Java自定义注解开发
一、背景
最近在自己搞一个项目时,遇到可需要开发自定义注解的需求,对于没有怎么关注这些java新特性的来说,比较尴尬,索性就拿出一些时间,来进行研究下自定义注解开发的步骤以及使用方式。今天在这里记下,方便以后学习复习以及分享给有需要的小伙伴们~
二、注解基本概念
什么是注解?
注解就是某种注解类型的一个实例,我们可以用它在某个类上进行标注,这样编译器在编译我们的文件时,会根据我们自己设定的方法来编译类。
注解的分类有哪些?

由上图可知:注解共分为:标记注解、标准元注解、一般注解三类。
注:Deprecated注解,除了多个删除线,并没有什么拦截功能。
标准元注解详解
标准元注解是自定义注解的注解,主要包含4个,都位于java.lang.annotation包中,我们创建自定义注解时会用到4个标准元注解。它们的名称以及含义如下:
1. @Documented:用于描述其它类型的annotation应该被作为被标注的程序成员的公共API,因此可以被例如javadoc此类的工具文档化。是一个标记注解,没有成员。
2. @Inherited:是一个标记注解阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。使用了@Inherited修饰的注解类型被用于一个class时该class的子类也有了该注解。
3. @Retention:定义了该注解的生命周期:某些注解仅出现在源代码中,而被编译器丢弃;而另一些却被编译在class文件中;编译在class文件中的注解可能会被虚拟机忽略,而另一些在class被装载时将被读取(请注意并不影响class的执行,因为注解与class在使用上是被分离的)。使用这个元注解可以对自定义注解的“生命周期”进行限制。
生命周期策略枚举
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME 注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS 默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得。
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含。
4. @Target:说明了注解所修饰的对象范围:注解可被用于 packages、types(类、接口、枚举、Annotation类型)、类型成员(方法、构造方法、成员变量、枚举值)、方法参数和本地变量(如循环变量、catch参数)。
修饰范围枚举
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR 作用于构造器
ElementType.FIELD 作用于域/属性
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE 用于描述局部变量
ElementType.METHOD 作用于方法
ElementType.PACKAGE 用于描述包
ElementType.PARAMETER 用于描述参数
ElementType.TYPE 用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明,最常用
三、开发自定义注解demo
1.开发自定义类注解
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:58:11
* @Description 自定义类注解
*/
@Documented //定义可以被文档工具文档化
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//声明周期为runtime,运行时可以通过反射拿到
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)//注解修饰范围为类、接口、枚举
public @interface ClassAnnotation {
public String name() default "defaultService";
public String version() default "1.1.0";
}
2.自定义方法注解
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.en.MethodTypeEnum; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:58:26
* @Description 自定义方法注解
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface MethodAnnotation {
public String name() default "defaultName";
public MethodTypeEnum type() default MethodTypeEnum.TYPE1;
}
3.自定义域注解
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:58:37
* @Description 自定义域注解
*/
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FieldAnnotation {
public String name() default "defaultName";
public String value() default "defaultValue"; }
4.方法类型枚举类
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.en; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 下午1:59:02
* @Description 方法类型枚举类
*/
public enum MethodTypeEnum {
TYPE1,TYPE2
}
5.测试注解Bean
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean; import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.ClassAnnotation;
import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.FieldAnnotation;
import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.MethodAnnotation;
import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.en.MethodTypeEnum; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 上午11:59:37
* @Description 测试使用的bean
*/
@ClassAnnotation(name="personBean", version="1.2.1")
public class Person {
@FieldAnnotation(name="description", value="This is my personal annotation")
private String description; public String getDescription() {
return description;
} public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
@MethodAnnotation(name="sayHello", type = MethodTypeEnum.TYPE2)
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello Annotation!");
}
}
6.自定义类注解测试类
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.test; import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.ClassAnnotation;
