吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(2)
import os
import sys
import itertools
import math
import logging
import json
import re
import random
from collections import OrderedDict
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import matplotlib.lines as lines
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon import utils
import visualize
from visualize import display_images
import model as modellib
from model import log %matplotlib inline ROOT_DIR = os.getcwd()
# Run one of the code blocks # Shapes toy dataset
# import shapes
# config = shapes.ShapesConfig() # MS COCO Dataset
import coco
config = coco.CocoConfig()
COCO_DIR = "path to COCO dataset" # TODO: enter value here
# Load dataset
if config.NAME == 'shapes':
dataset = shapes.ShapesDataset()
dataset.load_shapes(500, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
elif config.NAME == "coco":
dataset = coco.CocoDataset()
dataset.load_coco(COCO_DIR, "train") # Must call before using the dataset
dataset.prepare() print("Image Count: {}".format(len(dataset.image_ids)))
print("Class Count: {}".format(dataset.num_classes))
for i, info in enumerate(dataset.class_info):
print("{:3}. {:50}".format(i, info['name']))

# Load and display random samples
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 4)
for image_id in image_ids:
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)

# Load random image and mask.
image_id = random.choice(dataset.image_ids)
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
# Compute Bounding box
bbox = utils.extract_bboxes(mask) # Display image and additional stats
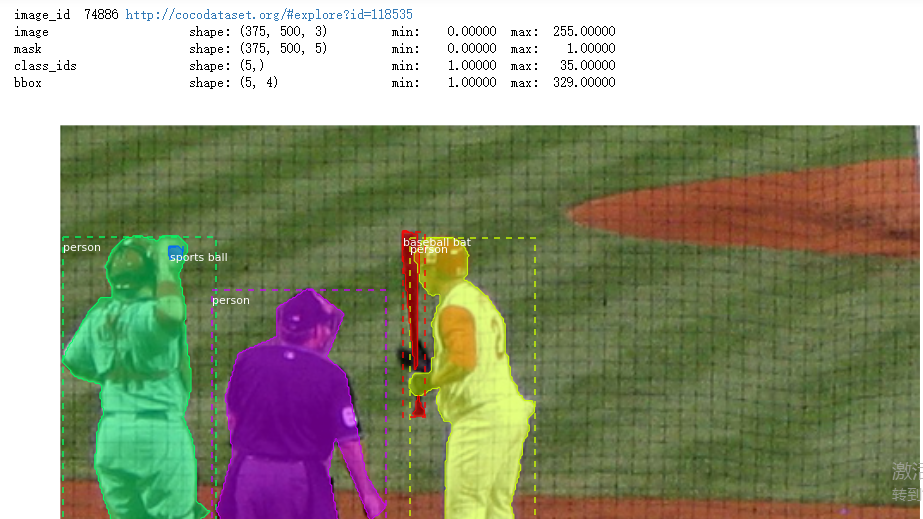
print("image_id ", image_id, dataset.image_reference(image_id))
log("image", image)
log("mask", mask)
log("class_ids", class_ids)
log("bbox", bbox)
# Display image and instances
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)
