用明文(不加密),内容可能会被窃听. 不验证通 ...
- 多态特征,instanceof关键字和abstract类
多态 对象有多种状态.作用:提高程序的可扩展性. 一个对象具备多种状态的能力,这个程序是可扩展的. 前提: 必须有层级关系 继承 实现 继承:子类和父类的关系,一个父类可以有多个子类,说明父类的引用有 ...
