机器学习作业(四)神经网络参数的拟合——Matlab实现
题目下载【传送门】
题目简述:识别图片中的数字,训练该模型,求参数θ。
第1步:读取数据文件:
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25; % 25 hidden units
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10) % Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n') load('ex4data1.mat');
m = size(X, 1); % Randomly select 100 data points to display
sel = randperm(size(X, 1));
sel = sel(1:100); displayData(X(sel, :)); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; fprintf('\nLoading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...\n') % Load the weights into variables Theta1 and Theta2
load('ex4weights.mat'); % Unroll parameters
nn_params = [Theta1(:) ; Theta2(:)];
第2步:初始化参数:
initial_Theta1 = randInitializeWeights(input_layer_size, hidden_layer_size);
initial_Theta2 = randInitializeWeights(hidden_layer_size, num_labels); % Unroll parameters
initial_nn_params = [initial_Theta1(:) ; initial_Theta2(:)];
其中randInitializeWeights函数实现初始化θ:
function W = randInitializeWeights(L_in, L_out)
% You need to return the following variables correctly
W = zeros(L_out, 1 + L_in);
epsilon_init = 0.12;
W = rand(L_out, 1 + L_in) * 2 * epsilon_init - epsilon_init;
end
第3步:实现nnCostFunction函数,计算 J 和 D:
function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, ...
X, y, lambda) % Reshape nn_params back into the parameters Theta1 and Theta2, the weight matrices
% for our 2 layer neural network
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1)); Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1)); % Setup some useful variables
m = size(X, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
Theta1_grad = zeros(size(Theta1));
Theta2_grad = zeros(size(Theta2)); % X:5000*400
% Y:5000*10
% a1:5000*401(后5000*400)
% z2:5000*25
% a2:5000*26(后5000*25)
% z3:5000*10
% a3:5000*10
% Theta1:25*401
% Theta2:10*26
% delta3:5000*10
% delta2:5000*25
% bigDelta1:25*401
% bigDelta2:10*26
% Theta1_grad:25*401
% Theta2_grad:10*26 Y = zeros(size(X, 1), num_labels);
for i = 1: size(X, 1),
Y(i, y(i, 1)) = 1;
end
a1 = [ones(m, 1) X];
z2 = a1*Theta1';
a2 = sigmoid(z2);
a2 = [ones(size(a2, 1), 1) a2];
z3 = a2*Theta2';
a3 = sigmoid(z3);
J = 1 / m * sum(sum(-Y .* log(a3) - (1 - Y) .* log(1 - a3))); Theta1_copy = Theta1(:, 2: end);
Theta2_copy = Theta2(:, 2: end);
J = J + lambda * (sum(sum(Theta1_copy.^2)) + sum(sum(Theta2_copy.^2))) / (2*m); delta3 = a3 - Y;
delta2 = delta3 * Theta2_copy .* sigmoidGradient(z2); bigDelta1 = zeros(size(Theta1));
bigDelta2 = zeros(size(Theta2));
bigDelta1 = delta2' * a1;
bigDelta2 = delta3' * a2;
Theta1_grad = bigDelta1 / m + lambda / m * Theta1;
Theta2_grad = bigDelta2 / m + lambda / m * Theta2;
Theta1_grad(:, 1) = bigDelta1(:, 1) / m;
Theta2_grad(:, 1) = bigDelta2(:, 1) / m; % Unroll gradients
grad = [Theta1_grad(:) ; Theta2_grad(:)]; end
其中sigmoid函数:
function g = sigmoid(z)
g = 1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z));
end
其中sigmoidGradient函数:
function g = sigmoidGradient(z)
g = zeros(size(z));
g = sigmoid(z) .* (1 - sigmoid(z))
end
第4步:梯度检测:
% Check gradients by running checkNNGradients
lambda = 3;
checkNNGradients(lambda);
其中checkNNGradients函数实现梯度检测:
function checkNNGradients(lambda)
if ~exist('lambda', 'var') || isempty(lambda)
lambda = 0;
end
input_layer_size = 3;
hidden_layer_size = 5;
num_labels = 3;
m = 5;
% We generate some 'random' test data
Theta1 = debugInitializeWeights(hidden_layer_size, input_layer_size);
Theta2 = debugInitializeWeights(num_labels, hidden_layer_size);
% Reusing debugInitializeWeights to generate X
X = debugInitializeWeights(m, input_layer_size - 1);
y = 1 + mod(1:m, num_labels)';
% Unroll parameters
nn_params = [Theta1(:) ; Theta2(:)];
% Short hand for cost function
costFunc = @(p) nnCostFunction(p, input_layer_size, hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, X, y, lambda);
[cost, grad] = costFunc(nn_params);
numgrad = computeNumericalGradient(costFunc, nn_params);
% Visually examine the two gradient computations. The two columns
% you get should be very similar.
disp([numgrad grad]);
fprintf(['The above two columns you get should be very similar.\n' ...
