【POJ2699】The Maximum Number of Strong Kings(网络流)
Description
A tournament can be represented by a complete graph in which each vertex denotes a player and a directed edge is from vertex x to vertex y if player x beats player y. For a player x in a tournament T, the score of x is the number of players beaten by x. The score sequence of T, denoted by S(T) = (s1, s2, . . . , sn), is a non-decreasing list of the scores of all the players in T. It can be proved that S(T) = (s1, s2, . . . , sn) is a score sequence of T if and only if
for k = 1, 2, . . . , n and equality holds when k = n. A player x in a tournament is a strong king if and only if x beats all of the players whose scores are greater than the score of x. For a score sequence S, we say that a tournament T realizes S if S(T) = S. In particular, T is a heavy tournament realizing S if T has the maximum number of strong kings among all tournaments realizing S. For example, see T2 in Figure 1. Player a is a strong king since the score of player a is the largest score in the tournament. Player b is also a strong king since player b beats player a who is the only player having a score larger than player b. However, players c, d and e are not strong kings since they do not beat all of the players having larger scores.
The purpose of this problem is to find the maximum number of strong kings in a heavy tournament after a score sequence is given. For example,Figure 1 depicts two possible tournaments on five players with the same score sequence (1, 2, 2, 2, 3). We can see that there are at most two strong kings in any tournament with the score sequence (1, 2, 2, 2, 3) since the player with score 3 can be beaten by only one other player. We can also see that T2 contains two strong kings a and b. Thus, T2 is one of heavy tournaments. However, T1 is not a heavy tournament since there is only one strong king in T1. Therefore, the answer of this example is 2.Input
The first line of the input file contains an integer m, m <= 10, which represents the number of test cases. The following m lines contain m score sequences in which each line contains a score sequence. Note that each score sequence contains at most ten scores.Output
The maximum number of strong kings for each test case line by line.Sample Input
5
1 2 2 2 3
1 1 3 4 4 4 4
3 3 4 4 4 4 5 6 6 6
0 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 6
0 3 3 3 3 3Sample Output
2
4
5
3
5
【分析】
主要是有一个贪心的思想,就是如果有一种情况使其中k个人是能力者的话,那么总有一种情况使分数最高的k个人是能力者。(因为交换一下胜利的场就可以了)。所以可以枚举有k个人是能力者,规定后k个人就是能力者,建立约束图,跑最大流判满流即可。
如下图(证明上面那一个贪心):

假设有一种情况使得有k个能力者,但不是后k个,证明有一种情况是后k个都是能力者。
上图,假设C是能力者但不是后k个,E不是能力者但是后k个。
因为C是能力者E不是,则在E的后面必有一个G(随便是什么),C赢了它,E没有赢他。
因为E的分数大于C,则在C之前必有一个A(随便是什么),C没有赢他,E赢了他。
那么我们交换一下胜负场,C、E分数都不变,然后E离能力者更近一步。
继续交换下去,后k个一定能成为能力者。
证毕。
于是建个图跑最大流。
差不多这样建图:
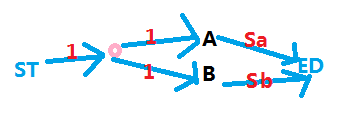
代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define Maxn 1100
#define Maxm 100100
#define INF 0xfffffff char s[];
int a[Maxn],al,lg[Maxn];
int dis[Maxn],first[Maxn]; struct node
{
int x,y,f,o,next;
}t[Maxm];int len; int st,ed,sum,h=; int mymin(int x,int y) {return x<y?x:y;} void ins(int x,int y,int f)
{
if(f==) return;
if(y==ed) sum+=f;
t[++len].x=x;t[len].y=y;t[len].f=f;
t[len].next=first[x];first[x]=len;t[len].o=len+;
t[++len].x=y;t[len].y=x;t[len].f=;
t[len].next=first[y];first[y]=len;t[len].o=len-;
} queue<int > q;
bool bfs()
{
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
memset(dis,-,sizeof(dis));
q.push(st);dis[st]=;
while(!q.empty())
{
int x=q.front();q.pop();
for(int i=first[x];i;i=t[i].next) if(t[i].f>)
{
int y=t[i].y;
if(dis[y]==-)
{
dis[y]=dis[x]+;
q.push(y);
}
}
}
if(dis[ed]==-) return ;
return ;
} int ffind(int x,int flow)
{
if(x==ed) return flow;
int now=;
for(int i=first[x];i;i=t[i].next) if(t[i].f>)
{
int y=t[i].y;
if(dis[y]==dis[x]+)
{
int a=ffind(y,mymin(flow-now,t[i].f));
t[i].f-=a;
t[t[i].o].f+=a;
now+=a;
}
if(now==flow) break;
}
if(now==) dis[x]=-;
return now;
} bool max_flow()
{
int ans=;
while(bfs())
{
ans+=ffind(st,INF);
}
if(ans==sum) return ;
return ;
} bool check(int x)
{
len=;sum=;h=ed;
memset(first,,sizeof(first));
for(int i=al-x+;i<=al;i++)
{
if(a[i]<lg[i]) return ;
ins(i,ed,a[i]-lg[i]);
for(int j=i+;j<=al-lg[i];j++)
{
ins(st,++h,);
ins(h,i,);
ins(h,j,);
}
}
for(int i=;i<=al-x;i++) ins(i,ed,a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=al-x;i++)
for(int j=i+;j<=al;j++)
{
ins(st,++h,);
ins(h,i,);
ins(h,j,);
} if(max_flow()) return ; return ;
} int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);getchar();
while(T--)
{
gets(s);
int l=strlen(s);
int now=;al=;
for(int i=;i<l;i++)
{
if((s[i]<=''||s[i]>='')&&(i>=&&s[i-]>=''&&s[i-]<=''))
{
a[++al]=now;
now=;
}
else if(s[i]>=''&&s[i]<='')now=now*+s[i]-'';
}
if(s[l-]>=''&&s[l-]<='') a[++al]=now;
for(int i=;i<=al;i++)
{
lg[i]=;
for(int j=i+;j<=al;j++) if(a[j]>a[i]) lg[i]++;
}
st=al+;ed=st+;h=ed;
int ans=;
for(int i=al;i>=;i--)
{
if(check(i)) {ans=i;break;}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
[POJ2699]
2016-06-05 10:17:08
【POJ2699】The Maximum Number of Strong Kings(网络流)的更多相关文章
- POJ2699 The Maximum Number of Strong Kings
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 2102 Accepted: 975 Description A tour ...
