Learning Cocos2d-x for WP8(8)——动作Action
原文:Learning Cocos2d-x for WP8(8)——动作Action
游戏很大程度上是由动作画面支撑起来的。
动作分为两大类:瞬间动作和延时动作。
瞬间动作基本等同于设置节点的属性,延时动作会执行一段时间,不需要清除这两种动作,一旦动作完成,就会从节点上清除并释放所占内存。
封装CCSpriteBatchNode的使用方法
CCSprite* SpriteActionLayer::BatchAnimatitonSprite(CCLayer* pLayer,CCSprite *pSprite, CCPoint* spriteStartPoint, const char *strFramesFileName,const char *strFramesFileNameImg,const char *strFirstFrameName,const char *strEachFrameName,int frameCount,float frameDelay)
{
//CCSpriteBatchNode
//创建批处理节点,读取plist文件
CCSpriteFrameCache* cache=CCSpriteFrameCache::sharedSpriteFrameCache();
cache->addSpriteFramesWithFile(strFramesFileName,strFramesFileNameImg); //起始精灵
pSprite=CCSprite::spriteWithSpriteFrameName(strFirstFrameName);//纹理plist中包含strfirstFrameName
pSprite->setPosition(ccp(spriteStartPoint->x,spriteStartPoint->y)); CCSpriteBatchNode* spritebatch = CCSpriteBatchNode::batchNodeWithFile(strFramesFileNameImg);//与CCSpriteFrameCache同一纹理
spritebatch->addChild(pSprite);
pLayer->addChild(spritebatch,); //创建逐帧数组
CCMutableArray<CCSpriteFrame*>* animFrames1=new CCMutableArray<CCSpriteFrame*>(frameCount);
char str1[]={};
for(int i=;i<frameCount;i++)
{
sprintf(str1,strEachFrameName,i);
CCSpriteFrame* pFrame=cache->spriteFrameByName( str1 );
animFrames1->addObject(pFrame);
} CCAnimation* animation1=CCAnimation::animationWithFrames(animFrames1,frameDelay);
pSprite->runAction(CCRepeatForever::actionWithAction(CCAnimate::actionWithAnimation(animation1,false))); animFrames1->release();
return pSprite;
}
重复动作
可以使一个动作或一系列的动作不停地重复无限循环,除非“外力”使其停止。
实例
//重复动作
CCSprite *role0=CCSprite::spriteWithFile("Sprite/Role.png");
role0->setPosition(ccp(,s.height-));
addChild(role0,);
CCRotateBy* role0RotateBy=CCRotateBy::actionWithDuration(2.0f,);
CCRepeatForever* role0Repeat=CCRepeatForever::actionWithAction(role0RotateBy);
role0->runAction(role0Repeat);
Sprite循环不停地旋转

流畅动画
CCEaseAction类能在一段时间内动作的流畅执行,使得更强大。而非简单地执行简单动画效果。
在实际运动过程中,匀速运动在启动和结束时往往会有一定的加速和减速的效果,这样更加的真实。
cocoos2d-x引擎提供了相关的API,免除了我们编写相关的算法实现的烦恼,实现起来相当的方便。
实现该方法的是CCActionEase中CCEaseRateAction系列,大体分成三类:
In:开始时候的加速度
Out:结束时候的加速度
InOut:开始结束时候的加速度
(以下图片来源其他博文,具体地址忘记了,以后再加上)
1.指数缓冲

EaseExponentialIn
EaseExponentialOut
EaseExponentialInOut
2.赛因缓冲

EaseSineIn
EaseSineOut
EaseSineInOut
3.弹性缓冲
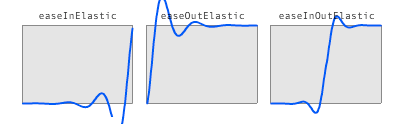
EaseElasticIn
EaseElasticOut
EaseElasticInOut
4.跳跃缓冲

EaseBounceIn
EaseBounceOut
EaseBounceInOut
5.回震缓冲

EaseBackIn
EaseBackOut
EaseBackInOut
实例
//流畅动画
CCSprite* role1=NULL;
role1=SpriteActionLayer::BatchAnimatitonSprite(this,role1,new CCPoint(,s.height/),"Sprite/Plist/RoleRun.plist","Sprite/Plist/RoleRun.png","RoleRun0.png","RoleRun%d.png",,0.2f);
CCMoveTo* role1Move=CCMoveTo::actionWithDuration(,CCPointMake(s.width-,s.height/));//CCMoveTo绝对位置移动
CCEaseInOut* role1MoveEase=CCEaseInOut::actionWithAction(role1Move,);//rate=4,决定流畅动画的明显程度,只有当它大于1时才能看到效果
role1->runAction(role1MoveEase);
可见,Sprite开始缓慢移动——加速——缓慢停止。