'(Left-Your Numerical Gradient, Right-Analytical Gradient)\n\n']);
% Evaluate the norm of the difference between two solutions.
% If you have a correct implementation, and assuming you used EPSILON = 0.0001
% in computeNumericalGradient.m, then diff below should be less than 1e-9
diff = norm(numgrad-grad)/norm(numgrad+grad);
fprintf(['If your backpropagation implementation is correct, then \n' ...
'the relative difference will be small (less than 1e-9). \n' ...
'\nRelative Difference: %g\n'], diff);
end
其中数值方法计算函数computeNumericalGradient实现:
function numgrad = computeNumericalGradient(J, theta) numgrad = zeros(size(theta));
perturb = zeros(size(theta));
e = 1e-4;
for p = 1:numel(theta)
% Set perturbation vector
perturb(p) = e;
loss1 = J(theta - perturb);
loss2 = J(theta + perturb);
% Compute Numerical Gradient
numgrad(p) = (loss2 - loss1) / (2*e);
perturb(p) = 0;
end end
其中测试数据初始化函数debugInitializeWeights函数:
function W = debugInitializeWeights(fan_out, fan_in)
% Set W to zeros
W = zeros(fan_out, 1 + fan_in);
% Initialize W using "sin", this ensures that W is always of the same
% values and will be useful for debugging
W = reshape(sin(1:numel(W)), size(W)) / 10;
end
第5步:训练模型,计算最优解:
% After you have completed the assignment, change the MaxIter to a larger
% value to see how more training helps.
options = optimset('MaxIter', 50); % You should also try different values of lambda
lambda = 1; % Create "short hand" for the cost function to be minimized
costFunction = @(p) nnCostFunction(p, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, X, y, lambda); % Now, costFunction is a function that takes in only one argument (the
% neural network parameters)
[nn_params, cost] = fmincg(costFunction, initial_nn_params, options); % Obtain Theta1 and Theta2 back from nn_params
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1)); Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
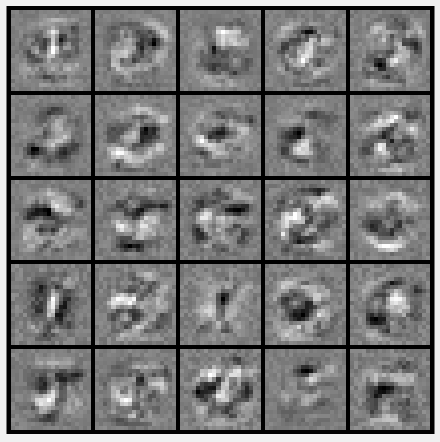
第6步:可视化隐藏层:
displayData(Theta1(:, 2:end));
运行结果:
第7步:计算准确率:
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);
其中predict函数:
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X) % Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); h1 = sigmoid([ones(m, 1) X] * Theta1');
h2 = sigmoid([ones(m, 1) h1] * Theta2');
[dummy, p] = max(h2, [], 2); end
运行结果:
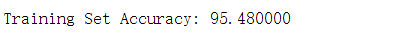
机器学习作业(四)神经网络参数的拟合——Matlab实现的更多相关文章
- 机器学习作业(四)神经网络参数的拟合——Python(numpy)实现
题目下载[传送门] 题目简述:识别图片中的数字,训练该模型,求参数θ. 出现了一个问题:虽然训练的模型能够有很好的预测准确率,但是使用minimize函数时候始终无法成功,无论设计的迭代次数有多大,如 ...
- 机器学习作业(七)非监督学习——Matlab实现
题目下载[传送门] 第1题 简述:实现K-means聚类,并应用到图像压缩上. 第1步:实现kMeansInitCentroids函数,初始化聚类中心: function centroids = kM ...
- 机器学习作业(二)逻辑回归——Matlab实现
题目太长啦!文档下载[传送门] 第1题 简述:实现逻辑回归. 第1步:加载数据文件: data = load('ex2data1.txt'); X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = dat ...