# Load random image and mask.
image_id = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 1)[0]
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
original_shape = image.shape
# Resize
image, window, scale, padding = utils.resize_image(
image,
min_dim=config.IMAGE_MIN_DIM,
max_dim=config.IMAGE_MAX_DIM,
padding=config.IMAGE_PADDING)
mask = utils.resize_mask(mask, scale, padding)
# Compute Bounding box
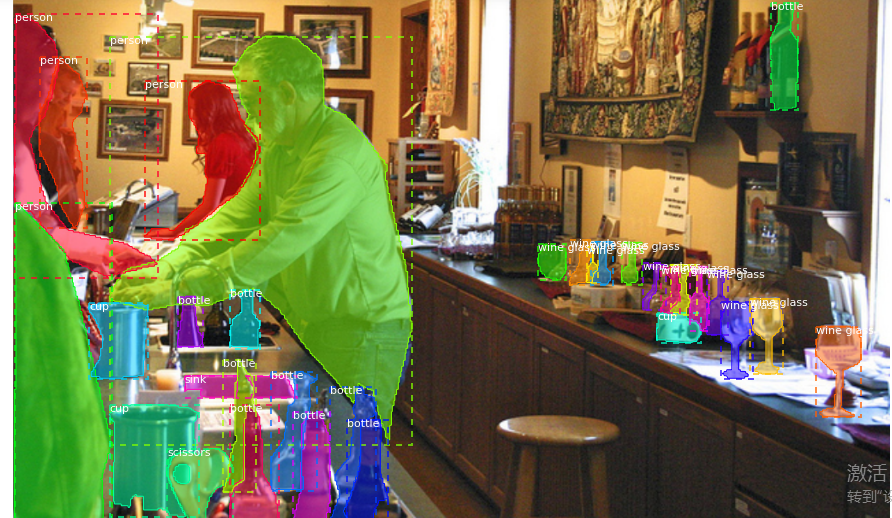
bbox = utils.extract_bboxes(mask) # Display image and additional stats
print("image_id: ", image_id, dataset.image_reference(image_id))
print("Original shape: ", original_shape)
log("image", image)
log("mask", mask)
log("class_ids", class_ids)
log("bbox", bbox)
# Display image and instances
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)

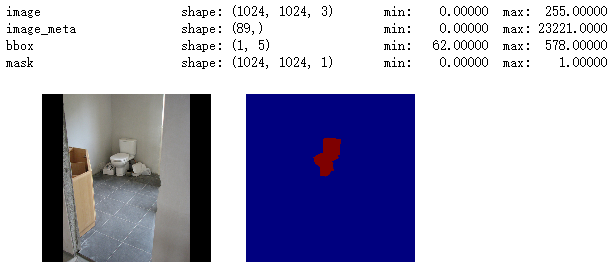
image_id = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 1)[0]
image, image_meta, class_ids, bbox, mask = modellib.load_image_gt(
dataset, config, image_id, use_mini_mask=False) log("image", image)
log("image_meta", image_meta)
log("class_ids", class_ids)
log("bbox", bbox)
log("mask", mask) display_images([image]+[mask[:,:,i] for i in range(min(mask.shape[-1], 7))])
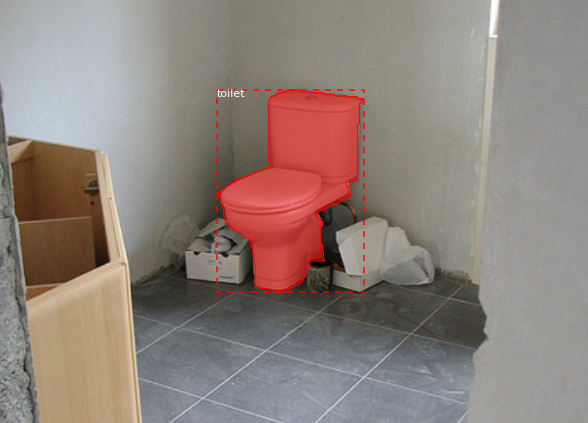
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)

