Handler,Looper,MessageQueue流程梳理
目的:handle的出现主要是为了解决线程间通讯。
举个例子,android是不允许在主线程中访问网络,因为这样会阻塞主线程,影响性能,所以访问网络都是放在子线程中执行,对于网络返回的结果则需要显示在主线程中,handler就是连接主线程和子线程的桥梁。
1.handler基本使用方法
看一下使用方法:
public static final int EMPTY_MSG = 0;
@SuppressLint("HandlerLeak")
Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what){
case 0:
Toast.makeText(MainActivitys.this, "接受到消息", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
handler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
}
}).start();
}
通过上边代码就完成了子线程向主线程发送消息的功能。
2. handler,Looper,MessageQueue 解释
handler:负责发送和处理消息
Looper:消息循环器,也可以理解为消息泵,主动地获取消息,并交给handler来处理
MessageQueue:消息队列,用来存储消息
3.源码分析
程序的启动是在ActivityThread的main方法中
public static void main(){
Looper.prepare(); //
Handler handler = new Handler();//
Looper.loop(); //
}
Looper.prepare()会初始化当前线程的looper
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
会调用到sThreadLocal.set()方法,ThreadLocal是线程安全的,不同的线程获取到的值是不一样的,下面先分析一下ThreadLocal是如何做到线程安全。
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
不同的线程会设置不同的looper,下面看一下ThreadLocalMap是如何存储数据的
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
}
ThreadLocalMap会创建一个数组,key是通过特殊的算法来创建出来,一个线程中会有一个ThreadLocalMap,这个map中会存多个ThreadLocal和values。
下面看下ThreadLocalMap是如何set一个值的
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
其实是遍历threadLocalMap中的table,如果当前table中存在threadLocal这个key就更新,不存在就新建。ThreadLocal的set方法到此结束。
下面看下Handler handler = new Handler()中执行了哪些操作:
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
}
重要的就是构造函数中这两个方法,在handler中初始化looper和messageQueue。这个就不展开讲了。
下面看一下Looper.loop()这个步骤,我做了一些精简,把无关的代码去掉了。
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
queue.next()是个无限for循环,其实也是个阻塞方法,其中比较重要的是下面这个方法,其作用是不会一直循环。底层采用的是pipe/epoll机制。
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
Message next() {
// Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed.
// This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit
// which is not supported.
final long ptr = mPtr;
if (ptr == 0) {
return null;
}
int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration
int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
for (;;) {
if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
}
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
synchronized (this) {
// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
Message msg = mMessages;
if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.
do {
prevMsg = msg;
msg = msg.next;
} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
}
if (msg != null) {
if (now < msg.when) {
// Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} else {
// Got a message.
mBlocked = false;
if (prevMsg != null) {
prevMsg.next = msg.next;
} else {
mMessages = msg.next;
}
msg.next = null;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);
msg.markInUse();
return msg;
}
} else {
// No more messages.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
}
// Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled.
if (mQuitting) {
dispose();
return null;
}
// If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run.
// Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message
// in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future.
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0
&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {
pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
}
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {
// No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.
mBlocked = true;
continue;
}
if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
}
mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
}
// Run the idle handlers.
// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.
for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler
boolean keep = false;
try {
keep = idler.queueIdle();
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
}
if (!keep) {
synchronized (this) {
mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
}
}
}
// Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.
pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;
// While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered
// so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
}
}
message.next()返回消息之后会接着调用 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);在这个方法里边会进行判断,来决定执行哪一种回调。
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
到此整个handler的流程就结束了。最后附上一张handler的时序图。
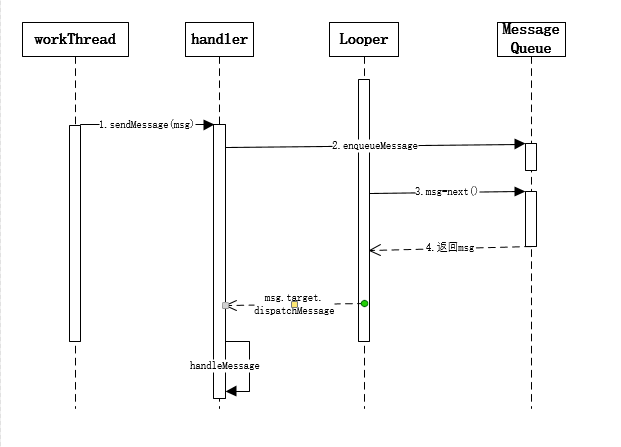
Handler,Looper,MessageQueue流程梳理的更多相关文章
- Handler+Looper+MessageQueue深入详解
概述:Android中的异步处理机制由四部分组成:Handler+Looper+MessageQueue+message,用于实现线程间的通信. 用到的概念: Handler: 主要作用是发送消息和处 ...
