吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言数据可视化绘图(3)
par(ask=TRUE)
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) # record current settings # Listing 11.1 - A scatter plot with best fit lines
attach(mtcars)
plot(wt, mpg,
main="Basic Scatterplot of MPG vs. Weight",
xlab="Car Weight (lbs/1000)",
ylab="Miles Per Gallon ", pch=19)
abline(lm(mpg ~ wt), col="red", lwd=2, lty=1)
lines(lowess(wt, mpg), col="blue", lwd=2, lty=2)
detach(mtcars)

# Scatter plot with fit lines by group
library(car)
scatterplot(mpg ~ wt | cyl, data=mtcars, lwd=2,main="Scatter Plot of MPG vs. Weight by # Cylinders", xlab="Weight of Car (lbs/1000)",ylab="Miles Per Gallon",id.method="identify",legend.plot=TRUE,boxplots="xy")

# Scatter-plot matrices
pairs(~ mpg + disp + drat + wt, data=mtcars,
main="Basic Scatterplot Matrix")

library(car)
scatterplotMatrix(~ mpg + disp + drat + wt, data=mtcars,
spread=FALSE, smoother.args=list(lty=2),
main="Scatter Plot Matrix via car Package")

# high density scatterplots
set.seed(1234)
n <- 10000
c1 <- matrix(rnorm(n, mean=0, sd=.5), ncol=2)
c2 <- matrix(rnorm(n, mean=3, sd=2), ncol=2)
mydata <- rbind(c1, c2)
mydata <- as.data.frame(mydata)
names(mydata) <- c("x", "y") with(mydata,
plot(x, y, pch=19, main="Scatter Plot with 10000 Observations")) with(mydata,
smoothScatter(x, y, main="Scatter Plot colored by Smoothed Densities")) library(hexbin)
with(mydata, {
bin <- hexbin(x, y, xbins=50)
plot(bin, main="Hexagonal Binning with 10,000 Observations")
})



# 3-D Scatterplots
library(scatterplot3d)
attach(mtcars)
scatterplot3d(wt, disp, mpg,
main="Basic 3D Scatter Plot") scatterplot3d(wt, disp, mpg,
pch=16,
highlight.3d=TRUE,
type="h",
main="3D Scatter Plot with Vertical Lines") s3d <-scatterplot3d(wt, disp, mpg,
pch=16,
highlight.3d=TRUE,
type="h",
main="3D Scatter Plot with Vertical Lines and Regression Plane")
fit <- lm(mpg ~ wt+disp)
s3d$plane3d(fit)
detach(mtcars)

# spinning 3D plot
library(rgl)
attach(mtcars)
plot3d(wt, disp, mpg, col="red", size=5)

# alternative
library(car)
with(mtcars,
scatter3d(wt, disp, mpg))

# bubble plots
attach(mtcars)
r <- sqrt(disp/pi)
symbols(wt, mpg, circle=r, inches=0.30,
fg="white", bg="lightblue",
main="Bubble Plot with point size proportional to displacement",
ylab="Miles Per Gallon",
xlab="Weight of Car (lbs/1000)")
text(wt, mpg, rownames(mtcars), cex=0.6)
detach(mtcars)

# Listing 11.2 - Creating side by side scatter and line plots
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
t1 <- subset(Orange, Tree==1) plot(t1$age, t1$circumference,
xlab="Age (days)",
ylab="Circumference (mm)",
main="Orange Tree 1 Growth") plot(t1$age, t1$circumference,
xlab="Age (days)",
ylab="Circumference (mm)",
main="Orange Tree 1 Growth",
type="b") par(opar)

# Listing 11.3 - Line chart displaying the growth of 5 Orange trees over time
Orange$Tree <- as.numeric(Orange$Tree)
ntrees <- max(Orange$Tree)
xrange <- range(Orange$age)
yrange <- range(Orange$circumference)
plot(xrange, yrange,
type="n",
xlab="Age (days)",
ylab="Circumference (mm)"
) colors <- rainbow(ntrees)
linetype <- c(1:ntrees)
plotchar <- seq(18, 18+ntrees, 1)
for (i in 1:ntrees) {
tree <- subset(Orange, Tree==i)
lines(tree$age, tree$circumference,
type="b",
lwd=2,
lty=linetype[i],
col=colors[i],
pch=plotchar[i]
)
}
title("Tree Growth", "example of line plot")
legend(xrange[1], yrange[2],
1:ntrees,
cex=0.8,
col=colors,
pch=plotchar,
lty=linetype,
title="Tree"
)

# Correlograms
options(digits=2)
cor(mtcars) library(corrgram)
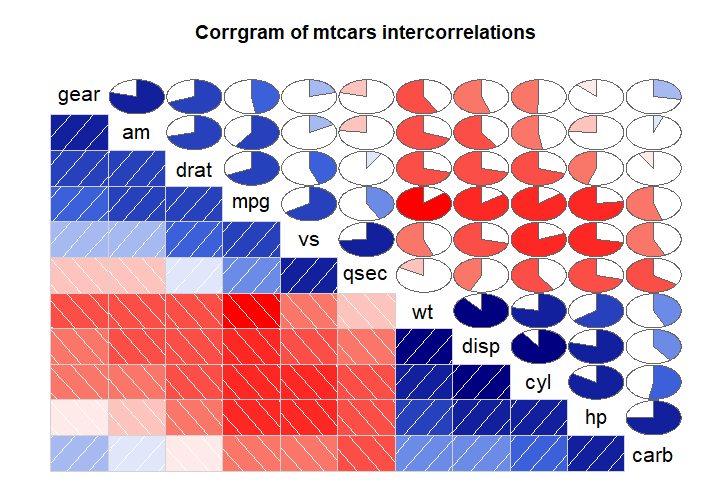
corrgram(mtcars, order=TRUE, lower.panel=panel.shade,
upper.panel=panel.pie, text.panel=panel.txt,
main="Corrgram of mtcars intercorrelations") corrgram(mtcars, order=TRUE, lower.panel=panel.ellipse,
upper.panel=panel.pts, text.panel=panel.txt,
diag.panel=panel.minmax,
main="Corrgram of mtcars data using scatter plots
and ellipses") cols <- colorRampPalette(c("darkgoldenrod4", "burlywood1",
"darkkhaki", "darkgreen"))
corrgram(mtcars, order=TRUE, col.regions=cols,
lower.panel=panel.shade,
upper.panel=panel.conf, text.panel=panel.txt,
main="A Corrgram (or Horse) of a Different Color")


