Matrices and Vectors
Matrices and Vectors
Matrices are 2-dimensional arrays:

A vector is a matrix with one column and many rows:The above matrix has four rows and three columns, so it is a 4 x 3 matrix.

Notation and terms:So vectors are a subset of matrices. The above vector is a 4 x 1 matrix.
- Aij refers to the element in the ith row and jth column of matrix A.
- A vector with 'n' rows is referred to as an 'n'-dimensional vector.
- vi refers to the element in the ith row of the vector.
- In general, all our vectors and matrices will be 1-indexed. Note that for some programming languages, the arrays are 0-indexed.
- Matrices are usually denoted by uppercase names while vectors are lowercase.
- "Scalar" means that an object is a single value, not a vector or matrix.
- R refers to the set of scalar real numbers.
- Rn refers to the set of n-dimensional vectors of real numbers.
Run the cell below to get familiar with the commands in Octave/Matlab. Feel free to create matrices and vectors and try out different things.
% The ; denotes we are going back to a new row.
A = [1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6; 7, 8, 9; 10, 11, 12] % Initialize a vector
v = [1;2;3] % Get the dimension of the matrix A where m = rows and n = columns
[m,n] = size(A) % You could also store it this way
dim_A = size(A) % Get the dimension of the vector v
dim_v = size(v) % Now let's index into the 2nd row 3rd column of matrix A
A_23 = A(2,3)
Addition and Scalar Multiplication
Addition and subtraction are element-wise, so you simply add or subtract each corresponding element:
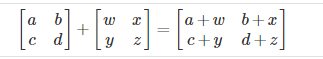
Subtracting Matrices:
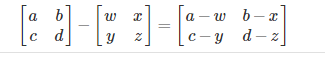
In scalar multiplication, we simply multiply every element by the scalar value:To add or subtract two matrices, their dimensions must be the same.
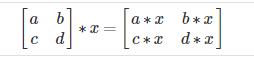
Experiment below with the Octave/Matlab commands for matrix addition and scalar multiplication. Feel free to try out different commands. Try to write out your answers for each command before running the cell below.In scalar division, we simply divide every element by the scalar value:
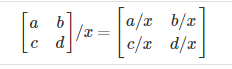
Experiment below with the Octave/Matlab commands for matrix addition and scalar multiplication. Feel free to try out different commands. Try to write out your answers for each command before running the cell below.
% Initialize matrix A and B
A = [1, 2, 4; 5, 3, 2]
B = [1, 3, 4; 1, 1, 1] % Initialize constant s
s = 2 % See how element-wise addition works
add_AB = A + B % See how element-wise subtraction works
sub_AB = A - B % See how scalar multiplication works
mult_As = A * s % Divide A by s
div_As = A / s % What happens if we have a Matrix + scalar?
add_As = A + s
Matrix-Vector Multiplication
We map the column of the vector onto each row of the matrix, multiplying each element and summing the result.
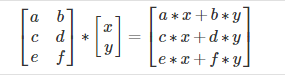
An m x n matrix multiplied by an n x 1 vector results in an m x 1 vector.The result is a vector. The number of columns of the matrix must equal the number of rows of the vector.
Below is an example of a matrix-vector multiplication. Make sure you understand how the multiplication works. Feel free to try different matrix-vector multiplications.
% Initialize matrix A
A = [1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6;7, 8, 9] % Initialize vector v
v = [1; 1; 1] % Multiply A * v
Av = A * v
Matrix-Matrix Multiplication
We multiply two matrices by breaking it into several vector multiplications and concatenating the result.
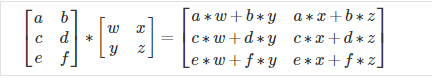
To multiply two matrices, the number of columns of the first matrix must equal the number of rows of the second matrix.An m x n matrix multiplied by an n x o matrix results in an m x o matrix. In the above example, a 3 x 2 matrix times a 2 x 2 matrix resulted in a 3 x 2 matrix.
For example:
% Initialize a 3 by 2 matrix
A = [1, 2; 3, 4;5, 6] % Initialize a 2 by 1 matrix
B = [1; 2] % We expect a resulting matrix of (3 by 2)*(2 by 1) = (3 by 1)
mult_AB = A*B % Make sure you understand why we got that result
Matrix Multiplication Properties
- Matrices are not commutative: A∗B≠B∗A
- Matrices are associative: (A∗B)∗C=A∗(B∗C)
The identity matrix, when multiplied by any matrix of the same dimensions, results in the original matrix. It's just like multiplying numbers by 1. The identity matrix simply has 1's on the diagonal (upper left to lower right diagonal) and 0's elsewhere.
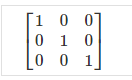
When multiplying the identity matrix after some matrix (A∗I), the square identity matrix's dimension should match the other matrix's columns. When multiplying the identity matrix before some other matrix (I∗A), the square identity matrix's dimension should match the other matrix's rows
.
% Initialize random matrices A and B
A = [1,2;4,5]
B = [1,1;0,2] % Initialize a 2 by 2 identity matrix
I = eye(2) % The above notation is the same as I = [1,0;0,1] % What happens when we multiply I*A ?
IA = I*A % How about A*I ?
AI = A*I % Compute A*B
AB = A*B % Is it equal to B*A?
BA = B*A % Note that IA = AI but AB != BA
Inverse and Transpose
The inverse of a matrix A is denoted A−1. Multiplying by the inverse results in the identity matrix.