- Handler Looper MessageQueue 之间的关系
Handler Looper MessageQueue 之间的关系 handler在安卓开发中常用于更新界面ui,以及其他在主线程中的操作.内部结构大概图为: 1.handler持有一个Looper对 ...
- 讲讲Handler+Looper+MessageQueue 关系
Handler+Looper+MessageQueue这三者的关系其实就是Android的消息机制.这块内容相比开发人员都不陌生,在面试中,或者日常开发中都会碰到,今天就来讲这三者的关系. 概述: H ...
- android学习11——Handler,Looper,MessageQueue工作原理
Message是Handler接收和处理的消息对象. 每个线程只能拥有一个Looper.它的loop方法读取MessageQueue中的消息,读到消息之后就把消息交给发送该消息的Handler进行处理 ...
- Android异步处理三:Handler+Looper+MessageQueue深入详解
在<Android异步处理一:使用Thread+Handler实现非UI线程更新UI界面>中,我们讲到使用Thread+Handler的方式来实现界面的更新,其实是在非UI线程发送消息到U ...
- Handler Looper 解析
文章讲述Looper/MessageQueue/Handler/HandlerThread相关的技能和使用方法. 什么是Looper?Looper有什么作用? Looper是用于给线程(Thread) ...
- Android线程之异步消息处理机制(二)——Message、Handler、MessageQueue和Looper
异步消息处理机制解析 Android中的异步消息处理主要有四个部分组成,Message.Handler.MessageQueue和Looper. 1.Message Message是在线程之间传递的消 ...
- Android消息机制:Looper,MessageQueue,Message与handler
Android消息机制好多人都讲过,但是自己去翻源码的时候才能明白. 今天试着讲一下,因为目标是讲清楚整体逻辑,所以不追究细节. Message是消息机制的核心,所以从Message讲起. 1.Mes ...
- Android的消息机制: Message/MessageQueue/Handler/Looper
概览 * Message:消息.消息里面可包含简单数据.Object和Bundle,还可以包含一个Runnable(实际上可看做回调). * MessageQueue:消息队列,供Looper线程 ...
随机推荐
- DS控件库 Win7链接列表框的仿Windows开始菜单样式
Win7链接列表框是依照Windows7的开始菜单开发的,同时进行了属性和功能的扩展. 效果图 项属性 控件属性 控件主要事件 点击项(Sender As Win7链接列表框, Itm As 链接项, ...
- .net Lambda表达式与Linq (LINQ TO object)
Lambda表达式,是用来写匿名方法的. 在委托用得比较多,因为委托是传递方法的. 定义几个委托: public delegate void DoNoThing();//无参无返回值 publ ...
- Flutter 即学即用系列博客——07 RenderFlex overflowed 引发的思考
背景 在进行 Flutter UI 开发的时候,控制台报出了下面错误: flutter: ══╡ EXCEPTION CAUGHT BY RENDERING LIBRARY >╞════════ ...
- 深度优先搜索(DFS)与广度优先搜索(BFS)的Java实现
1.基础部分 在图中实现最基本的操作之一就是搜索从一个指定顶点可以到达哪些顶点,比如从武汉出发的高铁可以到达哪些城市,一些城市可以直达,一些城市不能直达.现在有一份全国高铁模拟图,要从某个城市(顶点) ...
- Spring的PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer强制使用默认值的坑
1.问题 dubbo client配置: <dubbo:reference id="channelCustomerClient" interface="com.gt ...
- PHP中$GLOBALS和global的区别
很多人都认为$GLOBALS['var']和global $var只是写法上不同,其实并不是这样 根据官方的解释是 $GLOBALS['var']是外部全局变量$var的本身, 而global $v ...
- 使用 .NET Core 开发 BT Tracker 服务器
一.什么是 BT Tracker ? 在 BT 下载过程当中,我们如果拿到一个种子文件,在其内部会包含一组 BT Tracker 服务器信息.在开始进行下载的时候,BT 下载工具会根据种子内的唯一 H ...
- 网络协议 18 - CDN:家门口的小卖铺
[前五篇]系列文章传送门: 网络协议 13 - HTTPS 协议:加密路上无尽头 网络协议 14 - 流媒体协议:要说爱你不容易 网络协议 15 - P2P 协议:小种子大学问 网络协议 16 - D ...
- ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL - 第八章 在GraphQL中处理一对多关系
ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL - 目录 ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL - 第一章 Hello World ASP.NET Core中使用GraphQL - 第二章 中间 ...
- Java中的基本类型转换,数据溢出原理
java中的数据类型 java是一种强类型语言,在java中,数据类型主要有两大类,基本数据类型和引用数据类型,不同的数据类型有不同的数据存储方式和分配的内存大小. 基本数据类型中,各数据类型所表示的 ...