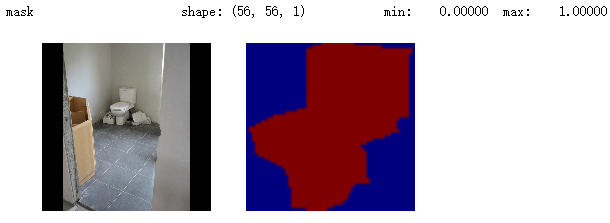
# Add augmentation and mask resizing.
image, image_meta, class_ids, bbox, mask = modellib.load_image_gt(
dataset, config, image_id, augment=True, use_mini_mask=True)
log("mask", mask)
display_images([image]+[mask[:,:,i] for i in range(min(mask.shape[-1], 7))])
mask = utils.expand_mask(bbox, mask, image.shape)
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)

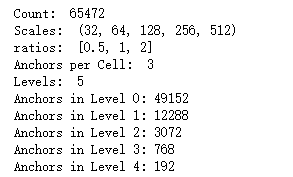
# Generate Anchors
anchors = utils.generate_pyramid_anchors(config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS,
config.BACKBONE_SHAPES,
config.BACKBONE_STRIDES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE) # Print summary of anchors
num_levels = len(config.BACKBONE_SHAPES)
anchors_per_cell = len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS)
print("Count: ", anchors.shape[0])
print("Scales: ", config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES)
print("ratios: ", config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS)
print("Anchors per Cell: ", anchors_per_cell)
print("Levels: ", num_levels)
anchors_per_level = []
for l in range(num_levels):
num_cells = config.BACKBONE_SHAPES[l][0] * config.BACKBONE_SHAPES[l][1]
anchors_per_level.append(anchors_per_cell * num_cells // config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE**2)
print("Anchors in Level {}: {}".format(l, anchors_per_level[l]))
## Visualize anchors of one cell at the center of the feature map of a specific level # Load and draw random image
image_id = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 1)[0]
image, image_meta, _, _, _ = modellib.load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(10, 10))
ax.imshow(image)
levels = len(config.BACKBONE_SHAPES) for level in range(levels):
colors = visualize.random_colors(levels)
# Compute the index of the anchors at the center of the image
level_start = sum(anchors_per_level[:level]) # sum of anchors of previous levels
level_anchors = anchors[level_start:level_start+anchors_per_level[level]]
print("Level {}. Anchors: {:6} Feature map Shape: {}".format(level, level_anchors.shape[0],
config.BACKBONE_SHAPES[level]))
center_cell = config.BACKBONE_SHAPES[level] // 2
center_cell_index = (center_cell[0] * config.BACKBONE_SHAPES[level][1] + center_cell[1])
level_center = center_cell_index * anchors_per_cell
center_anchor = anchors_per_cell * (
(center_cell[0] * config.BACKBONE_SHAPES[level][1] / config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE**2) \
+ center_cell[1] / config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE)
level_center = int(center_anchor) # Draw anchors. Brightness show the order in the array, dark to bright.
for i, rect in enumerate(level_anchors[level_center:level_center+anchors_per_cell]):
y1, x1, y2, x2 = rect
p = patches.Rectangle((x1, y1), x2-x1, y2-y1, linewidth=2, facecolor='none',
edgecolor=(i+1)*np.array(colors[level]) / anchors_per_cell)
ax.add_patch(p)

# Create data generator
random_rois = 2000
g = modellib.data_generator(
dataset, config, shuffle=True, random_rois=random_rois,
batch_size=4,
detection_targets=True)
# Get Next Image
if random_rois:
[normalized_images, image_meta, rpn_match, rpn_bbox, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks, rpn_rois, rois], \
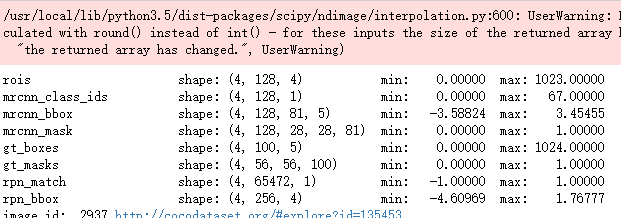
[mrcnn_class_ids, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask] = next(g) log("rois", rois)
log("mrcnn_class_ids", mrcnn_class_ids)
log("mrcnn_bbox", mrcnn_bbox)
log("mrcnn_mask", mrcnn_mask)
else:
[normalized_images, image_meta, rpn_match, rpn_bbox, gt_boxes, gt_masks], _ = next(g) log("gt_class_ids", gt_class_ids)
log("gt_boxes", gt_boxes)
log("gt_masks", gt_masks)
log("rpn_match", rpn_match, )
log("rpn_bbox", rpn_bbox)
image_id = image_meta[0][0]
print("image_id: ", image_id, dataset.image_reference(image_id)) # Remove the last dim in mrcnn_class_ids. It's only added
# to satisfy Keras restriction on target shape.
mrcnn_class_ids = mrcnn_class_ids[:,:,0]
b = 0 # Restore original image (reverse normalization)
sample_image = modellib.unmold_image(normalized_images[b], config) # Compute anchor shifts.