- 機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations) 机器学习基石 作业四 Q13-20 MATLAB实现
大家好,我是Mac Jiang,今天和大家分享Coursera-NTU-機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations)-作业四 Q13-20的MATLAB实现. 曾经的代码都 ...
- 机器学习(四)正则化与过拟合问题 Regularization / The Problem of Overfitting
文章内容均来自斯坦福大学的Andrew Ng教授讲解的Machine Learning课程,本文是针对该课程的个人学习笔记,如有疏漏,请以原课程所讲述内容为准.感谢博主Rachel Zhang 的个人 ...
- Stanford机器学习---第四讲. 神经网络的表示 Neural Networks representation
原文 http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7749309 本栏目(Machine learning)包括单参数的线性回归.多参数的线性回归 ...
- 【pytorch】学习笔记(四)-搭建神经网络进行关系拟合
[pytorch学习笔记]-搭建神经网络进行关系拟合 学习自莫烦python 目标 1.创建一些围绕y=x^2+噪声这个函数的散点 2.用神经网络模型来建立一个可以代表他们关系的线条 建立数据集 im ...
- Tensorflow保存神经网络参数有妙招:Saver和Restore
摘要:这篇文章将讲解TensorFlow如何保存变量和神经网络参数,通过Saver保存神经网络,再通过Restore调用训练好的神经网络. 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python人工智能] 十一. ...
- 有关 Azure 机器学习的 Net# 神经网络规范语言的指南
Net# 是由 Microsoft 开发的一种用于定义神经网络体系结构的语言. 使用 Net# 定义神经网络的结构使定义复杂结构(如深层神经网络或任意维度的卷积)变得可能,这些复杂结构被认为可提高对数 ...
随机推荐
- redis 5.0.7 源码阅读——整数集合intset
redis中整数集合intset相关的文件为:intset.h与intset.c intset的所有操作与操作一个排序整形数组 int a[N]类似,只是根据类型做了内存上的优化. 一.数据结构 ty ...
- [VB.NET Tips]创建匿名类型列表
在调用一些Web API时经常要发送或接收一些数据,在构造Json时可能要创建一些类. 很多都是在调用相关方法才使用到这些类,那使用匿名类型是个不错的选择.如果要传些表结构数据时,就要创建List. ...
- 0x01 C语言-编写第一个hello world
学习每一个编程语言都是从 "Hello world!" 开始的,这好像就是编程界一条不成文的规定一样. 在这篇文章中,我将教大家编写一个可以输出 "Hello world ...
- 怎样将应用程序快捷方式添加到win10开始菜单栏中去
怎样将应用程序快捷方式添加到win10开始菜单栏中去 找到需要固定的应用程序的安装文件的位置,右键,在弹出的菜单中选择“固定到开始屏幕”即可. 或者是找到需要固定到开始菜单的应用程序的快捷方式,右键, ...
- linux - top与ps间的区别
背景 在linux系统中提供了2个查询系统负荷值的命令,一个是 ps -o THREAD 一个是 top ,这两个命令都能够查询当前进程的CPU使用率情况,但是所代表的含义确实不一样的,ps -o T ...
- 持续更新phpstorm h和pycharm 激活码
1.hosts文件写入 0.0.0.0 account.jetbrains.com0.0.0.0 www.jetbrains.com 2.激活码: AHD9079DKZ-eyJsaWNlbnNlSWQ ...
- Qt的qDebug()改写为cout
经常用c++,qDebug()用的不习惯,将其改为cout,并且为了方便调试,还添加了文件名及行号. 代码如下: // __FILE__文件名,__LINE__行号,如果想看时间还可以添加__TIME ...
- 使用shell程序备份crontab中的.sh脚本文件
需求 线上环境有一些定时脚本(用crontab -l可查看当前用户的),有时我们可能会改这些定时任务的脚本内容.为避免改错无后悔药,需用shell实现一个程序,定时备份crontab中的.sh脚本文件 ...
- Pikachu-Sql Inject(SQL注入)
在owasp发布的top10排行榜里,注入漏洞一直是危害排名第一的漏洞,其中注入漏洞里面首当其冲的就是数据库注入漏洞.一个严重的SQL注入漏洞,可能会直接导致一家公司破产!SQL注入漏洞主要形成的原因 ...
- 44.Python实现简易的图书管理系统
首先展示一下图书管理系统的首页: 这是图书管理系统的发布图书页面: 最后是图书管理系统的图书详情页已经图书进行删除的管理页. 该图书管理系统为练习阶段所做,能够实现图书详情的查询.图书的添加.图书的删 ...