A non square matrix does not have an inverse matrix. We can compute inverses of matrices in octave with the pinv(A) function and in Matlab with the inv(A) function. Matrices that don't have an inverse are singular or degenerate.
The transposition of a matrix is like rotating the matrix 90° in clockwise direction and then reversing it. We can compute transposition of matrices in matlab with the transpose(A) function or A':
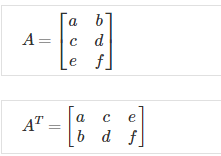
In other words:
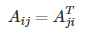
% Initialize matrix A
A = [1,2,0;0,5,6;7,0,9] % Transpose A
A_trans = A' % Take the inverse of A
A_inv = inv(A) % What is A^(-1)*A?
A_invA = inv(A)*A
Matrices and Vectors的更多相关文章
- RNN 入门教程 Part 2 – 使用 numpy 和 theano 分别实现RNN模型
转载 - Recurrent Neural Networks Tutorial, Part 2 – Implementing a RNN with Python, Numpy and Theano 本 ...
- [zt]矩阵求导公式
今天推导公式,发现居然有对矩阵的求导,狂汗--完全不会.不过还好网上有人总结了.吼吼,赶紧搬过来收藏备份. 基本公式:Y = A * X --> DY/DX = A'Y = X * A --&g ...
- Applying Eigenvalues to the Fibonacci Problem
http://scottsievert.github.io/blog/2015/01/31/the-mysterious-eigenvalue/ The Fibonacci problem is a ...
- 图像处理之image stitching
背景介绍 图像拼接是一项应用广泛的图像处理技术.根据特征点的相互匹配,可以将多张小视角的图像拼接成为一张大视角的图像,在广角照片合成.卫星照片处理.医学图像处理等领域都有应用.早期的图像拼接主要是运用 ...
- 对于fmri的设计矩阵构造的一个很直观的解释-by 西南大学xulei教授
本程序意在解释这样几个问题:完整版代码在本文的最后. 1.实验的设计如何转换成设计矩阵? 2.设计矩阵的每列表示一个刺激条件,如何确定它们? 3.如何根据设计矩阵和每个体素的信号求得该体素对刺激的敏感 ...
- Introduction to Gaussian Processes
Introduction to Gaussian Processes Gaussian processes (GP) are a cornerstone of modern machine learn ...
- The Model Complexity Myth
The Model Complexity Myth (or, Yes You Can Fit Models With More Parameters Than Data Points) An oft- ...
- SparkMLlib-----GMM算法
Gaussian Mixture Model(GMM)是一个很流行的聚类算法.它与K-Means的很像,但是K-Means的计算结果是算出每个数据点所属的簇,而GMM是计算出这些数据点分配到各个类别的 ...
- Machine-learning of Andrew Ng(Stanford University)
1.基础概念 机器学习是一门研究在非特定编程条件下让计算机采取行动的学科.最近二十年,机器学习为我们带来了自动驾驶汽车.实用的语音识别.高效的网络搜索,让我们对人类基因的解读能力大大提高.当今机器学习 ...
随机推荐
- SpringSecurity 登录 - 以及Md5加密
我们现在开放一个链接给其他系统,来访问我们的系统 http://localhost:8080/hulk-teller-web/haihui!init.jspa?loginId=teller01& ...
- 编译安装Nginx到Linux
之前安装的H2O不知道为啥,总是崩溃,换Nginx了下载包:http://nginx.org/download/ 配置:./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx -- ...
- 框架基础:ajax设计方案(六)--- 全局配置、请求格式拓展和优化、请求二进制类型、浏览器错误搜集以及npm打包发布
距离上一次博客大概好多好多时间了,感觉再不搞点东西出来,感觉就废了的感觉.这段时间回老家学习驾照,修养,然后7月底来上海求职(面了4家,拿了3家office),然后入职同程旅游,项目赶进度等等一系列的 ...
- python基础之七种运算符
废话不多说,上节说的是数据类型,本篇讲讲数据运算. 在算式"1+2"中,"1"和"2"被称为操作数,"+"被称为运算符 ...
- [js高手之路] html5 canvas系列教程 - 文本样式(strokeText,fillText,measureText,textAlign,textBaseline)
接着上文线条样式[js高手之路] html5 canvas系列教程 - 线条样式(lineWidth,lineCap,lineJoin,setLineDash)继续. canvas提供两种输出文本的方 ...
- E. Exposition
E. Exposition time limit per tes ...
- UWP brush
---some words---- 1.Alpha:透明度 2.Argb :Alpha red green blue 3.brush: [brʌʃ] 刷子,笔画,笔刷 4.fore 前头 5.F ...
- 简单Elixir游戏服设计-玩家进程注册
上回说用Registry 做本地注册(跨服可以用syn,只是稍微麻烦点,需要模拟global注册机制,写个封装模块). 修改game_server 项目的mix.exs, 增加应用启动 def app ...
- 运行Vue在ASP.NET Core应用程序并部署在IIS上
前言 项目一直用的ASP.NET Core,但是呢我对ASP.NET Core一些原理也还未开始研究,仅限于会用,不过园子中已有大量文章存在,借着有点空余时间,我们来讲讲如何利用ASP.NET Cor ...
- Angular - 预加载 Angular 模块
Angular - 预加载延迟模块 在使用路由延迟加载中,我们介绍了如何使用模块来拆分应用,在访问到这个模块的时候, Angular 加载这个模块.但这需要一点时间.在用户第一次点击的时候,会有一点延 ...