indices = np.where(rpn_match[b] == 1)[0]
refined_anchors = utils.apply_box_deltas(anchors[indices], rpn_bbox[b, :len(indices)] * config.RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV)
log("anchors", anchors)
log("refined_anchors", refined_anchors) # Get list of positive anchors
positive_anchor_ids = np.where(rpn_match[b] == 1)[0]
print("Positive anchors: {}".format(len(positive_anchor_ids)))
negative_anchor_ids = np.where(rpn_match[b] == -1)[0]
print("Negative anchors: {}".format(len(negative_anchor_ids)))
neutral_anchor_ids = np.where(rpn_match[b] == 0)[0]
print("Neutral anchors: {}".format(len(neutral_anchor_ids))) # ROI breakdown by class
for c, n in zip(dataset.class_names, np.bincount(mrcnn_class_ids[b].flatten())):
if n:
print("{:23}: {}".format(c[:20], n)) # Show positive anchors
visualize.draw_boxes(sample_image, boxes=anchors[positive_anchor_ids],
refined_boxes=refined_anchors)
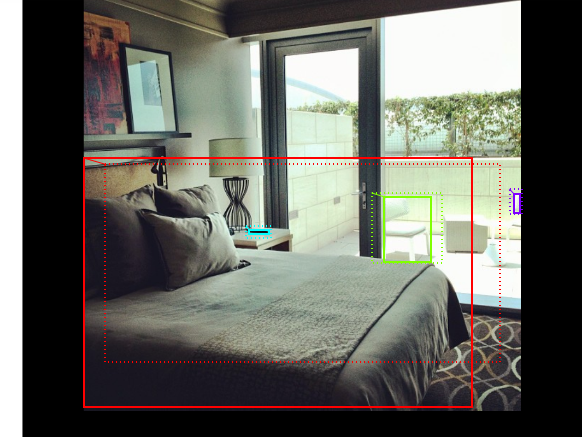

# Show negative anchors
visualize.draw_boxes(sample_image, boxes=anchors[negative_anchor_ids])
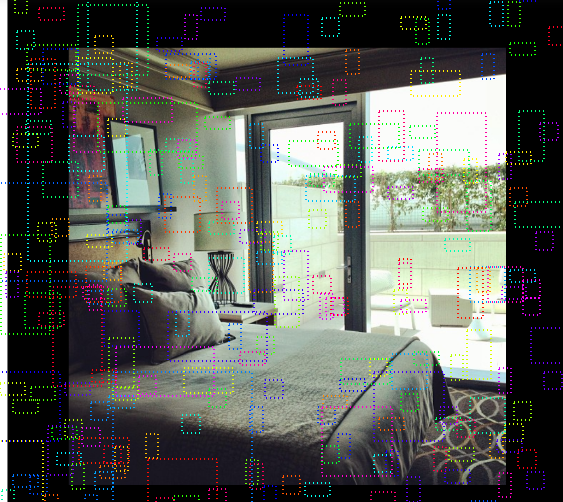

# Show neutral anchors. They don't contribute to training.
visualize.draw_boxes(sample_image, boxes=anchors[np.random.choice(neutral_anchor_ids, 100)])
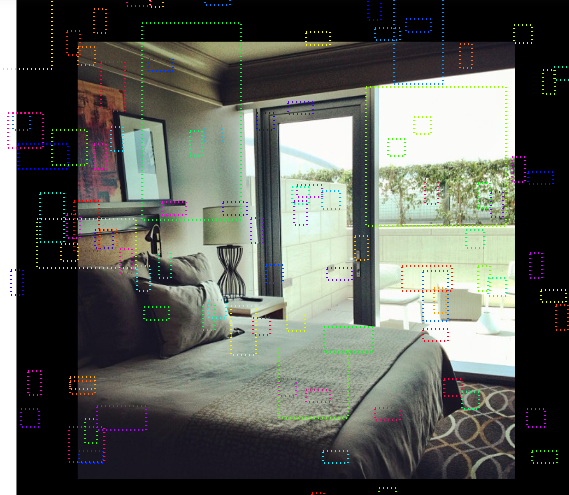

if random_rois:
# Class aware bboxes
bbox_specific = mrcnn_bbox[b, np.arange(mrcnn_bbox.shape[1]), mrcnn_class_ids[b], :] # Refined ROIs
refined_rois = utils.apply_box_deltas(rois[b].astype(np.float32), bbox_specific[:,:4] * config.BBOX_STD_DEV) # Class aware masks
mask_specific = mrcnn_mask[b, np.arange(mrcnn_mask.shape[1]), :, :, mrcnn_class_ids[b]] visualize.draw_rois(sample_image, rois[b], refined_rois, mask_specific, mrcnn_class_ids[b], dataset.class_names) # Any repeated ROIs?