- POJ2699:The Maximum Number of Strong Kings(枚举+贪心+最大流)
The Maximum Number of Strong Kings Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 2488 ...
- POJ2699 The Maximum Number of Strong Kings(最大流)
枚举所有Strong King的状态(最多1024种左右),然后判断是否合法. 判定合法用网络流,源点-比赛-人-汇点,这样连边. 源点向每场比赛连容量为1的边: 如果一场比赛,A和B,A是Stron ...
- POJ 2699 The Maximum Number of Strong Kings ——网络流
一定存在一种最优方案,使得分数前几个人是SK 所以我们可以二分答案或者枚举,然后就是经典的网络流建模. 另:输入很Excited #include <cstdio> #include &l ...
- POJ 2699 The Maximum Number of Strong Kings Description
The Maximum Number of Strong Kings Description A tournament can be represented by a complete graph ...
- 【POJ2699】The Maximum Number of Strong Kings(二分,最大流)
题意: 有n个队伍,两两都有比赛 知道最后每支队伍获胜的场数 求最多有多少队伍,他们战胜了所有获胜场数比自己多的队伍,这些队伍被称为SK N<=50 思路:把每个队伍和它们两两之间的比赛都当做点 ...
- 【poj2699】 The Maximum Number of Strong Kings
http://poj.org/problem?id=2699 (题目链接) 题意 给出1张有向完全图.U->V表示U可以打败V并得一分.如果一个人的得分最高,或者他打败所有比自己得分高的人,那么 ...
- The Maximum Number of Strong Kings
poj2699:http://poj.org/problem?id=2699 题意:n个人,进行n*(n-1)/2场比赛,赢一场则得到一分.如果一个人打败了所有比他分数高的对手,或者他就是分数最高的, ...
- 【POJ】【2699】The Maximum Number of Strong Kings
网络流/最大流/二分or贪心 题目大意:有n个队伍,两两之间有一场比赛,胜者得分+1,负者得分+0,问最多有几只队伍打败了所有得分比他高的队伍? 可以想到如果存在这样的“strong king”那么一 ...
随机推荐
- Android开发之UI更新交互机制与实例解析
android开发过程中,经常需要更新UI的状态和文案等.这是就需要对UI进行 更新.在android中更新UI一般有三种方法,handler机制.RunOnUiThread方法以及AsyncTask ...
- Android(java)学习笔记175:BroadcastReceiver之 外拨电话的广播接收者
首先我们示例工程一览表如下: 1.首先我们还是买一个收音机,定义一个OutCallReceiver继承自BroadcastReceiver,onReceive()方法中定义了监听到广播,要执行的操作: ...
- JavaScript与html5写的贪吃蛇完整代码
JavaScript与html5写的贪吃蛇完整代码 查看运行效果可访问http://www.codesocang.com/texiao/youxitexiao/2014/0402/7045.html# ...
- dubbo注册服务IP解析异常及IP解析源码分析
在使用dubbo注册服务时会遇到IP解析错误导致无法正常访问. 比如: 本机设置的IP为172.16.11.111, 但实际解析出来的是180.20.174.11 这样就导致这个Service永远也无 ...
- 当append里面的标签显示不出来的时候,用下面的方式做
$("#result_td").append(tem1+tem3) $("#result_td").append($(tem1+tem3))
- 解决Visual Studio 找不到报表控件、rdlc中文乱码
找回报表控件 运行安装程序中的 ..\packages\Reporting Services\RVAddon.msi 工具栏,右键选择ReportViewer,注意选择的版本 如果不能编辑报表文件(. ...
- Object-C Init
上一篇为Object-C类实现 我们可以创建一个init方法用来给我们的实例变量设置初始化值: - (id)init { if(self = [super init]) { [self setCapt ...
- jQuery 尺寸
通过 jQuery,很容易处理元素和浏览器窗口的尺寸. jQuery 尺寸 方法 jQuery 提供多个处理尺寸的重要方法: width() height() innerWidth() innerHe ...
- C++primer(第五版)读书笔记&习题解答---CHAPTER 3
C++标准库类型包括:string,vector和迭代器,其中string是可变长的字符序列,vector存放的是某种给定类型对象的可变长序列,迭代器是string和vector的配套类型,常被用于访 ...
- 为SQL Server表中的列添加/修改/删除注释属性(sp_addextendedproperty、sp_updateextendedproperty、sp_dropextendedproperty)
本篇基本完全参考:sql--sp_addextendedproperty和sp_updateextendedproperty (Transact-SQL) 三个存储过程用法一样,以sp_addexte ...