动作序列
通常情况下,Action动作执行添加多个动作时,它们会在同一时间运行,如上面的动作。但有时我们需要让动作一个接着一个运行。CCSequence将实现该功能。
实例
//动作序列
CCSprite* role2=NULL;
role2=SpriteActionLayer::BatchAnimatitonSprite(this,role2,new CCPoint(,s.height/),"Sprite/Plist/Role2Run.plist","Sprite/Plist/Role2Run.png","Role2Run0.png","Role2Run%d.png",,0.3f);
CCMoveBy* role2MoveBy=CCMoveBy::actionWithDuration(,CCPointMake(,));//CCMoveBy相对位置移动
CCJumpBy* role2JumpBy=CCJumpBy::actionWithDuration(,CCPointMake(-,),,);//CCJumpBy相当位置jump
role2->runAction(CCSequence::actions(role2MoveBy,role2JumpBy,NULL));
Sprite跑动到指定位置后,下个动作就是弹跳回起始位置


瞬间动作
有时在一串动作中,需要改变Sprite的属性,然后在继续执行下个动作。瞬间动作将实现该功能,通常情况下依赖与CCCallFunc动作。
实例
//瞬时动作
CCSprite* role3=CCSprite::spriteWithFile("Sprite/Role.png");
role3->setPosition(ccp(s.width-,s.height-));
addChild(role3,);
CCScaleTo * role3ScaleTo=CCScaleTo::actionWithDuration(,2.0f);
CCCallFuncN* role3FunN=CCCallFuncN::actionWithTarget(this,callfuncN_selector(SpriteActionLayer::repeatForever));
role3->runAction(CCSequence::actions(role3ScaleTo,role3FunN,NULL));
repeatForever方法
void SpriteActionLayer::repeatForever(CCNode* pSender)
{
CCRepeatForever* repeat=CCRepeatForever::actionWithAction(CCSkewBy::actionWithDuration(, 37.2f, -37.2f));//歪斜
pSender->runAction(repeat);
}
执行完ScaleTo后执行SkewBy