rows = np.ascontiguousarray(rois[b]).view(np.dtype((np.void, rois.dtype.itemsize * rois.shape[-1])))
_, idx = np.unique(rows, return_index=True)
print("Unique ROIs: {} out of {}".format(len(idx), rois.shape[1]))
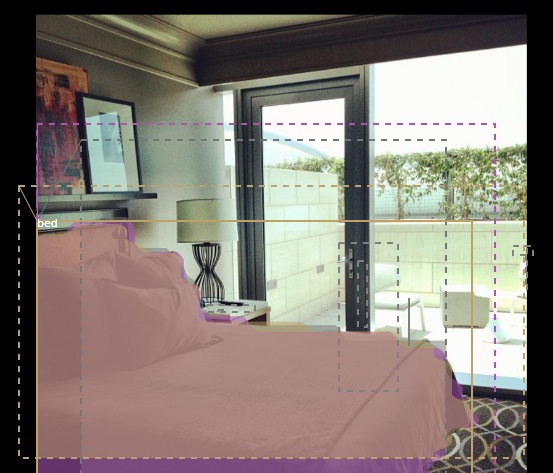

if random_rois:
# Dispalay ROIs and corresponding masks and bounding boxes
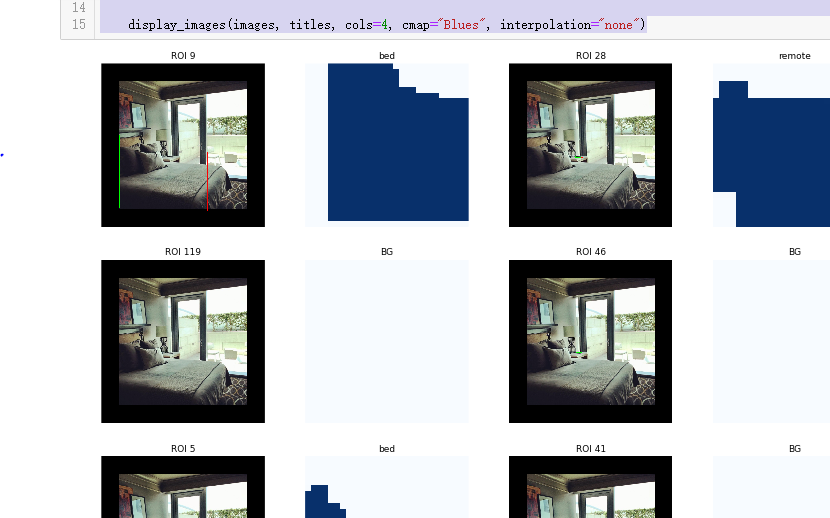
ids = random.sample(range(rois.shape[1]), 8) images = []
titles = []
for i in ids:
image = visualize.draw_box(sample_image.copy(), rois[b,i,:4].astype(np.int32), [255, 0, 0])
image = visualize.draw_box(image, refined_rois[i].astype(np.int64), [0, 255, 0])
images.append(image)
titles.append("ROI {}".format(i))
images.append(mask_specific[i] * 255)
titles.append(dataset.class_names[mrcnn_class_ids[b,i]][:20]) display_images(images, titles, cols=4, cmap="Blues", interpolation="none")