# Mosaic Plots
ftable(Titanic)
library(vcd)
mosaic(Titanic, shade=TRUE, legend=TRUE) library(vcd)
mosaic(~Class+Sex+Age+Survived, data=Titanic, shade=TRUE, legend=TRUE)


# type= options in the plot() and lines() functions
x <- c(1:5)
y <- c(1:5)
par(mfrow=c(2,4))
types <- c("p", "l", "o", "b", "c", "s", "S", "h")
for (i in types){
plottitle <- paste("type=", i)
plot(x,y,type=i, col="red", lwd=2, cex=1, main=plottitle)
}

吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言数据可视化绘图(3)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言数据可视化绘图(4)
par(ask=TRUE) # Basic scatterplot library(ggplot2) ggplot(data=mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) + geom_poin ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言数据可视化绘图(2)
par(ask=TRUE) opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) # save original parameter settings library(vcd) count ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言数据可视化绘图(1)
par(ask=TRUE) opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) # make a copy of current settings attach(mtcars) # be ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:R语言的安装与配置
下载R语言和开发工具RStudio安装包 先安装R
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:数据集和数据结构
数据集的概念 数据集通常是由数据构成的一个矩形数组,行表示观测,列表示变量.表2-1提供了一个假想的病例数据集. 不同的行业对于数据集的行和列叫法不同.统计学家称它们为观测(observation)和 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:导入数据
2.3.6 导入 SPSS 数据 IBM SPSS数据集可以通过foreign包中的函数read.spss()导入到R中,也可以使用Hmisc 包中的spss.get()函数.函数spss.get() ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:处理缺失数据的高级方法(续一)
#-----------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 18 # # Advanced methods for mi ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:R语言的简单介绍和使用
假设我们正在研究生理发育问 题,并收集了10名婴儿在出生后一年内的月龄和体重数据(见表1-).我们感兴趣的是体重的分 布及体重和月龄的关系. 可以使用函数c()以向量的形式输入月龄和体重数据,此函 数 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:使用键盘、带分隔符的文本文件输入数据
R可从键盘.文本文件.Microsoft Excel和Access.流行的统计软件.特殊格 式的文件.多种关系型数据库管理系统.专业数据库.网站和在线服务中导入数据. 使用键盘了.有两种常见的方式:用 ...
随机推荐
- Python3 os.path() 模块笔记
os.path 模块主要用于获取文件的属性. 以下是 os.path 模块的几种常用方法: 方法 说明 os.path.abspath(path) 返回绝对路径 os.path.basename(pa ...
- day01_前言、入门程序、常量、变量
day01_前言.入门程序.常量.变量 sysout :System.out.println(); Java 概述 本节主要内容: java 概述.常 DOS 命令.JRE.JDK 与 JVM.环境搭 ...
- SpringBoot + Mybatis 和ssm 使用数据库的区别
积少成多 ---- 仅以此致敬和我一样在慢慢前进的人儿 相关内容: https://www.cnblogs.com/h-c-g/p/10252121.html 引 言 接触SpringBoot 后, ...
- springboot-mybatis配置问题
org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Invalid bound statement (not found)问题
- Linux系统实现ansible自动化安装配置httpd
1.使用ansible的playbook实现自动化安装httpd 1)首先配置好ansible的hosts文件,让其对应主机能够受ansible控制 提示:我们在主机清单上配置了所管控的主机地址,但是 ...
- eclipse导入项目时的一些准备
导入前的工作: 1.因为别人项目的运行环境可能和我们不一样,所以首先要在要导入的项目里面找到.setting文件,修改下面的xml文件,这个文件里面是关于服务器的一些配置的信息,你可以改成与你电脑一样 ...
- 【5min+】 这些C#的运算符您都认识吗?
系列介绍 [五分钟的dotnet]是一个利用您的碎片化时间来学习和丰富.net知识的博文系列.它所包含了.net体系中可能会涉及到的方方面面,比如C#的小细节,AspnetCore,微服务中的.net ...
- pycham设置头文件内容
pycharm软件 设置头文件方法 File->settings->Editor->File and Code Templates->Python Script #!/usr ...
- NLP新秀 - Bert
目录 什么是Bert Bert能干什么? Bert和TensorFlow的关系 BERT的原理 Bert相关工具和服务 Bert的局限性和对应的解决方案 沉舟侧畔千帆过, 病树前头万木春. 今天介绍的 ...
- C++用rand()和srand()生成随机数
内容来自<编程实战宝典> 首先来看函数原型 int rand(void); void srand(unsigned int seed); 1.rand()函数不需要任何参数,直接返回一个随 ...
