.28-浅析webpack源码之compiler.resolvers
原本该在过WebpackOptionsApply时讲解这个方法的,但是当时一不小心过掉了,所以在这里补上。
compiler.resolvers
该对象的三个方法均在WebpackOptionsApply中生成,代码如下:
compiler.resolvers.normal = ResolverFactory.createResolver(Object.assign({
fileSystem: compiler.inputFileSystem
}, options.resolve));
compiler.resolvers.context = ResolverFactory.createResolver(Object.assign({
fileSystem: compiler.inputFileSystem,
resolveToContext: true
}, options.resolve));
compiler.resolvers.loader = ResolverFactory.createResolver(Object.assign({
fileSystem: compiler.inputFileSystem
}, options.resolveLoader));
由于调用的是一个工厂函数,所以用normal作为示例讲解。
/*
"resolve": {
"unsafeCache": true,
"modules": ["node_modules"],
"extensions": [".js", ".json"],
"mainFiles": ["index"],
"aliasFields": ["browser"],
"mainFields": ["browser", "module", "main"],
"cacheWithContext": false
},
*/
compiler.resolvers.normal = ResolverFactory.createResolver(Object.assign({
fileSystem: compiler.inputFileSystem
}, options.resolve));
其中参数中的resolve取了默认值,如注释所示。
ResolveFactory.createResolver
这个方法比较有意思,一块一块的来看源码,所有注释保留英文原文更好理解:
exports.createResolver = function(options) {
//// OPTIONS ////
// A list of directories to resolve modules from, can be absolute path or folder name
// 模块文件夹的目录或者文件夹名称
var modules = options.modules || ["node_modules"];
// A list of description files to read from
// 描述配置文件名
var descriptionFiles = options.descriptionFiles || ["package.json"];
// A list of additional resolve plugins which should be applied
// The slice is there to create a copy, because otherwise pushing into plugins
// changes the original options.plugins array, causing duplicate plugins
// 额外的插件
var plugins = (options.plugins && options.plugins.slice()) || [];
// A list of main fields in description files
// 不知道干啥的
var mainFields = options.mainFields || ["main"];
// A list of alias fields in description files
// 不知道干啥的
var aliasFields = options.aliasFields || [];
// A list of main files in directories
// 模块主入口文件名
var mainFiles = options.mainFiles || ["index"];
// A list of extensions which should be tried for files
// 默认的文件扩展名
var extensions = options.extensions || [".js", ".json", ".node"];
// Enforce that a extension from extensions must be used
var enforceExtension = options.enforceExtension || false;
// A list of module extensions which should be tried for modules
var moduleExtensions = options.moduleExtensions || [];
// Enforce that a extension from moduleExtensions must be used
var enforceModuleExtension = options.enforceModuleExtension || false;
// A list of module alias configurations or an object which maps key to value
// 别名
var alias = options.alias || [];
// ...还有一些其他奇奇怪怪的属性
//// options processing ////
// ...第二部分
};
这一步是包装参数,主要看注释,基本上对resolve参数下的各个key都做了解释,有一些实在不知道干啥用的就省略了。
基本上可能会自定义的大概只有extensions、alias两个属性。
下面来看第二部分:
exports.createResolver = function(options) {
//// OPTIONS ////
// ...第一部分
//// options processing ////
if (!resolver) {
// useSyncFileSystemCalls默认为undefined
resolver = new Resolver(useSyncFileSystemCalls ? new SyncAsyncFileSystemDecorator(fileSystem) : fileSystem);
}
// 数组包装
extensions = [].concat(extensions);
moduleExtensions = [].concat(moduleExtensions);
// 返回[['node_modules']]
modules = mergeFilteredToArray([].concat(modules), function(item) {
return !isAbsolutePath(item);
});
// 不懂这个参数干啥的
// 返回一个对象数组
mainFields = mainFields.map(function(item) {
if (typeof item === "string") {
item = {
name: item,
forceRelative: true
};
}
return item;
});
// 处理别名
if (typeof alias === "object" && !Array.isArray(alias)) { /**/ }
// 不知道什么东西
if (unsafeCache && typeof unsafeCache !== "object") {
unsafeCache = {};
}
//// pipeline ////
// ...第三部分
};
这一部分是处理参数,resolver是最后返回的对象,到调用的时候再细看。
几个参数由于不太懂什么作用,处理方法也很简单,就不做解释,这里看一下alias别名的处理:
/*
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'@': '../src'
}
*/
/*
alias:[
{
name: 'vue',
onlyModule: true,
alias: 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js'
},
{
name: '@',
onlyModule: false,
alias: '../src'
}
]
*/
if (typeof alias === "object" && !Array.isArray(alias)) {
alias = Object.keys(alias).map(function(key) {
var onlyModule = false;
var obj = alias[key];
// 测试是否以$结尾
if (/\$$/.test(key)) {
onlyModule = true;
key = key.substr(0, key.length - 1);
}
// alias的值是否为字符串
if (typeof obj === "string") {
obj = {
alias: obj
};
}
obj = Object.assign({
name: key,
onlyModule: onlyModule
}, obj);
return obj;
});
}
这里以vue-cli为例,展示了转换后的alias,看注释就OK了。
第三部分有点恶心,源码大概是这样子的:
exports.createResolver = function(options) {
//// OPTIONS ////
// ...第一部分
//// options processing ////
// ...第二部分
//// pipeline ////
// resolve
if (unsafeCache) {
plugins.push(new UnsafeCachePlugin("resolve", cachePredicate, unsafeCache, cacheWithContext, "new-resolve"));
plugins.push(new ParsePlugin("new-resolve", "parsed-resolve"));
} else {
plugins.push(new ParsePlugin("resolve", "parsed-resolve"));
}
// ...无穷多的if + plugins.push(...)