import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean.Person; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 上午11:56:34
* @Description 测试类注解
*/
public class TestClassAnnotation { private static Person person = new Person(); public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> clazz = person.getClass();
//因为注解是作用于类上面的,所以可以通过isAnnotationPresent来判断是否是一个具有指定注解的类
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(ClassAnnotation.class)) {
System.out.println("This is a class with annotation ClassAnnotation!");
//通过getAnnotation可以获取注解对象
ClassAnnotation annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(ClassAnnotation.class);
if(null != annotation) {
System.out.println("BeanName = " + annotation.name());
System.out.println("BeanVersion = " + annotation.version());
}else{
System.out.println("the annotation that we get is null");
}
}else{
System.out.println("This is not the class that with ClassAnnotation");
}
}
}
运行结果:

7.自定义方法注解测试类
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.test; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.MethodAnnotation;
import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean.Person; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 下午12:11:11
* @Description 测试方法注解
*/
public class TestMethodAnnotation { private static Person person = new Person(); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = person.getClass();
//因为是注解到method上的,所以首先要获取这个方法
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("sayHello");
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MethodAnnotation.class)) {
System.out.println("===This is a method with a annotation:MethodAnnotation===");
//通过getAnnotation可以获取注解对象
MethodAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MethodAnnotation.class);
if(null != annotation) {
System.out.println("MethodName = " + annotation.name());
System.out.println("MethodType = " + annotation.type());
}else{
System.out.println("the annotation that we get is null");
}
}else{
System.out.println("This is not the class that with MethodAnnotation");
}
}
}
运行结果:

8.自定义域注解测试类
package com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.test; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.FieldAnnotation;
import com.hafiz.zhang.annotation.bean.Person; /**
* @author hafiz.Zhang
* @Date 2016年5月18日 下午12:17:49
* @Description 测试域注解
*/
public class TestFieldAnnotation { private static Person person = new Person(); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = person.getClass();
//因为是注解到Field上的,所以首先要获取这个字段
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("description");
//判断这个Field上是否有这个注解
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FieldAnnotation.class)) {
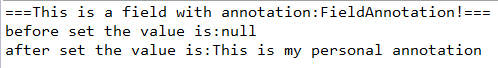
System.out.println("===This is a field with annotation:FieldAnnotation!===");
//如果有这个注解,则获取注解类
FieldAnnotation annotation = field.getAnnotation(FieldAnnotation.class);
if(null != annotation){
System.out.println("before set the value is:" + person.getDescription());
//通过反射给私有变量赋值
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(person, annotation.value());
System.out.println("after set the value is:" + person.getDescription());
}else{
System.out.println("the annotation that we get is null");
}
}else{
System.out.println("This is not the class that with FieldAnnotation");
}
}
}
运行结果:
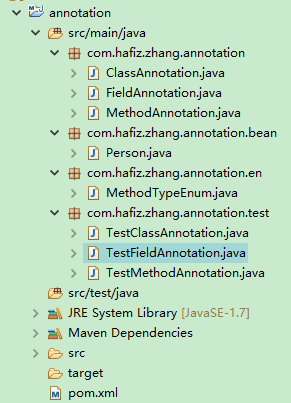
附:demo项目结构图
以上就是本人对自定义注解开发的理解以及开发测试了,如有错误希望大家能够批评指正!
Java自定义注解开发的更多相关文章
- Java实现自定义注解开发
Java实现自定义注解开发 一直都对注解开发挺好奇的,最近终于有时间自己实践了一把,记录一下 万一后期会用到呢 哈哈哈 首先我们了解一下自定义注解的标准示例,注解类使用 @interface 关键字修 ...
- java自定义注解注解方法、类、属性等等【转】
http://anole1982.iteye.com/blog/1450421 http://www.open-open.com/doc/view/51fe76de67214563b20b385320 ...
- java自定义注解学习(二)_注解详解
上篇文章,我们简单的实现了一个自定义注解,相信大家对自定义注解有了个简单的认识,这篇,这样介绍下注解中的元注解和内置注解 整体图示 内置注解 @Override 重写覆盖 这个注解大家应该经常用到,主 ...