完整源码
#ifndef _SPRITE_ACTION_TEST_
#define _SPRITE_ACTION_TEST_ #include "cocos2d.h"
using namespace cocos2d; class SpriteActionScene:public CCScene
{
public:
SpriteActionScene();
~SpriteActionScene(); virtual void onEnter(); }; class SpriteActionLayer:public CCLayer
{
public:
SpriteActionLayer();
~SpriteActionLayer(); public:
void repeatForever(CCNode* pTarget);
CCSprite* BatchAnimatitonSprite(CCLayer* pLayer,CCSprite *pSprite,CCPoint* spriteStartPoint,const char *strFramesFileName,const char *strFramesFileNameImg,const char *strFirstFrameName,const char *strEachFrameName,int frameCount,float frameDelay);
}; #endif
#include "pch.h"
#include "Classes\SpriteActionTest.h" //----------------------------------------
//
//SpriteActionLayer
//
//----------------------------------------
SpriteActionLayer::SpriteActionLayer()
{
CCSize s=CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getWinSize(); //重复动作
CCSprite *role0=CCSprite::spriteWithFile("Sprite/Role.png");
role0->setPosition(ccp(,s.height-));
addChild(role0,);
CCRotateBy* role0RotateBy=CCRotateBy::actionWithDuration(2.0f,);
CCRepeatForever* role0Repeat=CCRepeatForever::actionWithAction(role0RotateBy);
role0->runAction(role0Repeat); //流畅动画
CCSprite* role1=NULL;
role1=SpriteActionLayer::BatchAnimatitonSprite(this,role1,new CCPoint(,s.height/),"Sprite/Plist/RoleRun.plist","Sprite/Plist/RoleRun.png","RoleRun0.png","RoleRun%d.png",,0.2f);
CCMoveTo* role1Move=CCMoveTo::actionWithDuration(,CCPointMake(s.width-,s.height/));//CCMoveTo绝对位置移动
CCEaseInOut* role1MoveEase=CCEaseInOut::actionWithAction(role1Move,);//rate=4,决定流畅动画的明显程度,只有当它大于1时才能看到效果
role1->runAction(role1MoveEase); //动作序列
CCSprite* role2=NULL;
role2=SpriteActionLayer::BatchAnimatitonSprite(this,role2,new CCPoint(,s.height/),"Sprite/Plist/Role2Run.plist","Sprite/Plist/Role2Run.png","Role2Run0.png","Role2Run%d.png",,0.3f);
CCMoveBy* role2MoveBy=CCMoveBy::actionWithDuration(,CCPointMake(,));//CCMoveBy相对位置移动
CCJumpBy* role2JumpBy=CCJumpBy::actionWithDuration(,CCPointMake(-,),,);//CCJumpBy相当位置jump
role2->runAction(CCSequence::actions(role2MoveBy,role2JumpBy,NULL)); //瞬时动作
CCSprite* role3=CCSprite::spriteWithFile("Sprite/Role.png");
role3->setPosition(ccp(s.width-,s.height-));
addChild(role3,);
CCScaleTo * role3ScaleTo=CCScaleTo::actionWithDuration(,2.0f);
CCCallFuncN* role3FunN=CCCallFuncN::actionWithTarget(this,callfuncN_selector(SpriteActionLayer::repeatForever));
role3->runAction(CCSequence::actions(role3ScaleTo,role3FunN,NULL));
} void SpriteActionLayer::repeatForever(CCNode* pSender)
{
CCRepeatForever* repeat=CCRepeatForever::actionWithAction(CCSkewBy::actionWithDuration(, 37.2f, -37.2f));//歪斜
pSender->runAction(repeat);
} SpriteActionLayer::~SpriteActionLayer()
{} CCSprite* SpriteActionLayer::BatchAnimatitonSprite(CCLayer* pLayer,CCSprite *pSprite, CCPoint* spriteStartPoint, const char *strFramesFileName,const char *strFramesFileNameImg,const char *strFirstFrameName,const char *strEachFrameName,int frameCount,float frameDelay)
{
//CCSpriteBatchNode
//创建批处理节点,读取plist文件
CCSpriteFrameCache* cache=CCSpriteFrameCache::sharedSpriteFrameCache();
cache->addSpriteFramesWithFile(strFramesFileName,strFramesFileNameImg); //起始精灵
pSprite=CCSprite::spriteWithSpriteFrameName(strFirstFrameName);//纹理plist中包含strfirstFrameName
pSprite->setPosition(ccp(spriteStartPoint->x,spriteStartPoint->y)); CCSpriteBatchNode* spritebatch = CCSpriteBatchNode::batchNodeWithFile(strFramesFileNameImg);//与CCSpriteFrameCache同一纹理
spritebatch->addChild(pSprite);
pLayer->addChild(spritebatch,); //创建逐帧数组
CCMutableArray<CCSpriteFrame*>* animFrames1=new CCMutableArray<CCSpriteFrame*>(frameCount);
char str1[]={};
for(int i=;i<frameCount;i++)
{
sprintf(str1,strEachFrameName,i);
CCSpriteFrame* pFrame=cache->spriteFrameByName( str1 );
animFrames1->addObject(pFrame);
} CCAnimation* animation1=CCAnimation::animationWithFrames(animFrames1,frameDelay);
pSprite->runAction(CCRepeatForever::actionWithAction(CCAnimate::actionWithAnimation(animation1,false))); animFrames1->release();
return pSprite;
} //----------------------------------------
//
//SpriteActionScene
//
//---------------------------------------- SpriteActionScene::SpriteActionScene()
{} SpriteActionScene::~SpriteActionScene()
{} void SpriteActionScene::onEnter()
{
CCScene::onEnter();
CCLayer* spriteActionLayer=new SpriteActionLayer();
addChild(spriteActionLayer);
spriteActionLayer->release();
}