//// RESOLVER ////
plugins.forEach(function(plugin) {
resolver.apply(plugin);
});
return resolver;
};
虽然有非常多的plugin,但是内部处理形式大同小异。所以就一个常用参数作为例子,比如说:
// described-resolve
alias.forEach(function(item) {
plugins.push(new AliasPlugin("described-resolve", item, "resolve"));
});
简要的看一下内部,这里的alias就是上面转换后的对象数组。
class AliasPlugin {
constructor(source, options, target) {
this.source = source;
this.name = options.name;
this.alias = options.alias;
this.onlyModule = options.onlyModule;
this.target = target;
}
apply(resolver) {
var target = this.target;
var name = this.name;
var alias = this.alias;
var onlyModule = this.onlyModule;
resolver.plugin(this.source, function(request, callback) { /**/ });
}
}
第三部分所有的plugins都是这样的形式。
1、构造函数仅仅获取并初始化值
2、有一个apply方法,接受一个resolver参数
3、注入参数source的事件流
4、在source事件流最后,target参数会在resolver.doResolve方法中被调用,这里省略了代码
在函数的最后,可以看到有一个这样的调用:
plugins.forEach(function(plugin) {
resolver.apply(plugin);
});
这里就是依次执行所有plugin的apply方法,传入resolver作为参数。
所有的插件plugin流程以示意图的形式给出,这里就不一一分析了。
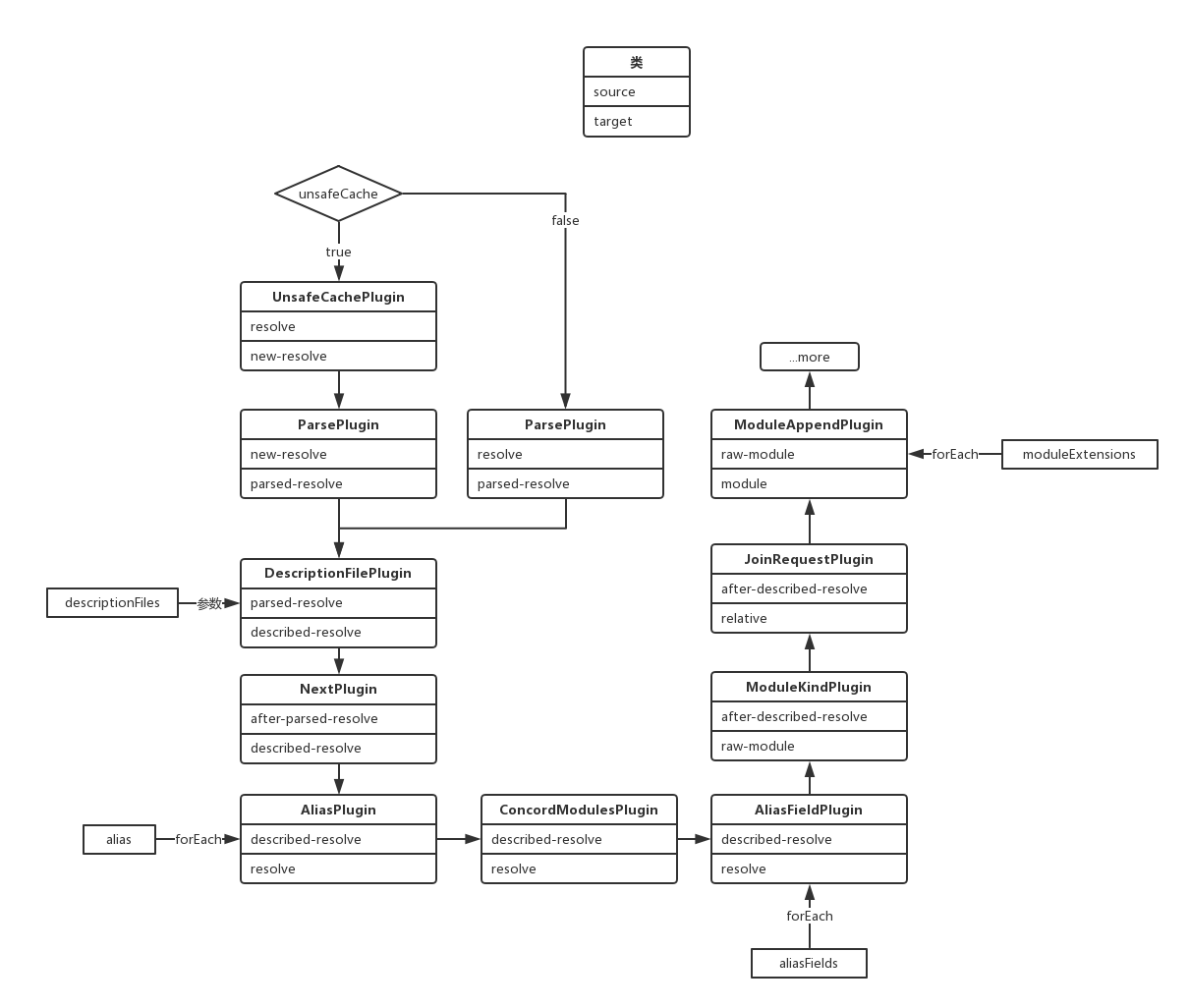
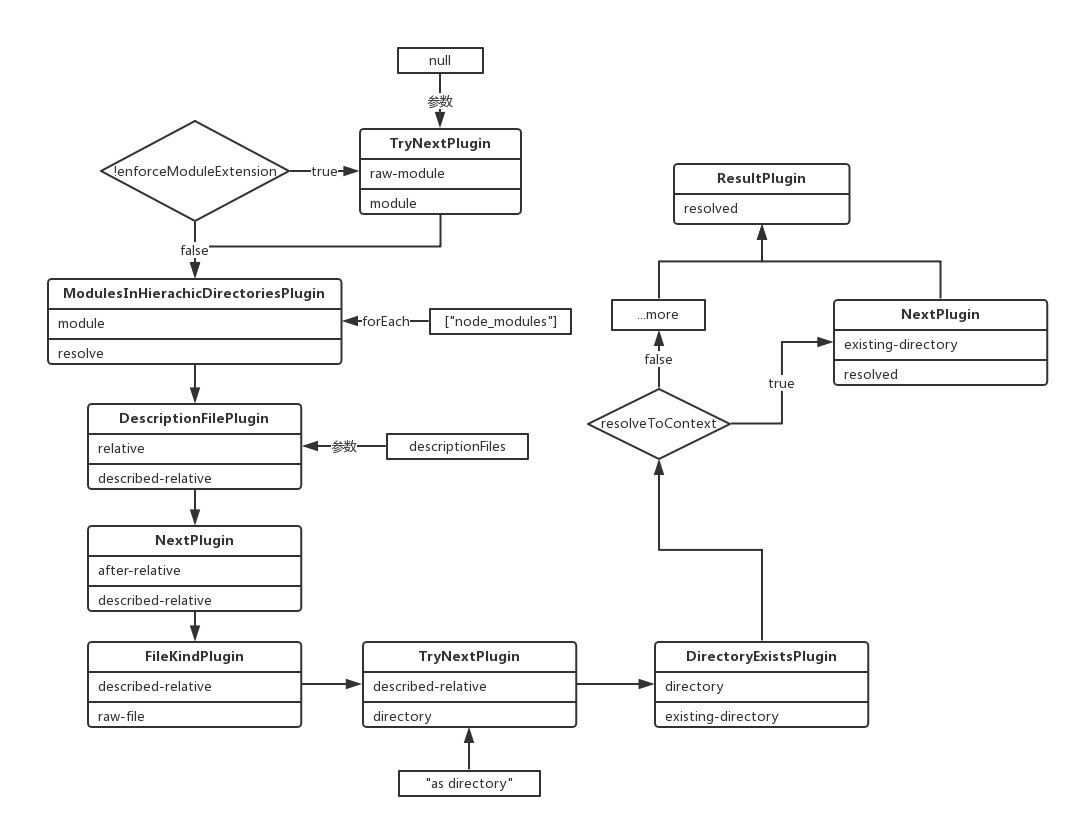

注入完所有的事件流后,返回这个resolver对象,也就是compiler.resolvers.normal(loader、context)。
.28-浅析webpack源码之compiler.resolvers的更多相关文章
- .30-浅析webpack源码之doResolve事件流(1)
这里所有的插件都对应着一个小功能,画个图整理下目前流程: 上节是从ParsePlugin中出来,对'./input.js'入口文件的路径做了处理,返回如下: ParsePlugin.prototype ...