- JAVA自定义注解 ------ Annotation
日常开发工作中,合理的使用注解,可以简化代码编写以及使代码结构更加简单,下面记录下,JAVA自定义注解的开发过程. 定义注解声明类. 编写注解处理器(主要起作用部分). 使用注解. 相关知识点介绍, ...
- java自定义注解类
一.前言 今天阅读帆哥代码的时候,看到了之前没有见过的新东西, 比如java自定义注解类,如何获取注解,如何反射内部类,this$0是什么意思? 于是乎,学习并整理了一下. 二.代码示例 import ...
- java自定义注解实现前后台参数校验
2016.07.26 qq:992591601,欢迎交流 首先介绍些基本概念: Annotations(also known as metadata)provide a formalized way ...
- java自定义注解知识实例及SSH框架下,拦截器中无法获得java注解属性值的问题
一.java自定义注解相关知识 注解这东西是java语言本身就带有的功能特点,于struts,hibernate,spring这三个框架无关.使用得当特别方便.基于注解的xml文件配置方式也受到人们的 ...
- Java自定义注解的实现
Java自定义注解的实现,总共三步(eg.@RandomlyThrowsException): 1.首先编写一个自定义注解@RandomlyThrowsException package com.gi ...
- Java自定义注解源码+原理解释(使用Java自定义注解校验bean传入参数合法性)
Java自定义注解源码+原理解释(使用Java自定义注解校验bean传入参数合法性) 前言:由于前段时间忙于写接口,在接口中需要做很多的参数校验,本着简洁.高效的原则,便写了这个小工具供自己使用(内容 ...
随机推荐
- 跨域攻击xss
要完全防止跨域攻击是很难的,对于有些站点是直接 拦截跨域的访问,在你从本站点跳转到其他站点时提醒,这算是一种手段吧. 而跨域攻击的发起就是在代码(包括html,css,js或是后台代码,数据库数据)里 ...
- Spark之集群搭建
注意,这种安装方式是集群方式:然后有常用两种运行模式: standalone , on yarn 区别就是在编写 standalone 与 onyarn 的程序时的配置不一样,具体请参照spar2中的 ...
- umeng
http://bbs.umeng.com/thread-5408-1-1.html 微博分享 http://dev.umeng.com/social/ios/operation#2_2 http:// ...
- ios 微博登录 21338错误 sso package or sign error
os中,是你项目的bundle id 和 连接的微博开发账户里面的bundle id 不一致造成的. 特别是,你把你注册的appKey放到你下载的官方的demo里面测试,肯定会出现这种情况, 所以,你 ...
- 关于ext3,ext4,xfs和btrfs文件系统性能对比
关于ext3,ext4,xfs和btrfs文件系统性能对比 应为原文:http://www.ilsistemista.net/index.php/linux-a-unix/6-linux-filesy ...
- BZOJ2171——K凹凸序列
好吧,我承认是sb题QAQ BZOJ2171弱化版QAQ 这题考试的时候写的我快吐血了QAQ 0.题目大意:给一个序列,你可以随便修改,修改是将一个数+1或-1,一次修改的代价是1,问把这个数修改成x ...
- Fedora 24最新工作站版本之四大重要改进
导读 2014年,Fedora.next倡议正式开始建立Fedora Linux未来十年的发展规划.从本质上讲,这项规划旨在进一步使Fedora不再只是一套汇聚多种开源产品的通用库(例如Debian) ...
- objc/runtime
"T@\"MyInnerObject\",&,N,V_myInnerObject" MyInnerObject "Td,N,V_cgfloat ...
- 剑指Offer 反转链表
题目描述 输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出链表的所有元素. 思路: 法1:用栈,压栈出栈 法2:头插法(有递归非递归2中) AC代码: /* struct ListNode { int va ...
- WebClient 访问https
解决SSH证书问题: webClient.getOptions().setUseInsecureSSL(true);//解决ssh证书访问https的问题