著作权声明:本文由http://www.cnblogs.com/suguoqiang 原创,欢迎转载分享。请尊重作者劳动,转载时保留该声明和作者博客链接,谢谢!
Learning Cocos2d-x for WP8(8)——动作Action的更多相关文章
- Java基础之处理事件——使用动作Action(Sketcher 6 using Action objects)
控制台程序. 动作Action是任何实现了javax.swing.Action接口的类的对象.这个接口声明了操作Action对象的方法,例如,存储与动作相关的属性.启用和禁用动作.Action接口扩展 ...
- 08 Zabbix4.0系统配置事件通知 - 动作Action
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 08 Zabbix4.0系统配置事件通知 - 动作Action 请点击查看Zabbix3.0.8版 ...
- [Cocos2d-x For WP8]ActionManager动作管理
在Cocos2d-x里面可以通过CCActionManger类来管理动作的暂停和恢复,CCActionMessage是管理所有Action的单例,一般情况下并不直接使用这个单例,而是使用CCNode的 ...
- 动作Action
/** * DelayTime延迟 * @param d Duration 延迟时间 */ auto delayTime = DelayTime::create(); sprite->runAc ...
- 创建一个动作-Action类:
让我们创建一个Java文件HelloWorldAction.java的Java资源> SRC下一个的包名com.yiibai.struts2与下面的内容. package com.yiibai. ...
- libgdx学习记录6——动作Action
libgdx中的Action类能够有效的帮助我们实现位移.旋转.缩放.淡入淡出等效果,对游戏的设计很有用. Action是一个抽象类,本身不可以实例化.一般使用的它的继承类,常用的有 MoveToAc ...
- Asp.Net MVC学习总结(二)——控制器与动作(Controller And Action)
一.理解控制器 1.1.什么是控制器 控制器是包含必要的处理请求的.NET类,控制器的角色封装了应用程序逻辑,控制器主要是负责处理请求,实行对模型的操作,选择视图呈现给用户. 简单理解:实现了ICon ...
- Struts2 In Action笔记_页面到动作的数据流入和流出
因为回答百度知道的一个问题,仔细查看了<Struts2 In Action>,深入细致的看了 “数据转移OGNL 和 构建视图-标签”,很多东西才恍然大悟. 一直觉得国外写的书很浮,不具有 ...
- 行为识别(action recognition)相关资料
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/kezunhai/article/details/50176209 ================华丽分割线=================这部分来 ...
随机推荐
- mysql存储过程及经常使用函数
一.函数 1.数学函数 CEIL()进一取整 SELECT CEIL(1.2);2 FLOOR()舍一取整 SELECT FLOOR(1.9);9 MOD取余数(取模) SELECT MOD(3,8) ...
- shell基础(转)
shell基础1:文件安全与权限 http://bbs.chinaunix.net/forum/viewtopic.php?t=434579&highlight=wingger 附:Linux ...
- 7个基于Linux命令行的文件下载和网站浏览工具
7个基于Linux命令行的文件下载和网站浏览工具 时间:2015-06-01 09:36来源:linux.cn 编辑:linux.cn 点击: 2282 次 Linux命令行是GNU/Linux中最神 ...
- iText 文本
iText中用文本块(Chunk).短语(Phrase)和段落(paragraph)处理文本. 文本块(Chunk)是处理文本的最小单位,有一串带格式(包括字体.颜色.大小)的字符串组成.如以下代码就 ...
- linux下C/C++,多线程pthread《转载》
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xianghang123/archive/2011/08/11/2134927.html ·线程创建 函数原型:int pthread_cr ...
- java中文排序问题(转)
在Java中,对一个数组或列表(在本文中统称为集合)中的元素排序,是一个很经常的事情.好在Sun公司在Java库中实现了大部分功能.如果集合中的元素实现了Comparable接口,调用以下的静态(st ...
- hdu1569find the safest road(floyd变形求最大安全值)
find the safest road Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Ot ...
- JAVA的反射机制学习笔记(二)
上次写JAVA的反射机制学习笔记(一)的时候,还是7月22号,这些天就瞎忙活了.自己的步伐全然被打乱了~不能继续被动下去.得又一次找到自己的节奏. 4.获取类的Constructor 通过反射机制得到 ...
- OpenCV五学习: 如何使用命令来启动或关闭OpenCV的CPU指令系统CV_SSE2,CV_SSSE4和其他优化
在这个博客.我想分享一下OpenCV源代码CPU指令系统CV_SSE2和其他相关知识 一个. CV_SSE系列指令集的预编译符号定义在opencv2/core/internal.hpp这个头文件 ...
- XML SelectSingleNode的使用 根据节点属性获取该节点
unit Unit1; interface uses Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Form ...