- .34-浅析webpack源码之事件流make(3)
新年好呀~过个年光打游戏,function都写不顺溜了. 上一节的代码到这里了: // NormalModuleFactory的resolver事件流 this.plugin("resolv ...
- .30-浅析webpack源码之doResolve事件流(2)
这里所有的插件都对应着一个小功能,画个图整理下目前流程: 上节是从ParsePlugin中出来,对'./input.js'入口文件的路径做了处理,返回如下: ParsePlugin.prototype ...
- .3-浅析webpack源码之预编译总览
写在前面: 本来一开始想沿用之前vue源码的标题:webpack源码之***,但是这个工具比较巨大,所以为防止有人觉得我装逼跑来喷我(或者随时鸽),加上浅析二字,以示怂. 既然是浅析,那么案例就不必太 ...
- .17-浅析webpack源码之compile流程-入口函数run
本节流程如图: 现在正式进入打包流程,起步方法为run: Compiler.prototype.run = (callback) => { const startTime = Date.now( ...
- 从Webpack源码探究打包流程,萌新也能看懂~
简介 上一篇讲述了如何理解tapable这个钩子机制,因为这个是webpack程序的灵魂.虽然钩子机制很灵活,而然却变成了我们读懂webpack道路上的阻碍.每当webpack运行起来的时候,我的心态 ...
- 浅析libuv源码-node事件轮询解析(3)
好像博客有观众,那每一篇都画个图吧! 本节简图如下. 上一篇其实啥也没讲,不过node本身就是这么复杂,走流程就要走全套.就像曾经看webpack源码,读了300行代码最后就为了取package.js ...
- webpack源码-依赖收集
webpack源码-依赖收集 version:3.12.0 程序主要流程: 触发make钩子 Compilation.js 执行EntryOptionPlugin 中注册的make钩子 执行compi ...
- .20-浅析webpack源码之compile流程-Template模块
这里的编译前指的是开始触发主要的事件流this-compilaiton.compilation之前,由于还有一些准备代码,这一节全部弄出来. 模块基本上只走构造函数,具体的方法调用的时候再具体讲解. ...
随机推荐
- linux系统日常管理复习题讲解
1. 如何看当前Linux系统有几颗物理CPU和每颗CPU的核数? 2. 查看系统负载有两个常用的命令,是哪两个?这三个数值表示什么含义呢? 3. vmstat r, b, si, so, bi, b ...
- Spring Dynamic DataSource Routing
Use AbstractRoutingDataSource to dynamicly switch datasources, see http://spring.io/blog/2007/01/23/ ...
- 配置linux下apache跨域问题
1.apache设置允许远程访问 打开FTP,登录服务器,找到etc文件夹下的httpd.conf文件,然后下载到本地 打开本地httpd.conf文件夹,找到对应的端口ip地址,修改如下 <V ...
- MHA高可用架构与Atlas读写分离
1.1 MHA简介 1.1.1 MHA软件介绍 MHA(Master High Availability)目前在MySQL高可用方面是一个相对成熟的解决方案,它由日本DeNA公司youshimaton ...
- .net 框架
目录 API 应用框架(Application Frameworks) 应用模板(Application Templates) 人工智能(Artificial Intelligence) 程序集处理( ...
- Java---hashCode()和equals()
1.hashCode()和equals() API hashCode()和equals()都来自上帝类Object, 所有的类都会拥有这两个方法,特定时,复写它们. 它们是用来在同一类中做比较用的,尤 ...
- Head First设计模式之工厂模式
一.定义 定义了一个创建对象的接口, 但由子类决定要实例化的类是哪一个. 工厂方法让类把实例化推迟到子类 二.结构 1.抽象工厂角色:这是工厂方法模式的核心,它与应用程序无关.是具体工厂角色必须实现的 ...
- Shell脚本实现文件遍历和删除操作
本文需要实现的功能如下:某文件夹下具有由按数字编号命名的文件夹,需要删除除最大编码外的文件. 具体实现 大致思路:循环遍历该文件夹下所有文件,正则匹配出最大编码文件:然后循环文件,删除除最大编码外的文 ...
- 理解css伪类和伪元素
伪类就是可以通过直接添加一个类样式达到同等效果,而伪元素,则需要先添加一个元素,然后在元素上添加样式才能达到同等效果 伪类 :active 向被激活的元素添加样式. :focus 向拥有键盘输入焦点的 ...
- Mongodb集群【三】
Mongodb常用三种集群 1 主从(Master/Slave) 不推荐,但是mongodb依然保留有.一主多从,不支持链式结构.简单主从,没有裁仲者不能自动恢复. 2 副本集(Relica Set) ...