# Check ratio of positive ROIs in a set of images.
if random_rois:
limit = 10
temp_g = modellib.data_generator(
dataset, config, shuffle=True, random_rois=10000,
batch_size=1, detection_targets=True)
total = 0
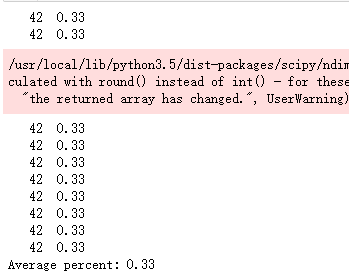
for i in range(limit):
_, [ids, _, _] = next(temp_g)
positive_rois = np.sum(ids[0] > 0)
total += positive_rois
print("{:5} {:5.2f}".format(positive_rois, positive_rois/ids.shape[1]))
print("Average percent: {:.2f}".format(total/(limit*ids.shape[1])))
吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(2)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 人工智能——基于MASK_RCNN目标检测(5)
import os import sys import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib import matplotlib. ...
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 人工智能——基于MASK_RCNN目标检测(4)
import os import sys import random import math import re import time import numpy as np import tenso ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(3)
import os import sys import random import math import re import time import numpy as np import cv2 i ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(1)
import os import sys import random import math import numpy as np import skimage.io import matplotli ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于神经网络算法在智能医疗诊断中的应用探索代码简要展示
#K-NN分类 import os import sys import time import operator import cx_Oracle import numpy as np import ...
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 人工智能——智能医疗系统后台智能分诊模块及系统健康养生公告简约版代码展示
#coding:utf-8 import sys import cx_Oracle import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tensorflow a ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——智能医疗系统后台用户复诊模块简约版代码展示
#复诊 import sys import os import time import operator import cx_Oracle import numpy as np import pand ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——智能医疗系统后台用户注册、登录和初诊简约版代码展示
#用户注册.登录模块 #数据库脚本 CREATE TABLE usertable( userid number(8) primary key not null , username varchar(5 ...
- TF项目实战(基于SSD目标检测)——人脸检测1
SSD实战——人脸检测 Tensorflow 一 .人脸检测的困难: 1. 姿态问题 2.不同种族人, 3.光照 遮挡 带眼睛 4.视角不同 5. 不同尺度 二. 数据集介绍以及转化VOC: 1. F ...
随机推荐
- Linux - Shell - 算数表达式 - 位运算
概述 shell 中基于 $(()) 的 位运算 背景 复习 shell 脚本 凑数吧 准备 环境 os centos7 1. 位运算 代码 #!/bin/bash # 位运算 arg1=2 arg2 ...
- altair package and altair_viewer
pip install altair pip install altair_viewer Altair is a declarative statistical visualization libra ...
- css+div上下左右自适应居中
主要记录自己日常积累的布局相关的东西,持续更新中. 1.登录框上下左右自适应居中 以前想要把登录表单始终放置在页面的中间,花了不少心思,一直以来用的解决方法都是用js,感觉有点麻烦不是很好,于是在网上 ...
- java 多线程实现四种方式解析Thread,Runnable,Callable,ServiceExcutor,Synchronized ,ReentrantLock
1.Thread实现: import java.util.Date; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; public class MyThread extends ...
- codeforces 1285E. Delete a Segment
链接:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1285/E 题意:给一个数轴上有n个线段集,线段集若有相交,则合并为一个新的合并线段集,比如[1,6]和[2 ...
- slice 实现原理
package main /* #include <stdlib.h> */ import "C" import ( "unsafe" " ...
- rf关键字
1.获取字典中的key ${b} Set Variable ${a}[0][dealer_buy_price] Log ${b} 2.${b}的float类型转换string 再和后面比较 Sho ...
- 第五十三篇 Linux相关——Web服务器
No.1. Apache基本操作 安装:sudo yum -y install httpd 启动:service httpd start 停止:service httpd stop 查看服务运 ...
- mysql中间件proxysql实现mysql读写分离
目录 1. mysql实现读写分离的方式 2. ProxySQL简介 3. ProxySQL安装 4. ProxySQL的Admin管理接口 5. 和admin管理接口相关的变量 5.1 admin- ...
- AcWing 907. 区间覆盖
//1.将所有区间按照左端点从小到大排序 //2.从前往后依次枚举每个区间 //首先选择能够覆盖左端点的区间当中右端点最靠右的端点 //在所有能覆盖start的区间当中,选择右端点最大的区间 //选完 ...
